Difference between diploid and haploid cells
There are two types of cells in the body, haploid cells and diploid cells. The biggest difference is related to the number of chromosomes that each cell contains, while diploid cells contain two chromosomes (2n), haploid cells contain a chromosome (1n).
| Diploid cells | Haploid cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | They contain two complete sets of chromosomes (2n). | They have half the number of chromosomes (n), that is, they contain only a complete set of chromosomes. |
| Cellular division | They reproduce by mitosis, producing daughter cells that are exact replicas. | Haploid cells are the result of the process of meiosis, a type of cell division in which diploid cells divide to form haploid germ cells. |
| Organisms | Humans and most animals are considered diploid organisms. | Algae and fungi are examples of organisms that are haploid for most of their life. Male bees, wasps, and ants are also haploid. |
| Cell example | Diploid cells are found in skin, blood, and muscle cells (also known as somatic cells). | Haploid cells are used in sexual reproduction, in sperm and eggs (also known as gametes). |
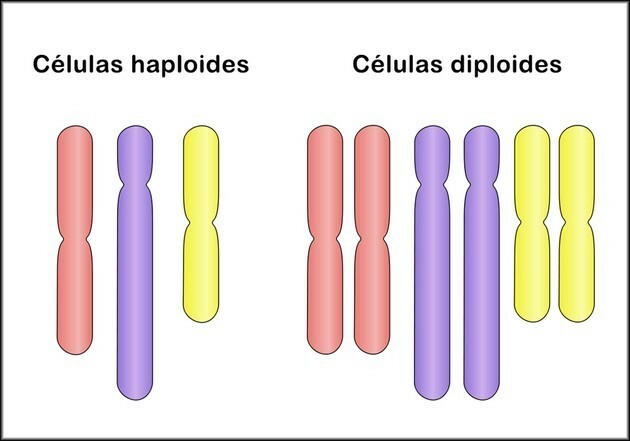
Which cells are haploid and diploid?
In humans, autosomal cells (or somatic) are diploid cells, they contain two sets of chromosomes (2n). These cells can be found in skin, blood, and muscle cells. The number of chromosomes (n) differs in different organisms, and in humans, the complete set (2n) comprises 46 chromosomes.
Haploid cells are found in the gametes or germ cells, and contain only one set of chromosomes (n). An example of haploid cells are cells found in sperm and in the egg.
Cell division and reproduction
Meiosis
All animal cells have a fixed number of chromosomes in the cells of the body, existing in homologous pairs (2n). Each pair of chromosomes consists of one chromosome from the mother and the second from the father.
During the process of meiosis (cell division for sexual reproduction), diploid cells (2n) divide to produce haploid cells, which contain only one set of chromosomes (n).
When the male and female gametes merge during fertilization and zygote formation, the number of chromosomes is restored back to 2n. Thus, diploid cells are those that contain a complete set of chromosomes, while haploid cells are those that have half the number of chromosomes in the nucleus (n).
This process does not occur in organisms that reproduce through asexual processes, such as bacteria. In plant cells, the "n", or haploid, stage makes up a large part of their life cycle.
Mitosis
Cell growth is the result of mitosis, a process by which stem cells become divide to give rise to identical haploid daughter cells, containing the same number of chromosomes.
This process differs slightly in different types of cells. Animal cells undergo an "open" mitosis, with the rupture of the nuclear membrane, while that organisms such as fungi and yeast undergo closed mitosis, maintaining their nuclear membrane intact.
See also Mitosis and meiosis.
In summary
1. A haploid cell has only one set of chromosomes (n), while diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes (2n).
2. In humans, somatic cells are diploid, while gametes they are haploid.
3. Diploid cells develop as a result of cell division mitotic, while haploid cells develop as a result of cell division meiotic.
4. Mitosis produces 2 identical daughter cells, where both stem and daughter cells are diploid. In meiosis, a diploid cell divides twice to produce 4 haploid daughter cells.
5. Humans and most animals are considered diploid organisms, while algae and fungi are examples of organisms that are haploid for most of their lives. Male bees, wasps, and ants are also haploid.

