Cell types (with examples and pictures)
Living things are made up of cells, the basic unit of life. There are many types of cells:
- according to their evolutionary origin: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell;
- according to its energy requirement: plant and animal cell;
- according to their functions: contraction, defense, transport, repair, among others.
Cell types according to their evolutionary origin
According to evolutionary origin, we have two types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cell
The prokaryotic cell is characterized by present their cellular content, especially genetic material, dispersed in the cytoplasm. This means that the prokaryotic cell has two main structures: the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm, and it does not have a nucleus.
The prokaryotic cell is the cell that distinguishes the domains Bacterium Y Archaea. Most prokaryotic cells are small and simple in appearance, and are widely distributed throughout the biosphere.
Prokaryotic cell example
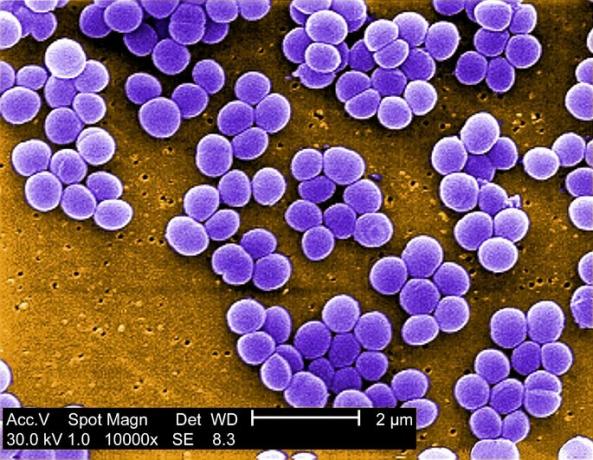
The Staphylococcus aureus It is a round-shaped Gram-positive bacteria that can be found on the skin and mucosa of humans. Infections with this agent have increased due to antibiotic resistant strains.
Eukaryotic cell
The eukaryotic cell is characterized by presenting its cellular content organized in membrane compartments, in particular, the genetic material (DNA) that is confined to the nucleus. In this way, the eukaryotic cell has three main structures:
- The plasma membrane: is the structure that surrounds and limits the content of the cell.
- The nucleus: it is the organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: it is the portion of the cell between the nucleus and the plasma membrane, where the rest of the organelles (mitochondria, ribosomes, vesicles, among others) and the aqueous medium where they float are found.
The eukaryotic cell is the hallmark of the domain Eukarya, where animals, fungi, plants and protozoa are classified. Most eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells, and can be found in unicellular (such as yeast) or multicellular (such as earthworms).
Eukaryotic cell example

The Giardia lamblia it is a unicellular protozoan, characterized by having a pear shape and four flagella that allow it to move. This parasite produces an intestinal infection characterized by abdominal pain and diarrhea.
For more details see eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell.
Eukaryotic cell types
We can classify eukaryotic cells into two large groups: animal cell and plant cell.
Plant cell
The plant cell is characterized by having a plasma membrane, cell nucleus and cytoplasm, where the organelles are found. It also has:
- Cellular wall: structure that covers the outside of the plasma membrane, composed mainly of cellulose fibers, which supports the cell.
- Chloroplasts: intracytoplasmic organelles with a double membrane, where the process of transformation of solar energy into organic compounds by photosynthesis takes place.
- Plasmodesmata: they are pores or passageways that exist in the cell wall that allow the exchange of material between plant cells.
- Glioxisomes: they are organelles found in seeds, where the necessary lipids are stored and degraded in the germination process.
- Central vacuole: water storage area within the plant cell.
Plant cell example

The cells of the leaves of plants, such as the Elodea canadensis, are specialized to capture sunlight and absorb carbon dioxide from the air, for the synthesis of carbohydrates. All plants are autotrophic beings, that is, they are independent of other organisms to obtain their energy.
Animal cell
The animal cell is characterized by having a plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus, like other eukaryotic cells. They are distinguished from plant cells in:
- they do not possess photosynthetic organelles or chloroplasts.
- His cell membrane is made up of cholesterol, which is not found in plant cells.
- It does not have a cell wall.
- Possess Centrosomes, structures that have a role in the process of cell division.
Animal cell example

Within the diversity of animals that populate the Earth, one of the easiest cells to distinguish with the naked eye are eggs. Some have a rigid protective covering, like the eggs of birds. Others are naked, as is the case with the eggs of amphibians and fish.
For more details see Animal and plant cell.
Main types of human cells
Within the human body, there is a great diversity of cells with specific functions.
Epithelial cells
Epithelial cells are found lining the exterior of the body (on the skin) and internal surfaces (such as the inside of the mouth and nose). They can be flat, cubic or cylindrical, depending on the tissue they are part of. They are strongly attached to each other, without intercellular spaces. Its main function is to act as a protective barrier.
Fibroblast
The fibroblast is the cell responsible for the formation and maintenance of connective tissue. They are also activated in the wound healing and repair processes. They are large, flattened and tapered, with a flattened, oval core.
Adipocytes

Adipocytes are lipid storage cells and are found in connective tissue and adipose tissue. They are very large and round, with a fine line of cytoplasm around a large fat vacuole.
Muscle cells

Muscle cells are mainly characterized by their ability to contract. They are elongated in the direction of the movement they perform. They are found in skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
Monocytes and macrophages
Monocytes are cells of the immune system that develop in the bone marrow and are released into the blood. After a short period of time, the monocytes leave the blood vessels and enter the tissues, transforming into macrophages.
Red blood cells
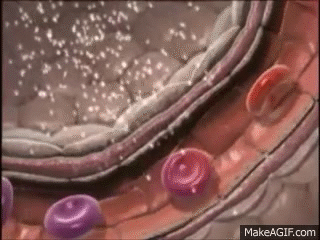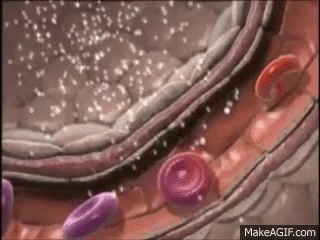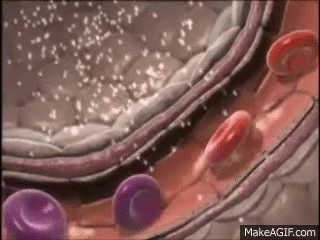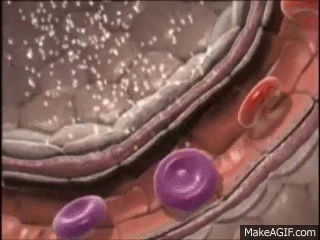
Red blood cells, red blood cells or erythrocytes are characterized by having a donut shape and being anucleated, due to the fact that in the process of formation in the bone marrow, in the last stage of maturation, they lose the core. Its main function is gas exchange:
- the transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and
- the removal of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
Bone cells
In bones there are several types of cells:
- The cells osteoprogenitor they appear in the fetal stage in the growth zones of the bone;
- the osteoblasts they are the bone-forming cells;
- the osteocytes they are the cells for maintaining bone quality;
- the osteoclasts They are the cells that break down bone.
You may also be interested in:
- Animal and plant cell
- Eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell

Doctor in Biochemistry from the Venezuelan Institute of Scientific Research (IVIC), with a degree in Bioanalysis from the Central University of Venezuela.



