VEGETABLE KINGDOM: characteristics and classification of plants

Organisms of the plant kingdom, vegetables or plants they are extremely important for the planet, ecosystems and man. Plants regulate the proportion of gases that form the atmosphere we breathe, it serves as food for Animals and humans, for construction, are the basis of many of the medicines we use daily, etc. Therefore, it is important that we know what exactly plants are, their characteristics and how they are classified. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review the plant kingdom: characteristics and classification of plants.
Index
- Characteristics of the plant kingdom: what are vegetables?
- Classification of the plant kingdom
- Bryophytes: the most primitive plants
- Vascular plants or tracheophytes: a very varied group
Characteristics of the plant kingdom: what are vegetables?
Vegetables are organism immobile and multicellular, that is, they are made up of more than one cell that does not have the capacity for movement. These cells have special characteristics: they have a more rigid wall than that of animals or bacteria, formed by
cellulose; In addition, these cells have inside them a substance called chlorophyll, which can be of different types, and which is responsible for the vegetables being able to carry out the photosynthesis. Different types of vegetables can have different types of pigments or chlorophylls, which makes them take better advantage of the light depending on the environment where they live, especially according to their depth.Most plant organisms are autotrophs since, thanks to the photosynthesisThey can take advantage of sunlight, water and inorganic matter to synthesize or manufacture their food. Some plants have lost the pigments that allow them to carry out photosynthesis, and have become heterotrophic.

Image: Vegetable kingdom
Classification of the plant kingdom.
Due to its amplitude and its great dispersion throughout the planet, vegetables are adapted to many different types of ecosystems. This makes classifying this group difficult and confusing for some. In fact, the first hurdle that researchers have encountered is the question of whether to include algae as a vegetable.
Algae, in general, are capable of carrying out the photosynthesis (thanks to pigments of different types) but they cannot form complex tissues. Therefore, most authors consider that algae are protists, a group that is a kind of "mixed bag" for those small organisms with different characteristics and that are halfway between bacteria and animals and plants.
What is clear is that within the plant kingdom we can find all terrestrial plants or embryophytes. Land plants would have algae as their predecessor, since with them they share the presence of chlorophyll and the ability to carry out photosynthesis. Within terrestrial plants we can find large groups, depending on the complexity of the tissues that can form:
- Bryophytes (mosses, liverworts and anthocera)
- Vascular plants (tracheophytes or cormophytes).
If you want to know more about the classification of the plant kingdom, keep reading!
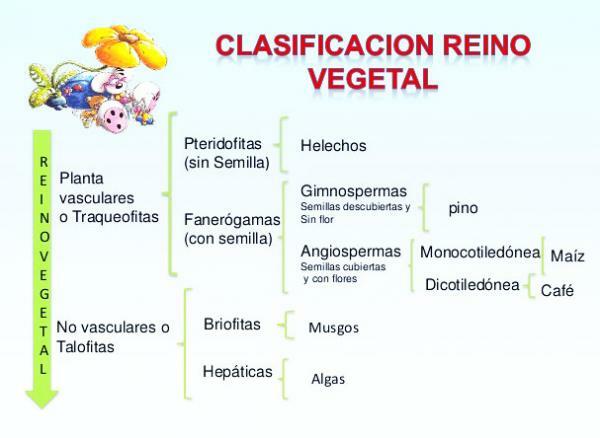
Image: Vegetable kingdom
Bryophytes: the most primitive plants.
Within the characteristics and classification of the plant kingdom, the most primitive group is formed by the bryophytes. Within the bryophytes we find three large groups of organisms: mosses, liverworts and anthocera.
Bryophytes are plants that need to live in an environment with large amount of moisture such as logs, rocks or soils from very climates damp although they can also be found in mountainous areas (especially at low altitude), tundras, etc. They are believed to be the direct descendants of green algae that, about 500 million years ago, they went from water to Earth and were able to adapt to life in these types of ecosystems damp.
These organisms are plants that they do not have xylem and phloem, a differentiated vascular tissue that acts as "pipes" through which substances circulate between the different parts of the plant. This makes bryophytes normally low-rise plants or directly crawling; Although they do not grow much in height, bryophytes can become the biomass base of an ecosystem and form true carpets.
Although they do not have vascular tissues, in this type of organisms we can differentiate three parts which, although they are not homologous, could be "similar" to those found in more complete terrestrial plants:
- Rhizoid (which would be similar to the root)
- Caulidia (similar to stems)
- Philidians (similar to leaves of vascular plants)
These plants lack seeds and they reproduce mainly thanks to spores, which disperse freely through the air.

Image: Slideplayer
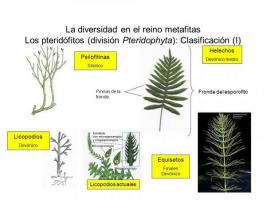
Vascular plants or tracheophytes: a very varied group.
The rest of terrestrial plants that are not classified as bryophytes are called vascular plants. This group is very diverse and the only thing they have in common is one thing: they have vascular tissues (xylem and phloem). Vascular tissues are a set of ducts, similar to pipes that carry water, mineral salts and other nutrients from the root to the roots. plant leaves (xylem) and sugary substances resulting from photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant (fruits, roots, etc.) (phloem).
Within vascular plants we can distinguish two large groups: club mosses and euphilophytes. Both have xylem and phloem, but while club mosses do not have seeds, euphylophytes do have seeds.
- The club mosses they have structures called sporophiles (leaves where the structures that produce the spores are located) in groups with a very characteristic pineapple-like appearance (strobili).
- For their part, euphilophytes They are a group that plants also very varied, ranging from ferns or horsetails (pteridophytes, without true roots or seeds) to gymnosperms and angiosperms, the most complex terrestrial plants that we all know and that have a great variety of differentiated tissues (vascular, reserve, etc.).

Image: CK12
If you want to read more articles similar to Vegetable kingdom: characteristics and classification, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Diarium. USal (s.f) Classification of living beings: kingdoms. Recovered from http://diarium.usal.es/gonzalopanzas/clasificacion-de-los-seres-vivos-los-reinos/
- Moro Hermoso, Ana (s.f). Vegetables. Recovered from http://ficus.pntic.mec.es/amoh0004/vegetales.html.html
- Judd, W. S. Campbell, C. S. Kellogg, E. TO. Stevens, P.F. Donoghue, M. J. 2007. Plant systematics: a phylogenetic approach, Third Edition. Sinauer Axxoc, USA.
- M. J. Simpson. 2005. Plant Systematics. Elsevier Academic Press.
- Helena Curtis, N. Sue Barnes, Adriana Schnek. 2008. "Biology of plants". In: Biology. 7th Ed. Panamericana Medical Editorial.
- Ray F. Evert, Susan E. Eichhorn. 2012. Biology of plants. 8th Ed. Editorial W. H. Freeman.