The 4 most important parts of the kidney, and their functions
The urinary system is responsible for the formation, conduction and storage of urine, a colored liquid yellowish by all known that is obtained as a result of the purification and filtering of the blood of the individual.
This mechanism It is essential for the maintenance of the balance in the organic fluids, as well as for the elimination of toxic substances and even the maintenance of blood pressure. Therefore, it is no surprise to anyone to learn that human beings excrete an average of a liter and a half of urine per day, depending on the food and liquids ingested.
We cannot talk about the urinary system without placing our eyes and mind on the kidneys, since they are one of the only two components that make up this apparatus, along with the urinary tract. Although every human has an overview of this pair of interesting organs, the kidneys hold many more secrets than it might at first appear. Therefore, today we talk about the parts of the kidney and their functions.
- Related article: "Excretory system: characteristics, parts and operation"
Kidney Parts and Their Functions: Beyond Urine Formation
If we think about the urinary system, the first thing that comes to mind is the production of urine (logical, since this word is included in the first term). Even so, the kidneys do not limit their functionality to blood purification. Therefore, in the first instance, we show you all the activities that the kidneys perform for the physiological and metabolic balance of human beings:
- Regulation of volume and osmolarity (particle concentration) of body fluids. This is achieved by balancing the concentration of ions and water.
- Excretion of waste products, either the product of normal cell function or the entry of foreign agents into the body.
- Synthesis of glucose from amino acids and other precursors. It accounts for 10% of the production of this monosaccharide at the body level.
- Regulation of erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells) through the secretion of the hormone erythropoietin.
- Regulation of blood pressure through the secretion of vasoactive factors such as renin (involved in the formation of angiotensin II)
- Regulation of the acid-base balance, mainly through the excretion of acidic substances. This is essential to keep the internal pH balanced.
- Production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (activated vitamin D), essential to maintain adequate calcium levels in the bones.
As we can see, we are facing multidisciplinary bodies, since they are not only responsible for the elimination of substances, but also they are also responsible for the synthesis of sugars such as glucose and hormones such as renin, erythropoietin or kallikrein, all with different functions on the organism.
It is incredible to think that a couple of organs that do not account for more than 1% of a person's body weight can become so key to their survival, right? All of this is put more into perspective when we discover that, for example, kidney irrigation accounts for approximately 22% of cardiac output. The volume of blood passing through these structures at any given moment is therefore not a negligible value.
Once we have cemented the functionality of these incredible structures, let's dive into their characteristic morphology.
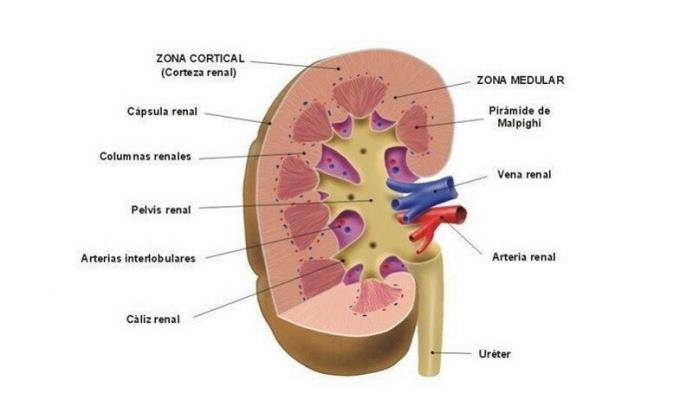
1. External protective fabrics
We are going to start from the outside and dissect the kidney mass little by little. First of all, it is necessary to note that each of these two organs is surrounded by three different layers of tissue:
- The outermost is known as the renal capsule, a transparent, fibrous and continuous membrane that serves to protect the kidney from possible infections.
- An adipose capsule, that is, a layer of fat of variable thickness that protects the kidney from blows and trauma and keeps it in place in the abdominal cavity.
- The renal fascia, a layer of connective tissue that separates the fat capsule from the pararenal fat.
It is especially important to remind readers that this system, as it is not in direct contact with the environment, it does not have a microbiome or bacterial agents associated beneficial to its functions. For this we have these protective tissues, in order not to strain pathogens and generate the dreaded urine infections.
