Amniotes and anamniotes: characteristics

The animals They can be classified according to numerous criteria. Are they animals that live in water, on land or in the air? Do they use lungs to breathe or do they use gills? Do they reproduce sexually or asexually? Other classifications, despite not being so simple, tell us a lot about their ability to adapt and how they live; one of them is the classification of animals into amniotes and anamniotes.
The amnion is a membrane that appeared in evolution to protect the embryo, but its appearance implies more things. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see exactly the characteristics of amniotes and anamniotes, differences between them and why the appearance of the amnion was so important in the evolution of the animal kingdom.
Index
- The amnion: a layer of protection
- The differences between the eggs of amniotes and anamniotes
- Fertilization of amniotes and anamniotes
- The amnion and the conquest of the terrestrial environment
- Examples of amniotic and anamniotic animals
The amnion: a layer of protection.
Animal embryos are covered with layers that protect them during their development. In animals more primitiveDuring the embryonic development of animals, only one membrane appears: the yolk sac.
The yolk sac It is essential for the maintenance of the embryo, since it is in charge of sustaining the gas exchange between the blood of the mother and that of the embryo and allows this not only to breathe, but also to eliminate some waste produced.
Later in evolution the amnion, another embryonic envelope. This second embryonic envelope is responsible for hold the embryo in position, protect it potential mechanical damage, but also helps with your feeding. These functions are further enhanced by the appearance of a liquid inside the cavity that covers the amnion: the amniotic fluid.
The amniotic fluid It is a liquid that allows the embryo to develop in an aqueous environment, in which the transfer of gases, food and toxins between the embryo and the mother is much more efficient. In addition, the amniotic fluid has bacterial properties, which protects the embryo from possible infections that may have infected the mother. The composition and volume of amniotic fluid change throughout pregnancy, but in general, it closely resembles maternal plasma and has a degree of salinity similar to seawater.
Here we discover more concisely the differences between amniotes and anamniotes.
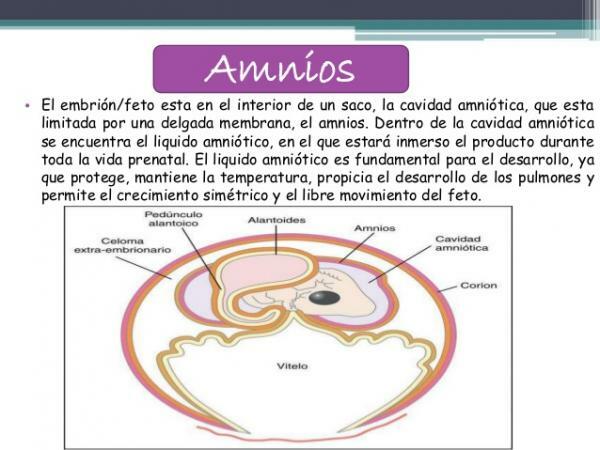
Image: Slideshare
The differences between the eggs of amniotes and anamniotes.
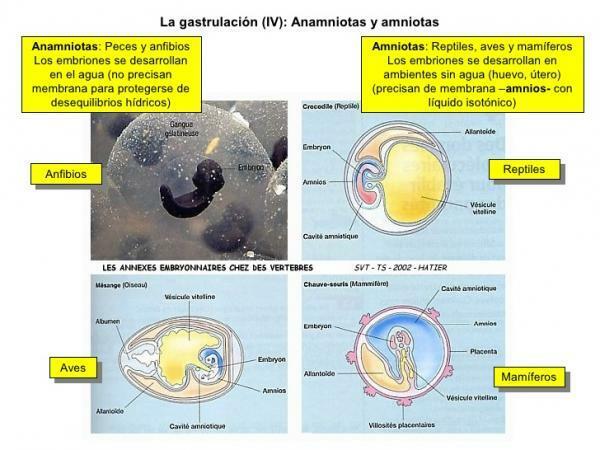
As we have already advanced in the previous section, the egg of the anamniotes has only one cover: yolk sac. Instead, the egg of the amniotes has four covers: chorion, allantois, amnion and yolk sac. These four covers allow an internal environment similar to an artificial pool to be created, in which the embryo is protected and well nourished.
- The yolk sac it is the innermost membrane of the embryo. It is the place where the gas exchange, which allows the embryo to breathe despite not having developed lungs yet. In addition, secondarily, it allows you to eliminate some waste (especially gaseous) produced during metabolism.
- The amnion It is located around the yolk sac and allows the appearance of amniotic fluid, which improves the diffusion of gases and functions as a "store" of fluid and nutrients for the mother.
- The allantois, is the first of these layers that is outside the body of the embryo, which is why it is said to be an extra-embryonic membrane. In addition to reinforcing the respiratory function, its function the allantois retains the substances produced by the embryo that cannot be eliminated at this stage.
- The chorionic membrane it is the last of the embryonic membranes of amniotes and surrounds the previous three. In humans, the chorionic membrane forms the chorionic villi, finger-like structures that penetrate the mother's endometrium and allow the exchange of nutrients between the two; in more advanced stages it collaborates with the formation of the placenta.
The fertilization of amniotes and anamniotes.
The appearance of all these covers on the amniote egg also produced a change in the type of fertilization. Within the anamniotes, fertilization is fundamentally external while the amniotes, fertilization must be internal.
Amniotes have two options to protect embryos from desiccation and dehydration:
- First, we can coat the egg with a hard protective cover, that protects them once they come out in the middle (as in chickens). In this case, if there was an external fertilization, the sperm could not cross that hard layer, so fertilization has to take place before it appears, inside the female.
- Second, you can prevent the new individual from going out into the environment until they are more or less independent organisms (as in the case of humans). In this case, fertilization must necessarily take place inside the female, where the embryo will remain until it is ready to leave it to the external environment.

