Who were the Ottomans

Image: Notes of History
During the Modern Age we will find a series of highly important countries that we can define as the superpowers of the time. Finding themselves in quite opposite poles, these two will have a series of warlike confrontations where they demonstrated their armament strength. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will clarify who were the ottomans, an empire that managed to subdue many Christian countries in the Mediterranean, even reaching the gates of Vienna.
Index
- The Ottoman people
- Ottoman economy
- Ottoman religion
- Culture of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman people.
Those known as Ottomans were, in reality, the well-known Turkish empire which was active from 1299 to 1923, therefore, we can say that it is one of the oldest empires throughout all of history. During that long period of time, they were gaining and losing land, as well as suffering enormous internal crises that made the forces before their enemies greatly diminish.
So the centuries XVI-XVII will be the most important within that great empire, for being the years of greatest splendor, compared to the rest of the European kingdoms. This empire It ended in 1923 after the First World War, during which many of its Caucasus provinces revealed themselves supporting their enemies, the Russian Empire and the Russian Empire British, that and the bad strategy caused that battles were lost throughout Asia Minor and Anatolia, until they were undone by full.
It will be a multi-ethnic kingdom, because will span from Asia Minor to Morocco, including the Anatolian peninsula in the north, even reaching the gates of Vienna. For this reason, we will find an endless number of peoples subjected to the power of the sultan, who, from the capital, directed all the affairs of power and as far as the tributes should go.

Image: Oriental dance in Egypt
Economy of the Ottomans.
Within our lesson on who the Ottomans were, we must mention the economy they practiced. Due to the strategic position they had and the control they exercised over the territories, they became the intermediaries of the famous silk and spice routeThese elements came from Asia and, since they had control of all the land routes that connected with Europe, they exercised supreme power.
It was for this reason that Christopher Columbus's trip was made, eager to find an alternative route to avoid the excessive tariffs of the Turks, in addition to obtaining a much faster route by means of the sea. We will also find the African ring road by the Portuguese seeking the same end.
In this way, the Ottomans on many occasions had to stand up to the christian kingdoms to try to maintain their status using, to a large extent, the use of corsairs and vassal kingdoms that had to attack both the merchant ships such as the military from the European kingdoms, turning the Mediterranean into the battlefield for excellence.
Thus one of the most important battles at sea that we know will be the battle of Lepanto, in which the Ottoman Empire lost, although the following year its fleet had doubled making the rest of the Mediterranean kingdoms see its power.
Ottoman religion.
Another important point in the lesson on who the Ottomans were, we will find it in the religious aspect. Since it was a heterogeneous conglomerate of countries that were being adhered over the centuries, we will find different religions and within these various diversifications. P
hear it, we will find a high core of christians coming from the old Byzantine Empire that in the year 1454 fell into the hands of the Ottoman Empire, being one of the hardest moments for the Christian kingdoms since Constantinople, was had as the door to The West, and therefore, as the Turks now controlled it, the danger of an invasion was intense, especially now that the Reconquest in the Iberian Peninsula was in the final stretch.
On the other hand, the Jews were also through these territories, since the entire Syro-Palestinian coast, Hungary and other parts of the empire were the nuclei par excellence of this religion. Both Jews and Christians they lived in relative peace, since they were protected minorities that had to pay a series of taxes in order to maintain their religion and have a certain security from the rest of the population.
In addition, we will find the various branches of Islam, from the most radical to the most moderate and that always coexisted between great tension, causing problems for the empire.
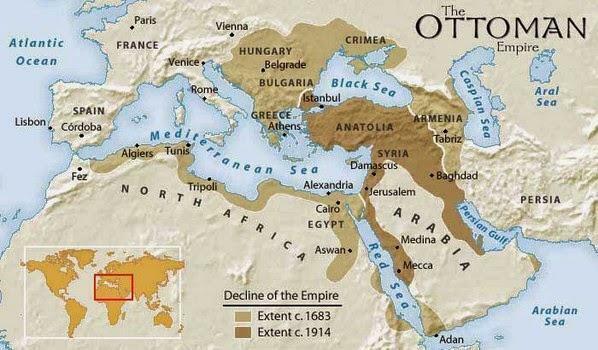
Image: What Happened in History
Culture of the Ottoman Empire.
We have to mention in a very brief way part of the culture that would become part of the Christian culture in its various commercial treaties. To this day, oriental products still have an aura of exotic objects and therefore many people want to own them; In the Modern Age and during the Contemporary Age, the same thing also happened and since the 16th S many nobles and aristocrats wanted to obtain oriental objects to decorate their houses.
In addition to this, we will find that the oriental style It became so strong that even in Rococo art we will find some elements of that origin. Likewise, in the exchanges, melon, apricot, legume and even coffee crops reached European tables, opening a new chapter in food.
In the same way, from the 17th century, we will see pictorial works alluding to oriental themes, as well as various literary works, in which encounters of Christians and Ottomans in activities around the Mediterranean were narrated.
If you want to read more articles similar to Who were the Ottomans, we recommend that you enter our category of Story.