- You may be interested in: "Major Cell Types of the Human Body"
2. Renal cortex
This layer responds to the outermost part of the kidney. It is one centimeter thick and has a brownish-red color. This area contains 75% of the glomeruli, which are a network of small blood capillaries By which the purification and filtration of blood plasma occurs, as the first part of the urine-forming process.
Therefore, the renal cortex receives 90% of the blood flow that enters these organs and has a filtration, reabsorption and secretion function. It should be noted that this outermost layer is not longitudinally separated from the renal medulla, since a series of protrusions called renal columns are produced towards them.
3. Renal medulla
The renal medulla, meanwhile, it is located in a deeper point of the kidney and presents a greater morphological complexity, as it is composed of conical-looking units (with the base facing the cortex) called renal pyramids. These are divided between them by renal columns and their number varies between 12 and 18. Therefore, we can say that the human kidney is a multilobed organ.
The vertex of each renal pyramid leads to a smaller calyx, and the union of several of them give rise to the greater calyces, which unite to form the renal pelvis. We have to imagine this structure as if it were a tree: the renal pelvis is the trunk, and the calyces each of the branches that lead to large leaves (the renal pyramids).
Finally, it is necessary to limit that the renal pelvis corresponds to the section of the ureterTherefore, the urine will travel through here to the bladder, where it will accumulate until it is emptied by the process of urination known to all.
4. The nephron
It seemed that this moment was not going to come, but we cannot leave the nephron in the pipeline: the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney, where the blood is filtered and purified. To put things in perspective we will say that there is an average of 1.2 billion nephrons in each kidney, which filter a whopping 1.1 liters of blood per minute.
As much as it is extremely difficult to make a mental image of this complex structure, we are going to describe its parts briefly:
- Glomerulus / renal corpuscle: already mentioned above, it is the set of capillaries where the clearance and filtration of blood plasma occurs.
- Bowman's capsule: A hollow sphere in which the substances to be excreted are filtered. It envelops the glomerulus.
- Proximal convoluted tubule: its function is to increase the surface of reabsorption and secretion of substances.
- Loop of Henle: a hairpin-shaped tube leading from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule.
- Distal convoluted tubule: Ion-permeable tube that collects waste substances that were not initially filtered into Bowman's capsule.
As confusing as this whole conglomeration of terminology may seem, the idea that must be clear is that the nephron is a highly specialized functional unit for the purpose of filtering blood. This is collected in four easy steps: filtration, tubular secretion, tubular reabsorption (recycling of nutrients and substances such as glucose, amino acids, 60-70% potassium and 80% bicarbonate) and excretion, that is, the emptying of the nephron.
It should be noted that, after 40 years of age, an average of 10% of nephrons are lost every 10 years. This happens since the kidneys are not able to regenerate them. Still, the remaining nephrons have been seen to adapt to maintain proper kidney function within normal limits.
Conclution
As we have seen, not only the parts of the kidney and their functions are highly complex, but each one of these organs is made up of millions of small individual filtering machines: the nephrons.
We must see the process of filtering and generating urine as a machinery in the shape of a tree.: from the small capillaries called glomeruli, where blood filtering occurs at the most microscopic level possible to the renal pelvis (collecting site from the kidneys to the bladder), the urine undergoes a series of changes and reabsorptions that lead to the yellowish fluid expel.
Bibliographic references:
- Rodrigues, C. F. S., Olave, E., Gabrielli, C., & Sousa, L. M. C. (1997). Anatomical considerations on renal fusion: a case report. Chilean Journal of Anatomy, 15 (1), 51-55.
- Cachofeiro, V., Lahera, V., & Tresguerres, J. TO. (1999). Anatomical and functional aspects of the kidney. HUMAN, 374.
- Anatomy of the Urinary System, stanfordchildrens.org. Picked up on September 9 in https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/es/topic/default? id = anatomyoftheurinarysystem-85-P04568
- Urinary system, Laboratory of Physical Anthropology and Human Anatomy. Picked up on September 9 in http://www.anatomiahumana.ucv.cl/morfo2/ren.html



