SENSORY organs of the human body and their FUNCTIONS
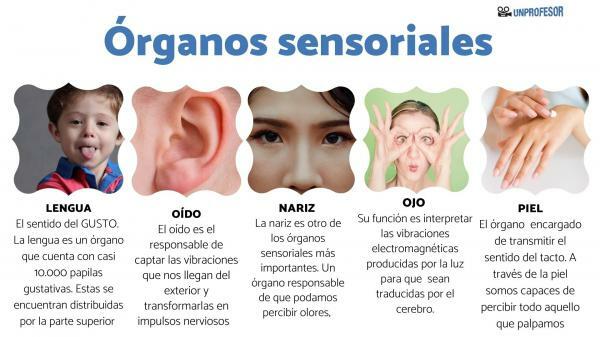
The correct operation of the sensory organs It is what endows both human beings and animals with the ability to relate directly to the environment. These sensory organs are linked to parts or areas of our body such as the tongue, ear, nose, eyes and skin. Thanks to these sensory organs we recognize as our five senses: taste, hearing, smell, sight and touch.
Do you want to learn more about its operation and importance? Well, we invite you to continue reading this lesson from a PROFESSOR so that you can expand your basic knowledge and discover more about your own body.
Index
- What are the main sensory organs of the human being?
- The tongue, one of the most important sensory organs
- The ear
- Nose
- The eye
- The skin
What are the main sensory organs of the human being?
The main sensory organs of the human being are:
- Language
- The ear
- Nose
- The eyes
- The skin
Next, we analyze each of these organs to get to know them better.
The tongue, one of the most important sensory organs.
As we have mentioned in the introduction, the sensory organs are those that grant powers to humans and other animals. In this case, we want to start by talking to you about sense of taste.
Thanks to it, we are able to perceive a wide range of flavors that, in turn, have repercussions multitude of responses to the different stimuli we receive from everything we feel through of the language. And it is that we do not only capture differentiated flavors thanks to it, but also the texture and temperature of the things we put in our mouths.
The tongue is an organ that has almost 10,000 taste buds. These are distributed over the upper part of it where, the most sensitive to sweet and salty flavors are found on the tip, and those capable of perceiving acid and bitter flavors are located on the sides and on the back respectively.
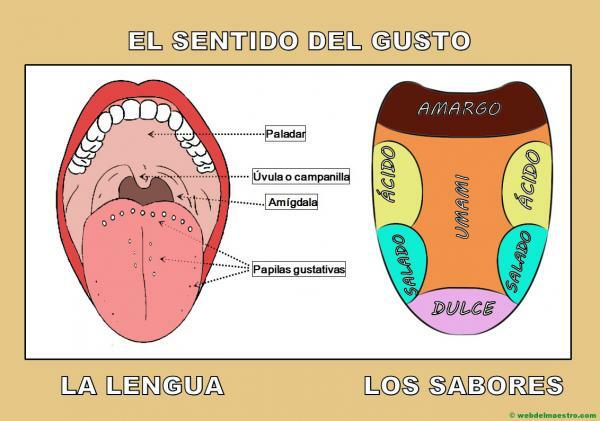
Image: Web master
The ear.
The ear is the responsible for capturing the vibrations that come to us from the outside and transform them into nerve impulses so that they reach our brain to be interpreted. The ear is divided into three zones all connected to each other.
- External ear area: It is made up of the pinna or ear and the external auditory canal. The outer ear has glands that produce wax and hair, through which it manages to direct sound waves to the next area: the middle ear.
- Middle ear area: It is made up of the eardrum, which is responsible for conducting sound waves to the inner ear. In addition, it is connected, thanks to the Eustachian tube, with the nose and throat that regulates the entry and exit of air in order to balance possible pressure differences.
- Inner Ear Zone: here are a series of membranous canals located in the dense part of the temporal bone and which are divided into three parts, the snail, the vestibule and the semicircular canals, communicating with each other.
It will be thanks to the air pressure collected by the external area that reaches the eardrum so that it is produces the vibration that after passing through the chain of ossicles sends the information to our brain. In the same way, the hairs also located in the external area will inform the position of the head with respect to pressure changes.
