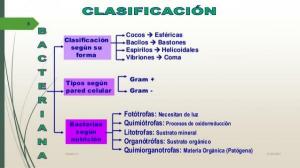
Examples of PARASITISM in the ANIMAL kingdom

The parasites they are very diverse organisms ranging from microorganisms to insects and birds. In the same way, the relationships of parasitism and the consequences of these in the organisms that suffer from them are also very diverse and sometimes surprising. In this lesson from a TEACHER you will see different examples of parasitism that constitute only a small sample of the complexity of this type of trophic relationships.
Index
- What is the parasitism ratio?
- Breeding parasitism in birds
- The malaria parasite
- Parasitic wasps
- Neural parasites, another example of parasitism
What is the parasitism ratio?
In an ecosystem, different species of organisms establish with each other trophic relationships. Trophic relationships are the relationships that are established between organisms of different species. One type of trophic relationship is known as parasitism.
In this type of trophic relationship, an organism called parasite or host, feeds at the expense of another organism, which does not derive any advantage from this relationship and is called
host.Breeding parasitism in birds.
One of the most studied examples of parasitism is the so-called brood parasitism in birds. In this parasitic relationship, the host does not build its own nest, but lays its eggs in the nest of another species so that the parents of the host species are responsible for the incubation of the eggs and the rearing of the chicks of the species parasite.
The best known example of this type of parasitism is that of the common cuckoo or gray cuckoo (Cuculus canorus). This species of bird is widely distributed in Europe and Asia during the time summer, while in winter it is distributed in areas of the south of the African continent and in the south from China. A female common cuckoo can lay up to 25 eggs, in different nests, during the breeding season. The cuckoo parasitizes more than 300 species of passerine birds (small birds).
The parasitism strategy of the common cuckoo is not limited to laying the egg in a foreign nest. Once the egg hatches, the cuckoo chick, which is much larger than its hosts, carries the eggs of the host species on its back to throw them out of the nest. In this way it is ensured that the parents of the parasitized nest concentrate all their efforts on feeding it only.
Brood parasitism supposes huge costs for the parasitized species. For this reason, throughout evolution these species have developed different strategies to defend themselves from parasitism, at the time that the parasitic species develops in parallel strategies to circumvent these defenses in one of the clearest examples of coevolution. Parasitized birds learn to recognize the eggs that are not their own, to "count" the number of eggs they lay or to locate their nests in habitats that the cuckoo does not frequent, such as inside buildings (as in the case of swallows).

The malaria parasite.
We continue to know the examples of parasitism to talk about malaria or malaria, a life-threatening parasitic disease, caused by parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of the female mosquito Anopheles. According to the WHO (World Health Organization), in 2019, it is estimated that a total of 229 million people were infected with malaria worldwide with a total of 409,000 deaths. Its about deadliest parasite in all of human history.
The Plasmodium They are sporozoa. They are single-celled organisms that are obligate parasites (they cannot survive outside the host organism). The biological cycle of Plasmodium is complex. It is a type of parasitism in which the parasite requires two species to complete its life cycle: humans and the Anopheles mosquito.
In a very summarized way, the stages of life cycle of this parasite are as follows:
- The sporozoite (an organism that reproduces by spores) lives in the salivary glands of the mosquito and is transmitted to humans through its bite.
- In humans the sporozoite will reproduce by asexual reproduction, first in the liver cells and then in the erythrocytes of the blood.
- When reproducing in erythrocytes, the sporozoite can give rise to some cells that reproduce sexually, the gametocytes.
- When the mosquito feeds on blood, the male and female gametocytes reach the digestive system of Anopheles, where the sexual reproduction in which male gametocytes fertilize female gametocytes to form fertilized cells.
- When they mature, to new sporozoites, thus closing the biological cycle of this parasite.
Parasitic wasps.
Parasitic wasps inoculate their eggs inside caterpillars butterfly. Inside the caterpillar, the eggs develop to give rise to larvae. When the larvae have finished their growth, they go outside, tearing the cuticle of the host caterpillar and causing its death. Once outside, the wasp larva forms a chrysalis where it will complete its metamorphosis to give rise to an adult specimen.
Caterpillars have developed strategies to defend themselves against parasitic wasps, their immune system is capable of detecting wasp eggs and encapsulating them to prevent them from developing. However, wasps have in turn developed strategies to avoid it. Besides the eggs, parasitic wasps inoculate caterpillars with large amounts of virus when they parasitize them.
This high viral load, the inoculated viruses rapidly inactivate the caterpillar's immune system, which stops feeding, does not form the chrysalis and dies prematurely, thus ensuring the success of the parasitic process of the wasp.

Neuronal parasites, another example of parasitism.
We finish this review of the parasitism examples to talk about neural parasites. Some organisms parasites They parasitize the nervous system of their hosts and thereby manage to alter their behavior, for their own benefit. An example is the rabies virus, which manipulates the host's brain to ensure contagion.
Rabies is transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, because its saliva contains a huge concentration of the virus. Through the bite, the rabies virus parasitizes nerve cells (neurons), jumping from one neuron to another, travels from the peripheral nervous system to the brain.
Once there, the virus is capable of producing the necessary changes to alter behavior of the animal or the parasitized person, managing to alter the behavior of the host that, in addition to producing a large amount of saliva, feels the irrepressible urge to bite.
If you want to read more articles similar to Examples of parasitism, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Francisco Ruiz-Raya, Manuel Soler. (2020) Breeding parasitism in birds: beyond laying. Research and Science. Barcelona: Scientific Press S.L
- Viviane Callier (2020) The malaria parasite, a mixture of strains Research and Science. Barcelona: Scientific Press S.L
- Nancy E. Beckage. (1998). The secret weapon of parasitic wasps. Research and Science. Barcelona: Scientific Press S.L
- Anna Von Hopffgarten (2019) Parasites in the nervous system.Mind and Brain. Barcelona: Scientific Press S.L