Difference between atoms and molecules
The atom it is the basic unit of matter. The molecule It is the result of the union of two or more atoms, that is, the molecules are made up of atoms.
| Difference | Atoms | Molecules |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The basic unit of matter | Two or more atoms linked by a bond |
| Composition | Neutrons, protons, electrons | Same or different atoms |
| Chemical links | Absent | Present |
| Examples |
Hydrogen:
Oxygen:
Sodium:
Chlorine:
|
Water H2OR:
Glucose C6H12OR6:
Molecular oxygen O2:
|
What is an atom?
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of the Universe. The definition of the atom is the least amount of matter that retains the chemical properties of the element.
For example, if we take a piece of silver Ag, which is an element, and divide it so many times to the point that it no longer can be further divided without losing the properties that characterize it as silver, we will be in the presence of an atom of silver.
The atom is composed of:
- a central core: made up of neutrons and protons.
- an electronic cloud: where are the electrons that surround the nucleus.
The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons determines the basic structure of an atom.
Examples of atoms
There are as many atoms as there are elements in the periodic table. Let's look at some examples of atoms and their characteristics.
Hydrogen H
Hydrogen is the simplest atom in the Universe, made up of a proton and an electron. Its atomic number is 1, making it the first element on the periodic table.
Oxygen O
Oxygen is one of the most important elements for living beings. Its atomic number is 8 and it is made up of 8 neutrons, 8 protons, and 8 electrons.
Carbon C

Carbon C is the atom present in all organic compounds; it has six neutrons and six protons in the nucleus and six electrons in the electron cloud. Of the six electrons, four are in the outermost shell, these are the electrons available to form bonds with other atoms and form molecules.
You may be interested in seeing:
- Elements, compounds and mixtures.
- Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What is a molecule?
A molecule is the result of the union of two or more atoms. Electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom (valence electrons) when shared between atoms, form a molecule.
The molecule is the smallest part of a substance. Molecules made up of two atoms are called diatomic, for example, the O2 molecular oxygen, nitrogen from air N2 and chlorine gas Cl2.
There are molecules made up of hundreds of atoms. For example, the chlorophyll molecule is made up of 55 carbon atoms, 72 hydrogen atoms, one magnesium atom, 4 nitrogen atoms, and 5 oxygen atoms, for a total of 137 atoms.
Examples of molecules
In the Universe there are an infinity of molecules, of which we only mention a few.
H2 diatomic hydrogen
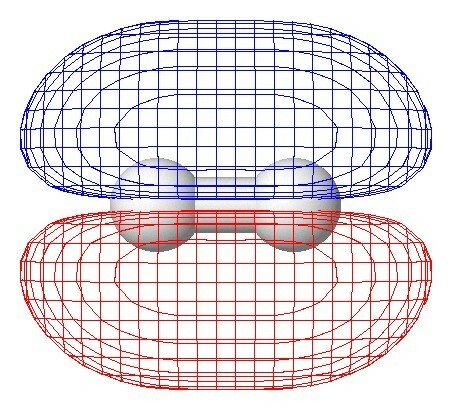
The simplest molecule is diatomic hydrogen H2, formed by two hydrogen atoms joined by a covalent bond, where the electrons are shared between the two atoms.
Water
Water H2O is a triatomic molecule, as it is made up of three atoms. Its particular structural conformation gives it a dipole character, with a negative partial charge on the oxygen end and two positive partial charges on the hydrogens.
Glucose
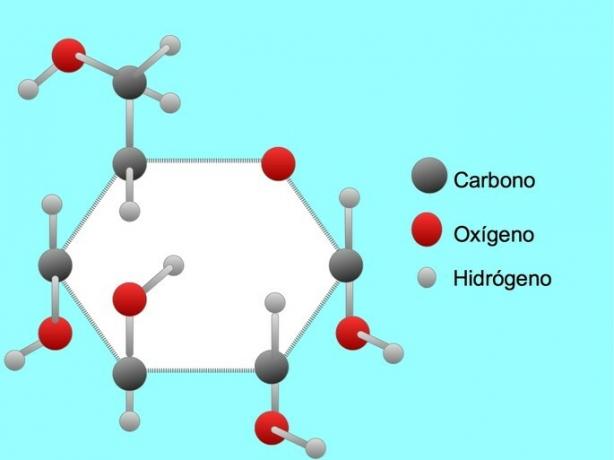
Glucose is a type of sugar. The sugar molecule contains six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms.
You may be interested in seeing:
- Types of chemical bonds.
- Cations and anions
- States of matter and properties of matter.



