We tell you how many CHROMOSOMES gametes have

In organisms that have a diploid chromosome endowment (2n), each somatic cell (cells that make up the body of the organism) has one pair of each chromosome. The gametes (or reproductive cells) are formed through a process of cell division called meiosis, which supposes the reduction of the chromosome endowment by half. Therefore, the gamete endowment is haploid (n)
In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to discover you how many chromosomes do gametes have so that, thus, you can better understand the functioning of our body.
Index
- Chromosome number of gametes
- What are gametes
- The chromosome endowment and its types
- Importance of meiosis in the processes of sexual reproduction
Chromosome number of gametes.
In this article by a PROFESSOR we will explain why the somatic cells that are part of the body of an organism have diploid envelope (2n chromosomes); while gametes have half the chromosomes, that is, they have haploid endowment (n chromosomes).
The diploid endowment of somatic cells implies that each cell contains two complete sets of chromosomes because they contain pairs of homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that contain the same genes). In contrast, the haploid endowment gametes contain a single complete set of chromosomes, ie. A single chromosome of those that constitute the pairs of homologues in the diploid envelope.

Image: Genotype
What are gametes.
Gametes or sex cells are highly specialized cells that are involved in the process of sexual reproduction. Two exists types of gametes: the female gamete, called Ovum, and the male gamete that receives the name of spermatozoon.
During the process of sexual reproduction, the male and female gametes fuse to form a fertilized zygote or ovum that will give rise to a new organism. In so-called diploid organisms (2n) the formation of sex cells (gametes) involves the reduction of the chromosome endowment by half through a specific cell division process called meiosis. Thus, the gametes generated by this process are haploid (n) and contain a single set of chromosomes.
In sexual reproduction, during fertilization, a female and male gametes merge to form a zygote or fertilized cell. In the zygote the fusion of the nuclei of the two gametes will give rise to a nucleus that contains two complete sets chromosomes: one from the female gamete (ovum) and the other from the male gamete (sperm).
Therefore, the zygote or fertilized cell will have diploid endowment and by successive divisions by mitosis(Cell division process typical of somatic cells and that does not imply variation in the number of chromosomes) will give rise to a new diploid organism with the same number of chromosomes as all individuals of its kind.
The gametesthey have haploid endowment (n) and have half the chromosomes of a somatic cell. At fertilization, the gametes fuse to form a zygote (fertilized egg). This zygote will have the same number of chromosomes as that of a somatic cell and, therefore, the chromosomal endowment of the species will remain constant.

The chromosome endowment and its types.
The chromosomesThey are complex molecular structures made up of DNA and proteins. Chromosome DNA contains most of the organism's genetic information. They are formed by the nuclear DNA packaging in the early phase of cell division, in a process called DNA condensation.
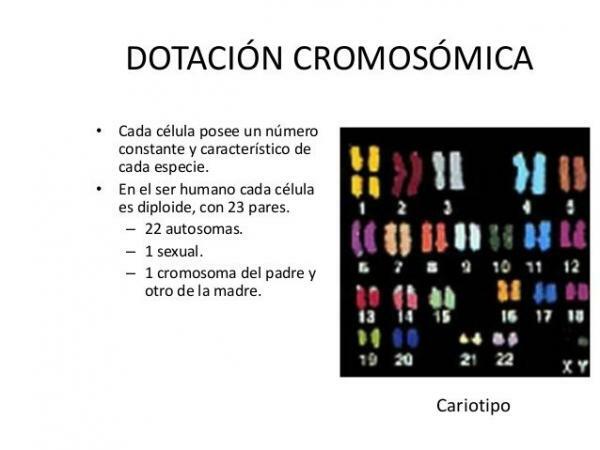
The set of chromosomes present in cells the organisms of a species are called the chromosomal endowment or karyotype. According to the type of chromosome endowment, two types of organisms are distinguished:
Diploid organisms (2n)
Each cell contains two sets of chromosomes, Each pair of like chromosomes (containing the same genes) are called homologous chromosome pairs and pair up during the process of cell division. Diploid organisms are humans and most animals. For example, in the case of humans, each somatic cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes or 46 chromosomes.
Of the total of the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 are pairs of homologous chromosomes and one pair are sex chromosomes (X chromosome and Y chromosome) that determine the sex of the organism. Although they form a pair of chromosomes during cell division, sex chromosomes, or heterochromosomes, do not have the same structure or contain the same genetic information. In human gametes we find only 23 chromosomes: one of the members of each of the 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes and one of the two sex chromosomes (X or Y)
Haploid organisms (n)
Each cell contains only one set of chromosomes. Haploid organisms are algae, fungi and some insects such as bees and ants.
Importance of meiosis in the processes of sexual reproduction.
The cell division process of meiosis is of Vital importance for two reasons:
1. Constant chromosome endowment
Meiosis keeps the chromosomal endowment of the species constant that reproduce sexually. The cells of any organism have a constant chromosomal endowment, that is, the number of chromosomes of a species is always the same throughout successive generations.
If the process of sexual reproduction did not include meiosis, the gametes generated by diploid organisms (2n) would not reduce their endowment by half. chromosome and the zygote formed by the fusion of these would double the number of chromosomes so that the generated individual would have a chromosomal endowment tetraploid (4n).
In this way, after a few generations, the number of sets of chromosomes present in the cells of a species would have increased in such a way that the cells would not be viable for two reasons:
- The large number of sets of chromosomes prevents correct distribution of genetic material during cell division.
- The amount of DNA would occupy such a large volume that the cell nucleus would not leave free space in the cytoplasm necessary to house the rest of organelles and cellular structures.
2. Generates genetic diversity in populations
During meiosis the process of rgenetic eccombination or crossing-over which consists of the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes (which contain the same genes). This process involves the appearance of new combinations of genetic information so that each of the gametes generated is different and unique.
In this way, the individuals generated by sexual reproduction are not identical to each other and the species has a diversity of individuals that facilitates the survival of the species.
If you want to read more articles similar to How many chromosomes do gametes have, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Martínez-Frías, M. L. (2010). Knowledge update on gamete formation. Meiosis and fertilization processes. SEMERGEN-Family Medicine, 36 (4), 216-220.
- García Haro, F. (2001). Chromosomal evolution in simiiform homologies, rearrangements and heterochromatin. Autonomous University of Barcelona.