FEUDALISM in the Middle Ages

Feudalism was the social, political and economic system predominant in medieval Europe, being a key element between the 9th and 15th centuries. The importance of feudalism was such that it is considered as the predominant element of medieval society, and therefore in this lesson from a Professor we offer you a summary of feudalism in the Middle Ages.
The feudalism was the social, political and economic system typical of much of Europe during the Middle Ages, serving as substitute for the slave system. It marked a huge change that demonstrated the transformation of the world between the Ancient and Middle Ages. The importance of this model was such that it affected all areas of medieval society, modifying life from the least influential person to the king.
The basic element of feudalism was the so-called fief, a contract created between two people (the so-called lord and the other the vassal) that symbolized an agreement different from the relationship that existed between slave and master during the Ancient Age.
The contract known as a feud consisted of a mutual relationship, in which the lord gave a land where to live for the vassal while promising protection through his military forces; the vassal in return was dependent on the lord, having to work for the lord and pay a series of taxes per year or part of his production.
This land-tie system makes the economic center of feudalism is the earth, being the possession of this what makes a person lord; therefore, it was the most important value of this historical stage.
The importance of the land is what caused the origin of the numerous wars that encompassed all Europe throughout the medieval period, being a time very marked by numerous conflicts warlike.

To know the beginning of the Middle Ages we must talk about the origin and causes of feudalism, to understand the reasons that led to the change from the slave system to a feudalism one.
Feudalism arises with the the fall of the Roman empire of the West and the decline of the Eastern Roman Empire, causing the European economy to change to adapt to the new times. The continuous attacks of the barbarian peoples and the spread of Islam made the peasants and lower-class citizens seek protection on the walls of the great lordsThis being the beginning of what would eventually be called a fiefdom.
With the arrival of Carolingian empire a system was created based on the existence of numerous lords who occupied small regions, creating lordships where people protected themselves from attacks. At the same time, the lords helped the emperor to maintain his status. This decentralization was maintained after the fall of Charlemagne, being the origin of most of Feudal European states and, especially, of the Germanic zone that would give rise to the Holy German Empire.
The diminishing power of kings caused the feudal lords to gain great power over time, causing the creation of decentralized empires in which the feudal lords had enormous power, even being hierarchically below the monarchs.
Slowly, all of western Europe became feudal creating huge land holdings and an economic and social system based on land ownership and protection. This is how the vassalage agreements known as fiefdoms.
To continue this lesson on feudalism in the Middle Ages, we must talk about the main characteristics of feudalism, in order to understand the main elements that define this part of the European history. The main characteristics of feudalism are as follows:
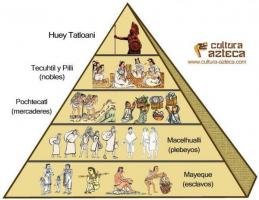
- Relationship between a feudal lord and a vassal, receiving both benefits from this agreement and being the center of the entire feudal system.
- Three closed social classes and with different privileges, being the nobility, the clergy and the third state or common people, arising over the years new classes within each of these as the lower clergy or the bourgeoisie of the third condition.
- Construction of castles and walls as defense of external enemies and barbarians, being the possessors of these walled enclosures those who received the positions of nobles and lords.
- Economy based on agriculture and livestock, these tasks being performed by the vassals but the nobles receiving most of the profits from these elements. Other activities such as crafts were less common, although they remained of the common people.
- The importance of the land As a vital good of feudalism, it increased wars between nations, since all sought as much ground as possible to increase their power.
- The economy was based in part on tributes, being payments that the common people paid to the nobility and the clergy, supporting the non-privileged classes to the privileged ones. The tributes could be of many kinds, increasing over the years to pay for almost everything.
- The Church had great power During feudalism, religion was already an essential power for the monarchs and nobles, maintaining an enormous amount of tributes that were directed to enrich the Catholic Church.
- The enormous power of the nobility, greater than that of the king, it provoked great decentralized powers due to the importance of the fiefdoms.