Difference between physical and chemical phenomena
The physical phenomena are those events or events where the composition of the material is not modified, that is, it maintains its physical properties. The chemical phenomena are those events that happen due to alterations in the composition of matter.
We get physical and chemical phenomena in our day to day, from boiling water, frying an egg to the blue color of the sky. Physics and chemistry are the sciences that allow us to explain all these phenomena.
| Physical phenomena | Chemical phenomena | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Events that occur without affecting the molecular composition of matter. | Events that occur due to changes in the molecular structure of matter. |
| Difference | Compounds stay the same |
New compounds are produced |
| Types |
|
|
| Examples |
|
|
What are physical phenomena?
Physical phenomena are events that occur in nature in which the composition of matter is not altered. These phenomena can be explained by the laws of physics. Here are some examples of physical phenomena.
Sound barrier

The sound barrier is a acoustic physical phenomenon result of the collision of sound waves in the air. Sound is a wave that travels through the air at a speed of 343 meters per second. When an airplane exceeds this speed, a noise similar to an explosion is produced. This is known as "breaking the sound barrier."
Rainbow

The rainbow is a luminous physical phenomenon that we can observe in the sky when sunlight is reflected and refracted by raindrops. The water droplets in this case act like a prism, separating the bands of colors that make up the light.
Mirages

A mirage is a optical physical phenomenon It is produced because light bends as it passes through layers of air with different temperatures. It is an optical illusion that makes us perceive the presence of water in the distance, which is not real.
Optical fibers
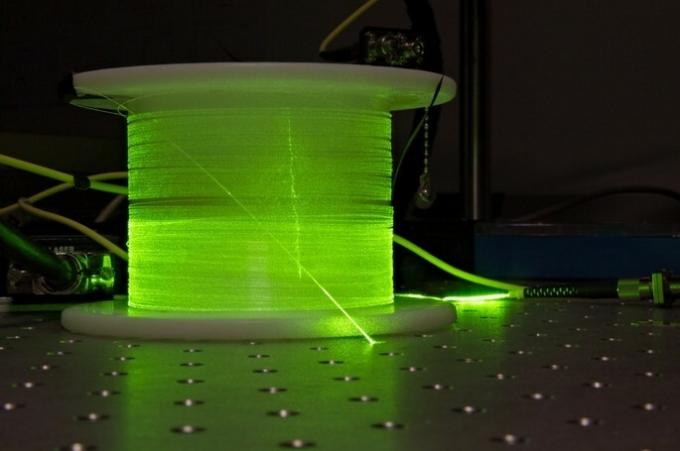
Optical fibers are a optical physical phenomenon which is characterized by the fact that light travels through cables or long fibers of glass or plastic. This happens because light is reflected internally off the cable, causing it to bounce across the fiber without getting lost in the external environment. They are widely used for the transmission of data, images and sound.
You may also be interested in knowing about Reflection and refraction of light.
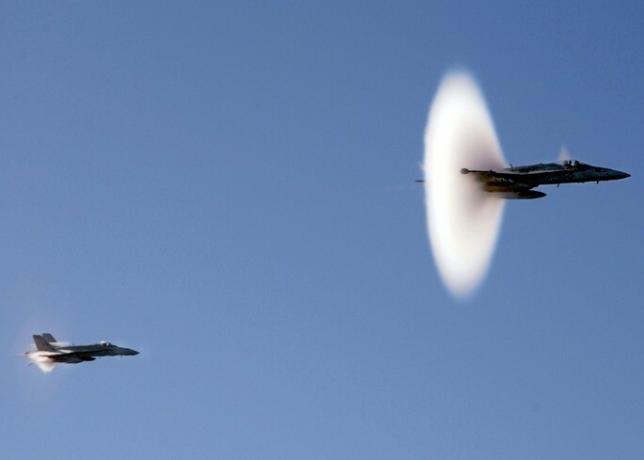
Lightning bolts

Lightning bolts are electromagnetic phenomena that occur in the atmosphere. They are electrical discharges that generally occur during storms. This is due to a separation of electrical charges between the earth's surface and the clouds. When lightning strikes, so much energy is released that it lights up the sky and generates heat.
What are chemical phenomena?
Chemical phenomena are the events that occur when the composition of matter is altered. In everyday life we come across different chemical phenomena that sometimes go unnoticed. Here are some examples of chemical phenomena.
Fireworks

