PROTISTA kingdom: characteristics and classification

Image: WikiSabio
All living things are classified into five kingdoms. The most diverse kingdom and, according to some, the most unknown, is the kingdom of the protists. This kingdom collects protozoa and unicellular algae and it is of great importance: they constitute part of the plankton, benthos and edaphon, they can be the cause of serious diseases such as malaria or malaria or sources of compounds widely used in the pharmaceutical industry and cosmetic. In addition, a large number of them live in close relationship with other organisms with which they cohabit and with which they are symbionts, parasites or with those who have mutualistic relationships. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will look at the characteristics and classification of the protist kingdom. If you want to know more about these microorganisms, keep reading!
Index
- Characteristics of the protist kingdom
- Protozoa: characteristics and classification
- Algae: characteristics and classification
Characteristics of the protist kingdom.
We begin this lesson on characteristics and classification of the protist kingdom by talking about the most differentiating elements of this kingdom. We should know that the protist kingdom is one of the most varied on planet Earth. This is due, in part, to the fact that the two major groups that compose it, protozoa and algae, do not have a known common ancestor. It is what in biology is called a group paraphyletic.
The features Generals of this group are:
- They are beings eukaryotes, that is, they have a cell with its DNA collected within a core, with cell envelopes, and organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, etc. In the case of photosynthetic organisms we can find within their cells chloroplasts, which can have different pigments depending on how they capture energy of one wavelength or another.
- They may be unicellular or multicellular. Something very characteristic of some protists such as red and brown algae is the appearance of cells that communicate with each other; These cells can cooperate but do not form complex tissues like plants or animals.
- Protists can be autotrophs or heterotrophs. In fact, some of these organisms can alternate from being autotrophic to heterotrophic at their convenience.
- Some are immobile while others are move by flagella, cilia or pseudopods.
- Protists can be classified into organisms of life freee, that inhabit very humid environments or organisms that live inside other living beings, with which they have a relationship of parasitism, mutualism or symbiosis.
- Finally, protists can breed so asexual (creating clones of themselves) or by breeding sexual with alternation of generations.
As we have seen previously, the classification of protists begins by differentiating two groups: protozoa and algae. The difference between them is that algae are autotrophic, that is, they carry out photosynthesis, while protozoa are heterotrophs and feed mainly on other microorganisms either by hunting them (predators) or by parasitism, mutualism, etc.

Image: Kingdom Protista
Protozoa: characteristics and classification.
Within the classification of the protist kingdom we must take into account that this kingdom it is subdivided into two large groups, very differentiated between them: the first is that of the protozoa.
Within the classification of living beings, protozoa they are the simplest eukaryotes. Protozoa are microorganisms heterotrophs: most of them feed on other microscopic organisms through predation although others can feed of dead organic matter (detritivores), being parasites of other organisms such as plants, animals or humans, etc.
Protozoa are mobile organisms, and their classification is made according to their mode of locomotion:
- Flagellated protozoa: Within the classification of protists, flagellate protozoa are the most primitive. These microorganisms move thanks to one or more long filaments and can be found "swimming" freely, as parasites of other organisms or in symbiosis with them. A curious case of symbiosis is the one that occurs between these microorganisms and termites.
- Ciliated protozoa. Unlike the previous ones, these microorganisms move thanks to a series of short and very numerous filaments. These types of organisms are usually found in fresh waters.
- Rhizopods or sarcodinos. These protozoa move thanks to pseudopods. Pseudopods are deformations of the cytoplasm and the membrane that covers these organisms, which allows them to move like an amoeba in addition to ingesting (engulfing) their food. These animals are usually found in water and some can cause diseases such as amebiasis.
- Sporozoans. Sporozoa are the only type of protozoa that cannot move and are normally parasites of other life forms. A well-known example is the sporozoan Plasmodium, which parasitizes the mosquito Anopheles and that it can be transmitted to humans causing malaria or malaria.
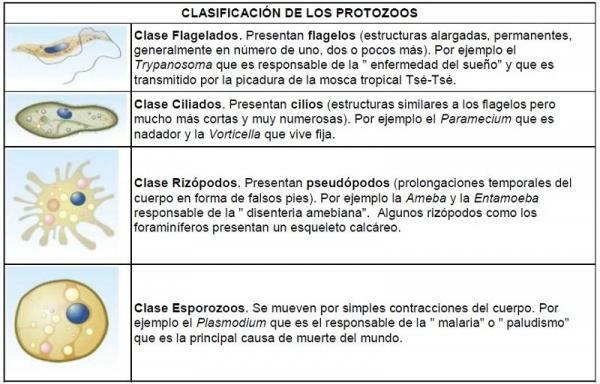
Image: Animalsde.net
Algae: characteristics and classification.
The second classification group of the protist kingdom is algae. Unlike protozoa, algae are organisms autotrophs that are nurtured by carrying out the photosynthesis. These organisms carry out photosynthesis in the same way that plants carry out it all we know instead they do not have roots, stem, leaves or the more developed tissues that do have the plants.
Within the algae we can find:
- Unicellular algae. Single-celled algae can be found as a free cell or as clustered cells, which form colonies. These microorganisms are very important for marine ecosystems, since they are part of phytoplankton, a group of small organisms that in addition to being a great source of food for other animals, help to maintain the production of oxygen in the seas and oceans.
- Multicellular algae. Multicellular algae are organisms made up of many cells but, unlike animals or plants, these cells do not form tissues but less complex webs called thallus. Within multicellular algae, depending on the pigment they contain, we can find algae of different colors: green algae, which live on the surface of bodies of fresh or salty water; brown algae, which live deeper or red algae, which live at great depths and help maintain marine reefs.

Image: Slideplayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Protista kingdom: characteristics and classification, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.