Difference between open system, closed system and isolated system
Thermodynamic systems are classified as open, closed, or isolated. The open system It is where energy and matter can enter or leave the system. The system closed It is one where there is transfer only of energy. The isolated system it allows neither the entry nor the exit of energy or matter.
In thermodynamics, a system It is the part or portion of the Universe that is being studied. The system typically consists of a specific amount of chemical substance (s) or matter within defined limits. Anything that is outside the limits of the system is classified as surroundings. One system can be the Earth or a container of water on the kitchen table.
| Open system | System closed | Isolated system | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thermodynamic system where there is exchange of energy and matter with the surroundings. | Thermodynamic system where there is energy exchange with the surroundings. | Thermodynamic system where there is no exchange of energy or matter with the surroundings. |
| Energy | Get in or out. | Get in or out. | It neither enters nor leaves. |
| Matter | There is an exchange of matter with the surroundings. | There is no exchange of matter with the surroundings. | There is no exchange of matter with the surroundings. |
| Examples | The Earth, an uncovered pot of boiling water, the cell. | A bottle of water in the refrigerator, | A closed thermos. |
What is open system?
An open system is a thermodynamic system where the entry and exit of matter and energy occurs to and from the surroundings. For example, the Earth is an open system since radiant energy from the Sun and material such as meteorites and gases enters, and artificial satellites, gases and radiation leave the Earth.
Energy exchange in an open system
An open system can exchange energy with its surroundings in two ways: work and heat. The job It is given by the movement of an object carried out by a force. The hot It is given by the transfer of thermal energy.
Open system examples
The earth

If the Earth were an isolated system, life would not be possible, since it depends on the energy of the Sun and on matter from outer space.
The human body
In order to live, humans require pottery and energy, which we obtain from food. In addition, we also release energy, in the form of heat and work, and matter, such as biological waste, sweat, and breath.
You may also be interested in seeing Difference between heat and temperature.
What is a closed system?
A closed system is a thermodynamic system where energy input and output occurs to and from the surroundings. In this case, the matter or substances contained in the system do not vary in quantity.
A very simple example is when we put a lid on a pot while the soup is cooking. By heating the pot we are providing thermal energy, while what is inside the pot cannot get out and the water condenses on the walls of the pot.
Examples of closed system

An example of a closed system is that of gardens sealed in glass. We can grow a mini-garden inside a sealed jar: autotrophic plants only require radiant energy to produce photosynthesis. The air and water inside the jar do not go in or out.
In fact, this type of system was frequently used on long voyages across the world in the colonization era, to transport plants.
What is an isolated system?
An isolated system is a thermodynamic system where there is no entry and / or exit of matter and energy to and from the surroundings. This is actually an idealized condition, the closest we know to an insulated system is a closed thermos or Dewar jug. The insulating walls of the thermos keep the substances inside hot or cold, so that the exchange of energy with the outside is not established.
Isolated system example
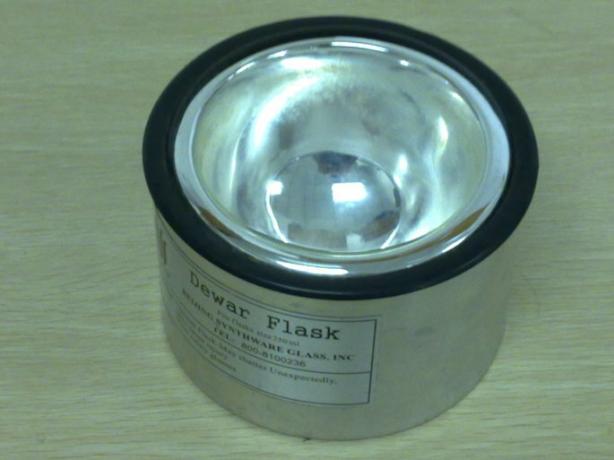

Dewar jugs are manufactured in order to keep gases or liquids very cold (for example, liquid nitrogen or dry ice) or very hot, for a longer amount of time. They are the closest thing to an isolated system in the laboratory. They are characterized by having a double wall vacuum sealed, so there is no intermediate air to allow heat flow.
You may be interested in knowing more about:
- Endothermic and exothermic reaction
- Kinetic and potential energy
- States and properties of matter