Fireworks are chemical phenomena that are produced by the heating of metals in an explosion. For example, strontium produces a deep red color, sodium produces a yellow color, copper produces a green color, and potassium produces a lilac color.
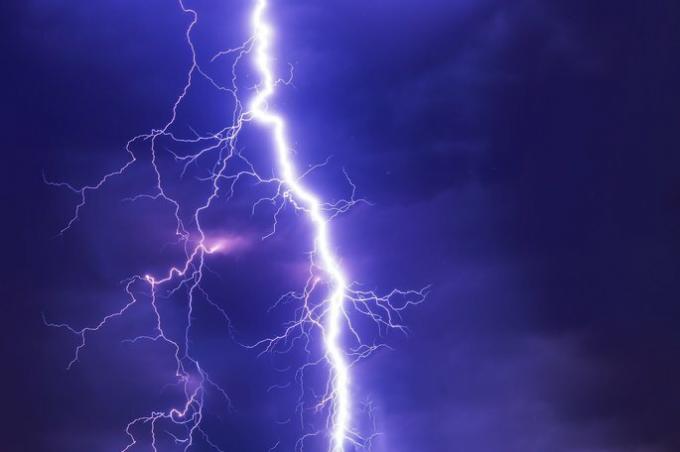
Rust
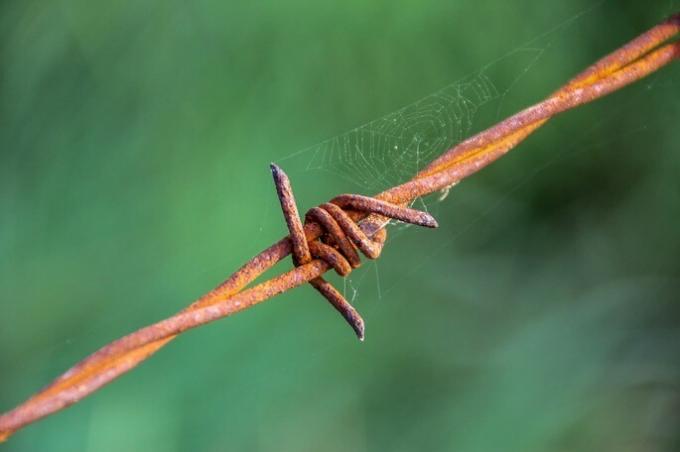

Rust is a chemical phenomenon that we find in materials made of iron or other metals as a result of oxidation and reduction reactions. This phenomenon involves the chemical transformation of iron to iron oxide in the presence of oxygen, either from air or water, with the characteristic light brown color.
Ozone gap

The ozone gap is the result of decreasing ozone levels (O3) in the atmosphere, by chemical reaction with compounds known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). The O3 It is a molecule found in the atmosphere that protects the planet against ultraviolet rays from the Sun.
CFCs are compounds used initially as refrigerants and in aerosols. Once in the air, the CFC reacts with the oxygen and the ozone disappears. The atmosphere at the level of the Antarctic region has the lowest concentration of ozone, which is popularly known as the ozone gap.
Acid rain

Acid rain is a chemical phenomenon that results from increased acidity in rainwater due to air pollution. Industrial processes produce gaseous sulfur dioxide, which reacts with rainwater turns into sulfuric acid, a strong acid that is highly corrosive.
Another polluting gas is nitrogen oxide (IV) which reacts with water to form nitrous acid (HNO2) and nitric acid (HNO3).
Acid rain has detrimental effects on the environment:
- Alteration of the pH of aquatic environments.
- Dissolution of minerals.
- Corrosion of metals and constructions.
Hydrangea color

The color of the sepals of hydrangeas (Hydrangea macrophyla) is a chemical phenomenon product of soil pH:
- In acid soils (less than 7): the sepals are blue.
- In basic soils (greater than 7): the sepals are pink / purple.
This is due to the solubility of aluminum in water at acidic pH, which allows the absorption of this element by plants. As a result, the aluminum binds to the anthocyanin pigment in the sepals, producing the color blue.
At neutral (7) or basic (greater than 7) pH, aluminum is insoluble in water, so it cannot be absorbed by plants. In this way, the color of the sepals of hydrangeas depends on anthocyanin, which is naturally a purple pigment.
You may be interested in seeing Natural phenomena.
References
Commons, C., Commons, P. et al. (2016). Heinemann Chemistry 1. 5th edition. Pearson Australia.
Ito, D., Shinkai, Y., Kato, Y., Kondo, T., Yoshida, K. (2009). Chemical studies on different color development in blue- and red-colored sepal cells of Hydrangea macrophylla. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 73: 1054-1059.
Ozone Hole 2015 (s.f.). NASA earth observatory. Recovered from: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/86869/ozone-hole-2015