Layers of the atmosphere
The atmosphere is the envelope of gas that surrounds the Earth. Depending on the study area, the atmosphere can be divided into several layers from the surface to outer space.
In physics, when temperature patterns are compared, the atmosphere is divided into four layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. In chemistry it is divided into homosphere and heterosphere depending on the composition of gases. Depending on the function, the atmosphere is divided into ozonosphere and ionosphere.
Below we present the different layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics.
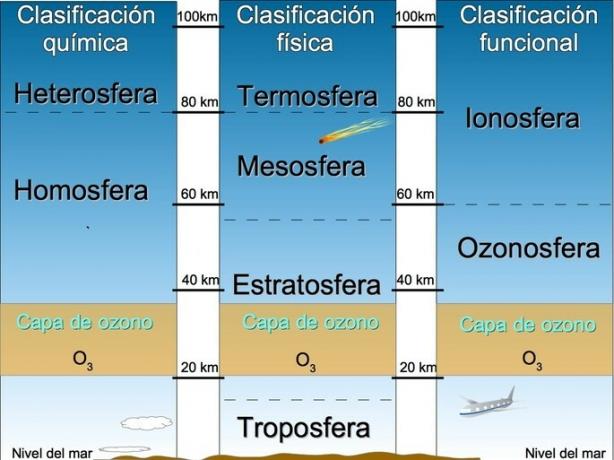
Troposphere
The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in contact with the earth's surface. It is the most important for the development of life and where climatic events occur, such as snowfall, storms, winds and clouds.
It extends from 0 km to 10 km high at the poles to 17 km high at the equator. Temperatures in the troposphere decrease as one rises in height.
The tropopause it is the transition phase between the troposphere and the next layer which is the stratosphere.
You may also be interested in seeing Cloud types.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second layer of the atmosphere that extends from 20 km to 58 km of altitude. In this layer is the ozone layer, a protective strip against ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. You can also get water in the form of ice clouds.
The temperature of the stratosphere remains constant at -57ºC up to an altitude of 32 km, and then rises to approximately 10ºC upon reaching the stratopause, the transition phase towards the mesosphere.
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the third layer of the atmosphere that extends between 58 km and 80 km in altitude. Temperatures drop from 10º C to -80º C as you go up in height. When the meteorites reach this layer, they vanish.
The mesopause it is the transition phase between the mesosphere and the next layer, the thermosphere.
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the last layer according to the physical classification that goes from 80 km to 800 km. In this layer the temperatures can rise up to 1100º C.
The International Space Station and some artificial satellites orbit in this layer of the atmosphere. The auroras also occur here.
Functional classification of the atmosphere
An alternative classification of the atmosphere is based on the function of the layers of the atmosphere. In this sense, the atmosphere is divided into two layers: the ozonosphere and the ionosphere.
Ozonosphere
This layer ranges from 15 to 50 km above the surface, the ozonosphere includes the ozone layer whose function is to filter ultraviolet rays.
Ozone is a molecule made up of three oxygens O3 which is toxic to life on the earth's surface. However, without the ozone layer high in the atmosphere, all UV radiation would reach Earth, causing burns and damage to living things.
The ozonosphere corresponds to the troposphere, the stratosphere and part of the mesosphere of the physical classification.
Ionosphere

The ionosphere fulfills the function of shielding the Earth against harmful radiation from outer space. It extends from 60 km to 400 km on Earth. The ionosphere corresponds to the mesosphere and the thermosphere.
The ionosphere name refers to the ionization of molecules and atoms that occurs in this layer. Ionization occurs when an atom is transformed into an ion when it gains or loses electrons, due to X and UV rays and gamma and UV radiation.
Communication signals are also transmitted in the ionosphere and auroras occur.
You may also be interested in seeing Natural phenomena.
Chemical classification of the atmosphere
Atmospheric chemists divide the atmosphere according to its chemical composition into the homosphere and the heterosphere.
Homosphere
This layer starts at the surface and goes up to 80 km. The composition of gases remains more or less homogeneous (from the Greek homo, equal). Nitrogen N2 It is found in a higher proportion with 78%, followed by oxygen O2 with 21%; the rest is represented by noble gases, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, ozone and water vapor.
Heterosphere
Above 80 km is the heterosphere, where gases begin to separate into different strata. Nitrogen that is heavier is found lower while lighter gases such as atomic hydrogen are concentrated outside.
References
Gabler, R.E., Petersen, J.F., Trapasso, L.M. Sack, D. (2009) Physical Geography 9th ed. Brooks / Cole Cengage Learning. USES.


