The phases of the moon and the lunar cycle
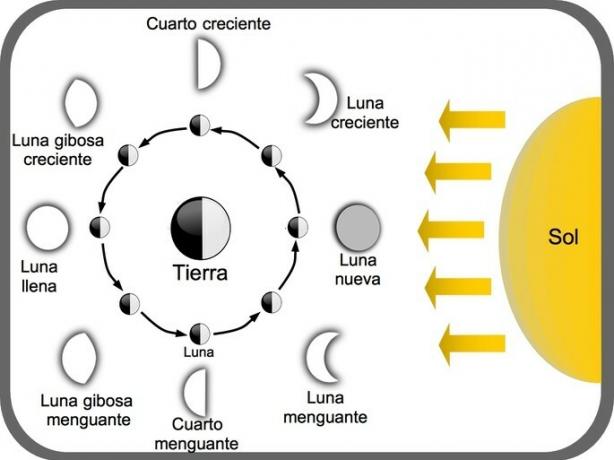
The phases of the Moon are four: new moon, first quarter, full moon and last quarter. These are the different ways we see the Moon as a consequence of its translational motion around the Earth.
The Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth, that is, it is a celestial body that orbits or revolves around our planet. Despite not having its own light, the Moon reflects the light it receives from the Sun.
Depending on the position of the Moon with respect to the Sun and the Earth, we can see the different lunar phases:
- The new moon: it is not visible on Earth as it is located between the Sun and the Earth.
- The crescent quarter: shows an illuminated half of the Moon, which is in the first quarter of its journey.
- Full moon: appears fully illuminated at the point of the lunar orbit furthest from the Sun.
- The last quarter: the other half of the moon is illuminated, and it is one quarter away from completing the lunar cycle.

1. New Moon
It is the phase in which the lunar cycle begins, also called the new moon. It is when we cannot see the Moon because the illuminated part is on the opposite side to the one we see on Earth.
When the Moon is between the Sun and the Earth we do not see it because none of the rays of the Sun that illuminate it are reflected towards us.
As the Moon moves in its orbit away from the Sun, an illuminated part of the Moon begins to be seen, known as Crescent moon.
The crescent Moon in the southern hemisphere grows from left to right, as it grows from right to left in the northern hemisphere.
2. Crescent quarter
It is when we can see half of the Moon illuminated by the Sun. The line connecting the Moon and the Earth makes a 90 degree angle with the line connecting the Earth and the Sun. At this point, the Moon has traveled a quarter of its orbit. This phase can be seen between noon to midnight.
After the first quarter, as the Moon continues its journey, it lights up beyond the middle of the lunar circle, giving it a hump or "hump" appearance. Astronomers call this transition Crescent gibbous moon.
3. full moon
It is when we see the Moon fully illuminated as a circle of light. At this point, the Moon has traveled half its orbit and is in the farthest part of it, opposite the Sun.
We can observe this phase between sunset and sunrise.
The days following the full Moon, it moves towards the Sun, decreasing the portion of the Moon that we can see. It returns to the hunchbacked form, but is called Waning gibbous moon.
4. Last quarter
It is when we see half of the lunar circle illuminated after the full Moon. At this point, it lacks a quarter of its travel to complete its orbit. It appears at midnight and hides at noon.
As the Moon approaches the Sun again, the illuminated side that we can see is reduced. This is what we know as waning moon.
Lunar cycle
The lunar cycle begins when the Moon is not visible from Earth and appears "off" (new moon). Then, it begins to light up halfway (crescent moon). The Moon continues to light up until the circle is completed (Full Moon). From here, the illumination begins to decrease until it reaches half (last quarter) and continues to decrease until it is no longer visible from Earth. (New Moon).
Half of the Moon is always illuminated by the Sun (except when the lunar eclipse occurs). As the Moon orbits the Earth, the line between the Earth, the Moon and the Sun changes its angle. This explains the different phases that we observe from Earth.
The Moon makes a complete revolution around the Earth in 27.3 days. However, the period of time that elapses between two equal phases is called the synodic lunar month or lunation and is equal to 29 days, 12 hours and 44 minutes.
You may also be interested in seeing:
- Rotational and translational movement.
- 21 natural phenomena.
References
Kriner, A. (2004). The phases of the Moon, how and when to teach them? Science & Education 10: 11-120
Maran, S.P. (2013). Astronomy for Dummies. Banshee digital editor.