Find out how fungi reproduce
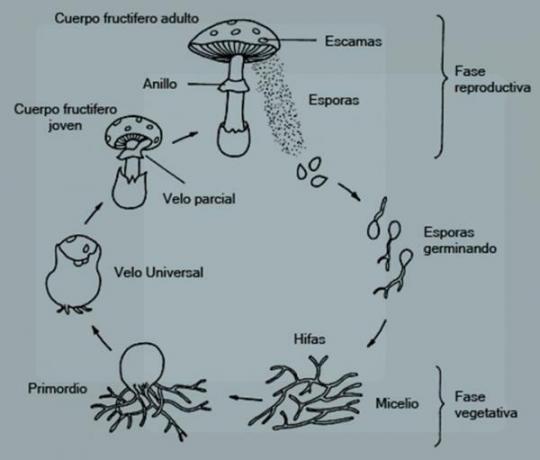
Image: The Fungi Kingdom
With more than 100,000 species described and an estimate of more than 1.5 million, the fungi kingdom It is one of the great forgotten in biology. Fungi or fungi are eukaryotic organisms, with different shapes, which can range from mushrooms and mushrooms that we all know to molds, yeasts, etc. Fungi have many peculiarities, among which are their mode of reproduction. Fungi reproduce through different mechanisms, which can be both sexual and asexual and, with or without the formation of a structure called a spore. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see How do mushrooms reproduce.
Fungi are part of the fungi kingdomand the vast majority of them reproduce both asexually and sexually. The same species of fungus can alternate between one form of reproduction or another, depending on the situation in which it is found, since each one provides advantages over the other. In addition, as we will see below, a fungus can have more than one sexual or asexual reproduction mechanism at the same time. As you can see, the reproduction of fungi is very varied!
- For one thing, fungi can have a asexual reproduction phase, which is called the imperfect phase or anamorphic. Asexual reproduction does not provide genetic variability, since a spore is generated with the genetic material exactly the same as the parental one, but it is much faster than sexual reproduction. It is used, for example, by infectious fungi that seek to spread at high speed in a culture or living being. It usually occurs especially when environmental conditions are stable, that is, what the fungus is proposing is to multiply as much as possible.
- On the other hand, fungi may have another phase during their life cycle in which they reproduce by methods of sexual reproduction. These phases (or fungi, in the event that the fungus only has this type of reproduction) are called perfect or teleomorph. Sexual reproduction, unlike asexual, generates genetic variability but requires more time, so it is especially useful when the fungus intends to survive in an environment with continuous changes or an environment in which a great change has occurred that endangers your survival. In this case, the fungus aims to create diversity, allowing at least some of its mechanisms to work and its genes to be passed on to the next generation. Sexual reproduction in fungi is quite complex, as we will see below.

Image: Slideplayer
To know how fungi reproduce, you have to know that, in the event that they reproduce in a asexual, employ four mechanisms, mainly:
- Fragmentation of the mycelium or mycelium. The mycelium is the vegetative part of the fungi. In mushrooms, it would be the part under the ground that holds them together to the ground (if we compare them with a plant they would be the "roots" of the mushroom) while with yeasts they would be the same cells. If the mycelium is cut or fragmented, each of these pieces can generate a new individual. This form of reproduction is especially useful in research laboratories to keep fungi in constant culture.
- By budding. Fungi can reproduce in a similar way to bacteria through budding. The fungus creates a bump or bud, where it distributes half of its genetic material and a small part of its cytoplasm. If you want to know more about budding reproduction you can take a look at this other lesson: Reproduction by budding.
- Through conidia. Conidia are asexual spores produced in specialized parts of the fungus called conidiophores, by budding or fragmentation. In the case that they are produced by fragmentation, the conidia are also called arthrospores.
- By sporangia. Sporangia are cells, normally supported by a foot, within which asexual sporangiospores are formed. Unlike conidia, sporangiospores can be mobile (although not all are) and grow protected from the external environment by a membrane that covers the sporangium.
Image source: Fungi Kingdom
The sexual reproduction of fungi is very complex, so in this lesson from a TEACHER we will only touch on the main forms of reproduction, but there may be many more rare and complex mechanisms by which fungi can reproduce in a sexual.
The sexual reproduction of some fungi begins with the formation of the gametes, male or female, it is a structure called gametangium. Once formed, if they are lucky, the male and female gametes come into contact. This contact entry is called plasmogamy and, shortly after it occurs, the nuclei of the male gamete and the female gamete fuse (karyogamy). As a result, a diploid cell is obtained, with two sets of chromosomes. This is the cycle that certain types of fungi have, but the vast majority of them (the so-called true mushrooms) work differently.
True mushrooms are beings haploid during most of its life cycle, so the diploid zygote usually lasts a short time and, instead of growing into an adult fungus, it undergoes a meiosis. Through meiosis, the diploid zygote (called zygospore, which is usually enclosed in a resistance spore) generates haploid spores and from these the new fungi will emerge.
Types of classification of sexual reproduction of fungi
There are different types of classification of sexual reproduction of fungi: according to the shape of the spores, according to the size relationship between them, according to the size of the organs producing the spores spores, etc. but one of the most important is the way in which plasmogamy occurs:
- Through planegametos. Planogametes are mobile gametes. In this case, the two mobile gametes come into contact, connect and fuse their cytoplasms in a fairly simple way.
- For gametangia gametangial contact. In this case the antheridium (male) and oogonium (female) contact through a fertilization tube. Then, the first yields the gametic nuclei to the second.
- Through gametangial copulation. in gametangial copulation, it is directly the gametangia, not the sex cells, that come into contact. The gametangia join to give rise to the zygote, which is protected by a resistance spore created by the walls of the gametangia.
- For spermatization. In this case, a spermace (a cell similar to a sperm but without a flagellum) reaches the oogonium and fertilizes it.
- For somatogamy. Somatogamy is simply the union of two vegetative hyphae. It is a fairly simple method, although it does have a vegetative incompatibility mechanism to prevent the unwanted formation of certain combinations that is not fully understood. It is the simplest form of sexual reproduction and, surprisingly, the one used by the most complex and evolved fungi.
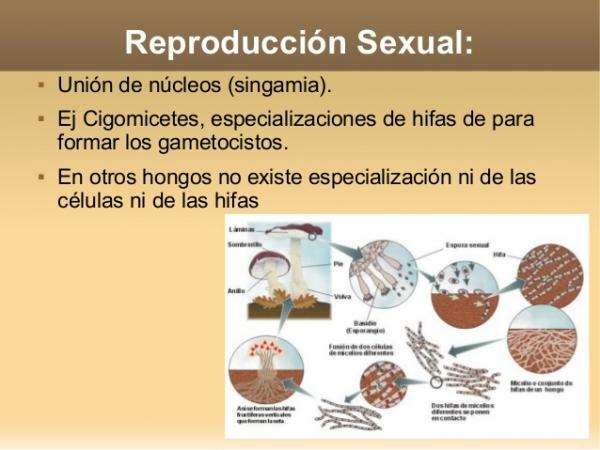
Image: Slideshare



