French colonies in Africa: 19th century and present
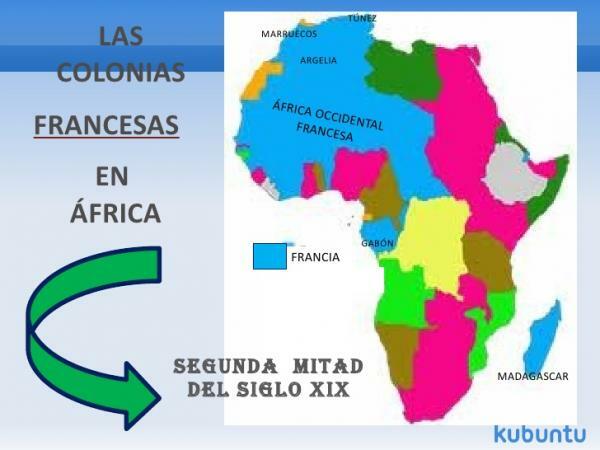
Image: Slideshare
From the 17th to the 20th century France has been a country with numerous colonies worldwide. Although the French country has had colonies on almost every continent, the most important ones are those they had in Africa throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. To learn about this important phase of colonialism today in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we are going to talk about the French colonies in Africa: 19th century and present.
To understand the French colonies we must first understand what are the colonies and what they were like at that time, since the term changes a lot depending on whether we refer to a current colony or an old one. We must also understand what we mean when we speak of colonialism, since if we do not understand what this system is, it will be more difficult for us to explain the reason for the French expansion.
The colonies are a political and economic term which is applied to a population that is under the government of another country, the country that rules over the colony is called a metropolis.
Much of America and Africa, and part of Asia, have been colonies of European countries, being France one of the countries that more possessions came to have between the nineteenth and twentieth century. Currently there are still colonies, but their characteristics are very different from the colonies of the nineteenth century, some of their largest differences are as follows:
- In the current colonies, the citizens of the colony and the metropolis have the equal rights, whereas in the classic colonies the local population did not have the same rights.
- The policy of the new colonies allows promoting movements for independence, while in the classical colonies many political facets are excluded, especially those related to independence.
- The systems were imposed in the classic colonies, while in the new ones it has greater autonomy.
On the other hand is the colonialism, which is is a economic system in which a foreign country exploits a colony. Colonialism consists of an appropriation of the resources of a territory, thereby seeking an increase in the economic power of the metropolis, to the detriment of the colony.
Some causes of colonialism are as follows:
- Economic causes: Raw materials had been used less and labor was much cheaper.
- Political causes: As for example the search to look like a great international power or nationalism.
- Demographic causes: In the years of colonization, the birth rate had increased, and the existence of colonies made it possible to emigrate to these less inhabited areas.
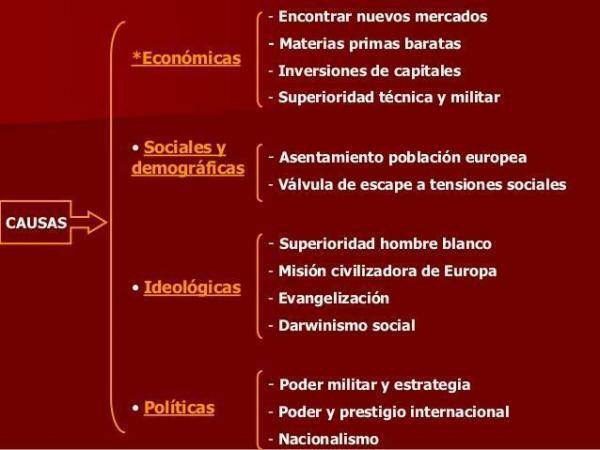
Image: Social Sciences
The beginning of the second French colonial empire, that is, the one that occupies the 19th and 20th centuries, takes place in 1830 with the invasion of France into Algeria. The conquest of Algeria lasted 17 years, and it came to be named as a department of France. Algeria was a French colony from 1830 to 1932, being the colony that has remained under French control the longest.
France started a expansion across much of the African continent, seeking to achieve a great position of power, because his influence had been reduced in recent years. In 1881, France established a protectorate in Tunisia, and little by little it spread to numerous territories throughout Africa (Senegal, Mauritania, Guinea, Mali, Republic of the Congo, Chad, Niger, Benin and Ivory Coast). Thanks to this, France occupied a large part of North, Central and West Africa.
A little later, in 1884, France and UK they called a meeting in Berlin, called the Berlin Conference, to deal with issues related to colonialism in Africa and which was basically based on the distribution of Africa among European countries. The division was of such caliber that only two countries escaped, Ethiopia and Liberia, although the latter thanks to the protection of the United States.
The Partition of Africa caused France to occupy much of the continent, possibly being the largest profit from the conference. The African countries that France had after the meeting are as follows:
- Algeria
- Tunisia
- Morocco
- Mauritania
- Senegal
- Mali
- Guinea
- Cameroon
- Ivory Coast
- Niger
- Burkina faso
- Benin
- Gabon
- Congo
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Madagascar
It should be noted that several of these countries joined in federations, the most important being the so-called "French West Africa" and the "French Equatorial Africa", the first formed by the French West African colonies, and the second by countries of the center of the continent.
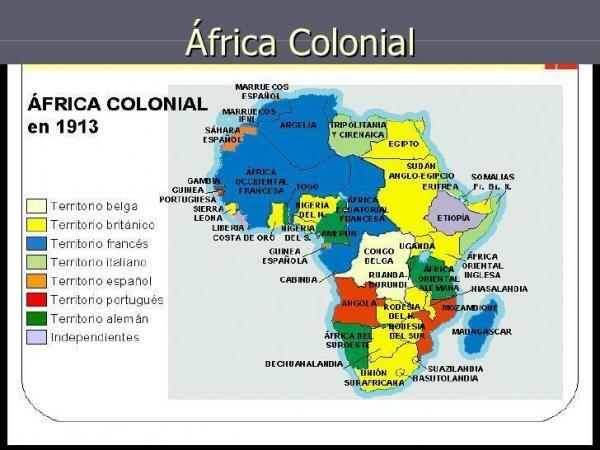
Image: Newspaper Center
To conclude this lesson on the French colonies in Africa of the 19th century and today, we must talk about the few colonies that France still has. Over the years, Francia was losing the vast majority of colonies that it owned all over the world, being very numerous the independences that took place in the 20th century. And that is why they currently have only a few colonies.
According to the United Nations Decolonization Committee there are currently 18 colonies, of which two are French. These two colonies are New Caledonia and French Polynesia, being the first of them in talks to become independent from France.