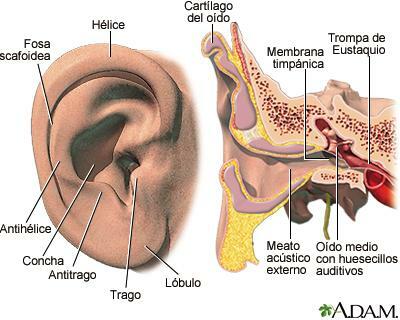
Image: Medline Plus
Nose.
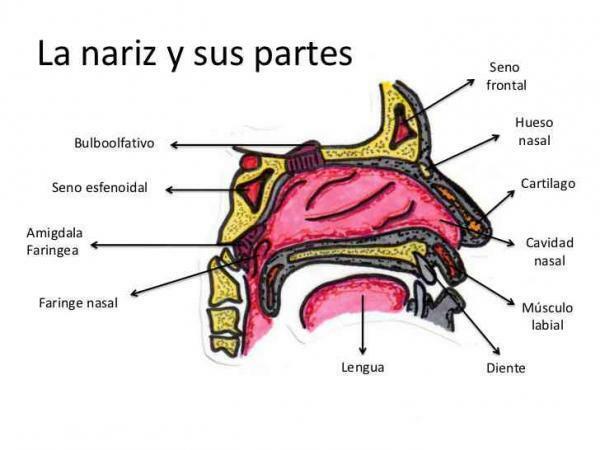
The noseit is another of the most important sensory organs. An organ responsible that we can perceive odors, although it is not limited to this. In fact, many of the sensations that we perceive in our mouth and that we attribute to the sense of taste are actually olfactory and have their origin in the olfactory nerves. Smell is also our sense more closely memory related.
The nose is divided into an internal region, formed by both nostrils, the nasal appendix and the external region. In the nostrils there are also a large number of strong hairs, which make it difficult for foreign bodies to pass.
Currently accepted seven types of receivers, which recognize seven main volatile molecules and which, when combined, give rise to a myriad of different odors. These seven main odor molecules or types are as follows:
- Camphor
- Musk
- flowers
- Mint
- Ether (dry cleaning liquid)
- Acre (vinegary)
- Rotten
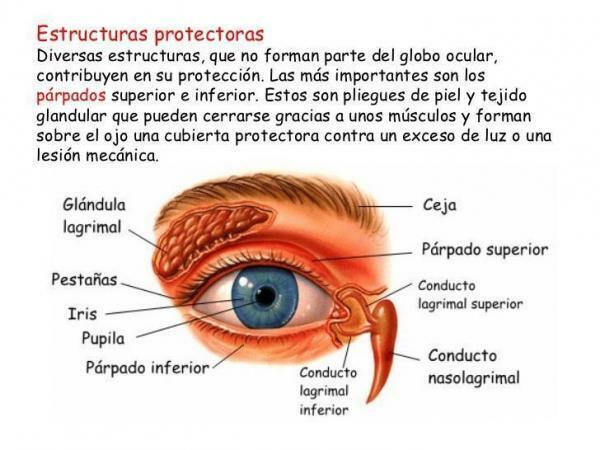
The eye.
Its function is interpret electromagnetic vibrations produced by light so that they are translated by the brain thanks to the optic nerve. The eye or eyeball It has a spherical shape and is composed of three layers:
- The sclera, whose function is to protect the eye
- The uvea formed by the choroid
- The ciliary body and iris
- Finally, the retina, which is the area sensitive to light and therefore the most important.
Every movement of the eyeball, no matter in which direction you focus, is done thanks to six eye muscles.
The skin.
Finally, we end with the sensory organ in charge of transmitting the sense of touch. Through the skin we are able to perceive everything that we touch or that is in direct contact with our body, from objects to substances.
All this is achieved thanks to touch receptors located in the outer layer of the skin called the epidermis. In this way all the sensations captured by the receptors will be sent to the brain through the nerve fibers.
An important detail is that each area of the skin does not have the same number of receptors hence it is more or less sensitive.
If you want to read more articles similar to Sensory organs and their functions, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- TO. Jean Ayres. Editorial Tea Editions. (2008) Sensory integration in children: Hidden sensory challenges.
- Ignacio Morgado. Editorial Ariel. (2019) The senses. How we perceive the world.



