Types of sugar: difference between fructose, glucose and sucrose
Fructose, glucose, and sucrose are different types of sugars or carbohydrates. The fructose it is a simple six-carbon sugar with a ketone group on the second carbon; the glucose it is a simple six carbon sugar but with an aldehyde group on the first carbon. The saccharose It is a disaccharide, that is, it is made up of the two monosaccharides glucose and fructose.
These three sugars are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, so they are organic compounds. The functional chemical groups that characterize carbohydrates are the hydroxyl group (-OH) and the carbonyl group (-C = O).
| Fructose | Glucose | Saccharose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Six-carbon monosaccharide ketohexose. | Six-carbon monosaccharide aldohexose. | Disaccharide formed by the union of fructose and glucose. |
| Number of carbons | 6 carbons |
6 carbons |
12 carbons |
| Functional group |
Ketone and poly- hydroxyls |
Aldehyde and poly- hydroxyls |
Cop- hydroxyls |
| Chemical formula | C6H12OR6 | C6H12OR6 | C12H22OR11 |
| Where to get | Fruits, honey. | Fruits, as part of starches in vegetables. | Common table sugar, extracted from sugar cane or beets. |
What is fructose?
Fructose is a simple sugar or monosaccharide, of formula C6H12OR6. The word "fructose" derives from Latin fructus which means "fruit". Therefore, the greatest source of fructose is found in fruits.
Fructose chemical structure
The fructose molecule is characterized by having a carbonyl group on the second carbon of a chain of six, which is why it is described as a ketone and hexose or ketohexose.
Monosaccharides that have six carbons tend to form a cyclic structure, in this case it reacts the hydroxyl of carbon 5 with carbon 2 of the ketone group, forming a five-sided ring or cyclopentane. Since fructose cyclopentane resembles the compound furan, it is also called fructofuranose.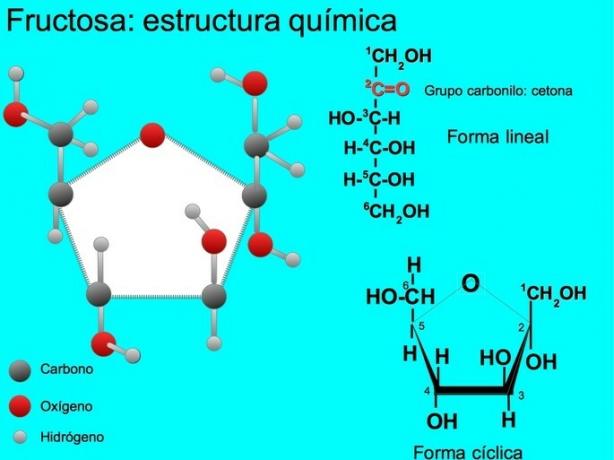
Fructose metabolism
Fructose is absorbed in the small intestine and passes into the portal vein. In the liver, all fructose is taken up and transformed into fructose-1-phosphate by the enzyme fructokinase. Fructose-1-phosphate can then enter the glycolytic pathway. The metabolism of fructose does not require the participation of the hormone insulin.
When there is an excess of fructose in the intake, especially from the consumption of sweetened beverages, this can also be transformed into triglycerides, so the consumption of fructose is associated with the liver fatty.
Fructose sources

Fructose represents one third of the sugars found in honey. However, the fructose in honey is mainly in the form of a six-sided ring or pyranose. This fructopyranose is much sweeter than fructofuranose.
Fruits are an important source of fructose but we also get it as part of the sucrose molecule, the common sugar in kitchens. Corn syrup used as a sweetener in the food industry is made up of fructose.
What is glucose?
Glucose is the most abundant carbohydrate on Earth. It is a simple sugar or monosaccharide, of formula C6H12OR6, like fructose, so both monosaccharides are isomers of each other.
Glucose is the monosaccharide component of the storage polysaccharides: starch (in plants) and glycogen (in animals). It is also a constituent part of the structural polysaccharide of plant cell walls (cellulose). Plants produce glucose through the process of photosynthesis, from carbon dioxide, water and solar energy.
Glucose is also the source of energy for most heterotrophic organisms, through the process of glycolysis.
In humans, glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen. On the other hand, when we talk about blood sugar, we are referring to the amount of glucose that circulates in the blood.
Chemical structure of glucose
Glucose is characterized by having a carbonyl group on the first carbon of a chain of six, which is why it is described as an aldehyde and hexose or aldohexose. It also has five hydroxyl groups (-OH) so it is also identified as a polyol.
As it has six carbons, it tends to form a cyclic structure by reacting the hydroxyl of carbon 5 with carbon 1 of the carbonyl group, forming a six-sided ring or cyclohexane. Since glucose cyclohexane resembles the pyran compound, it is also called glucopyranose.
 Glucose metabolism
Glucose metabolism
Glucose in plants and animals has three metabolic pathways:
- Storage.
- Glycolysis to obtain ATP.
- Oxidation via pentoses to obtain biosynthetic precursors.
Glucose is absorbed into intestinal cells by membrane transporters and rapidly passes into the bloodstream. Glucose metabolism in humans is regulated by the pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon.
Chronic excess blood glucose is what we know as diabetes.
Glucose sources

The main source of glucose comes from starches in vegetables. Starches are linked glucose chains; In the digestive system there are enzymes that are responsible for releasing these glucose that are absorbed in the small intestine.
Free glucose is also found in fruits and glucose is part of the lactose molecule, which is the sugar in milk.
What is sucrose?
Sucrose is a disaccharide of formula C12H22OR11, formed by the union between glucose and fructose. It is what we commonly know as table sugar, which is extracted mainly from sugar cane or beets.
It is formed only in plants, and it is the compound that plants use to transport excess sugar precursors from the leaves to the other parts of the leaves.
Sucrose chemical structure
Sucrose has a glycosidic bond that forms between carbon 1 of glucose and the hydroxyl oxygen on carbon 2 of fructose. It is denoted as glucopyranosyl (ɑ 1 → 2ß) fructofuranose.
 Sucrose metabolism
Sucrose metabolism
Sucrose in the digestive system is separated into glucose and fructose by the action of the enzyme sucrase-isomaltase, each of the sugars being absorbed by the intestinal cells.
Sucrose sources

Sucrose is the form of transport of carbohydrates in plants to storage organs, where it is transformed into starch.
The table sugar that we use on a daily basis is extracted mainly from sugar cane and eggplant.
Glucose, fructose and sucrose content in food
Here is a table with the values of the glucose, fructose and sucrose content of different foods (in percentage of solids):
| Sugar content by percentage of solids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Glucose | Fructose | Saccharose |
| Apple | 7 | 38 | 24 |
| Apricot | 12 | 9 | 40 |
| peach | 7 | 9 | 54 |
| Pear | 7 | 50 | 12 |
| Plum | 19 | 9 | 28 |
| Beet | 2 | 1 | 55 |
| Carrot | 7 | 7 | 35 |
| Sweet corn | 2 | 2 | 13 |
| Sweet potato, sweet potato | 2 | 1 | 15 |
| Pumpkin | 7 | 9 | 12 |
You may also like:
- Food and nutrition.
- Overweight and obesity.

Doctor in Biochemistry from the Venezuelan Institute of Scientific Research (IVIC), with a degree in Bioanalysis from the Central University of Venezuela.