The amnion and the conquest of the terrestrial environment.
The appearance of the amniotes' own egg, with various protective covers, allowed reptiles to make the ecological transition to the terrestrial environment. The amniotic egg, and especially the appearance of the last layer, hard but permeable to gases, allowed the protection of the embryos during their development.
Most of the animals at that time lived in the aquatic environment because, it is to be expected, that the older ones predators they were most of the time aquatic. The appearance of the amniota egg allowed the reptiles to begin to move the egg-laying away from the environment aquatic, with the consequent adaptive selection of this type of eggs, which were less attacked by the predators. This adaptive selection is believed to have been even greater because cycles of floods and droughts, which favored the eggs laid on land over the eggs, for example, of amphibians.
This conquest of the eggs of the terrestrial environment did not stop there since it allowed the amniotic animals to continue developing other structures for adaptation to the terrestrial environment like the appearance of lungs, the appearance of Dry Skin with protection mechanisms against desiccation, etc.
Examples of amniotic and anamniotic animals.
The most characteristic examples of amniotic eggs that we know best are those of turtles, crocodiles, birds or monotamos like the platypus and echidnas although if we study the embryonic development of other mammals like humans we can also identify the embryonic envelopes themselves. In some cases we can see modifications (such as the appearance of the umbilical cord).

If you want to read more articles similar to Amniotes and anamniotes: characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Carlson, B. M. (2019). Human embryology and developmental biology. Elsevier.
- Sadler, T. W., & Langman, J. (2019). Medical embryology. Wolters Kluwer.
- Villagrán Santacruz, M. (2013). The amniotic egg and the evolution of vertebrates. Sciences, (007).
- Morgan-Ortiz, F., Morgan-Ruiz, F. V., Quevedo-Castro, E., Gutierrez-Jimenez, G., & Báez-Barraza, J. (2015). Anatomy and physiology of the placenta and amniotic fluid. Rev Med UAS, 5 (4).