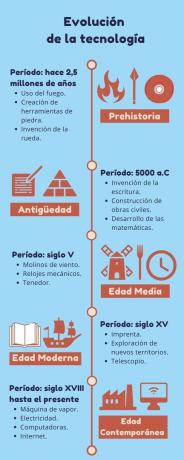
Technology evolution (with timeline)
The evolution of technology is the different stages of technological development through which humanity has passed to reach the current level of innovation.
Although it is common to associate the term technology with computers, the Internet and electronic devices, the technology is all the knowledge and tools that are created to satisfy a need or solve a trouble.
For this reason, it is possible to identify relevant technological advances in each of the historical stages of humanity, as we will see below.
| Stage | Period | Featured Technological Advances |
|---|---|---|
| Prehistory | 2.5 million years ago to 5000 BC. C |
|
| Antiquity | 5000 BC C to the 5th century |
|
| Middle Ages | 5th century to 15th century |
|
| Modern age | 15th century to the middle of the 18th century |
|
| Contemporary age | From the middle of the 18th century to the present |
|
Prehistory: fire, tools and wheel
Technological evolution began 2.5 million years ago with the Homo habilis, the first humans to develop stone tools. The technology of that period also included:
The use of fire
The knowledge of the creation and use of fire was crucial for the survival of the first humans who left Africa and moved to colder areas such as Asia or Europe. This technology allowed them to eat cooked food and survive low temperatures.
The first agricultural techniques
This allowed them to abandon the nomadic lifestyle and become sedentary, which had an impact on the formation of the first archaic societies.
The invention of the wheel
It is estimated that the wheel was invented between 5000 and 3000 BC. C. At first, it was used as an ornament for certain small artifacts, until its application as a rudimentary means of transport was discovered.
The work with molten metals in fire marks the end of prehistory in technological terms and gives way to the Ancient Age.
See also:
Nomads and sedentary
The evolution of man
Antiquity: writing, civil works and mathematics
Antiquity began with the development of the first writing systems, such as the one created by the Sumerian civilization in about 5000 BC. C, the oldest recorded so far. Other contributions from this time were:
Urban Development
Technological evolution was expressed in the creation of the first cities with their respective infrastructures: aqueducts, drainage systems, public toilets, etc. The Egyptians engineered monumental stone pyramids and farming systems.
Math and tools
The Greeks developed advanced mathematics and invented the lever, the hydraulic pump, and the astrolabe, among other tools. In what is now the American continent, the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas developed solar and lunar calendars, complex number systems, and astronomical observation.
Antiquity ended with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476.
Middle Ages: windmills, clocks and fork
The Middle Ages began in the 5th century, when the cultivation of cereals was done with water mills, which worked with hydraulic power. The invention of windmills was a technological development that allowed to grow food in places where there were no water flows, massifying agriculture. Other technological advances of that time were:
Mechanical watches
Another important step in the technological evolution of the Middle Ages was the creation of mechanical watches, much more accurate than their predecessors, the sundials. With this invention, the idea of time divided into fractions, called hours, became widespread.
Use of the fork
Another important artifact that is essential today is the fork. Although there were already tools to carve food, in Europe it was eaten with the hands, putting vegetables and meat on a slice of bread. The popularization of the fork revolutionized the way of eating in the Middle Ages, giving way to a much more hygienic way of consuming food.
The Middle Ages ends with the fall of the Byzantine Empire (or Eastern Roman Empire) in 1453.
Modern age: printing press, telescope and exploratory travels
Two events mark the beginning of the Modern Age: the invention of the printing press and the discovery of the American continent.
Guttenberg's printing house
The great technological leap of the modern age was driven by Johannes Guttenberg with the invention of the printing press in 1450. The Chinese had invented paper, but it was in medieval times that its use reached Europe and the The printing press allowed the reproduction of texts on paper, giving rise to books just as the we know.
Galileo's telescope
Galileo Galilei invented the telescope in 1609. This allowed him to make fundamental contributions in the field of astronomy, such as the description of the lunar surface and the confirmation that the Earth was not the center of the universe.
The meeting of two worlds
In the Modern Age also began the exploratory trips that resulted in the discovery of the American continent by Europeans, led by Christopher Columbus in the year 1492. This began a period of discoveries of techniques, technology and raw materials that had a profound impact on later technologies.
The end of the Modern Age was marked by the outbreak of the French Revolution in 1789.
Contemporary age
The Contemporary Age is the historical period of greatest technological evolution and it could be divided, in turn, into three stages: the one corresponding to the Industrial Revolution, which began in the 18th century; the era of computing and informatics, in the twentieth century, and today, in which technology points towards quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI).
Steam engine, steam train, electricity (Industrial Revolution)
While France was going through a process of political revolution, the Industrial Revolution was brewing in Great Britain. This transformation was driven by inventions such as the steam engine, an engine that transformed thermal energy into mechanical energy and which, in turn, allowed the development of the steam train.
The steam engine had multiple applications, allowing the growth of various types of industries, such as mining and exploitation of hydrocarbons, while the train became a new form of transport much more efficient than drawn carts by horses. And already at the end of this time, in 1833, it is when electricity began to be used in a massive way to illuminate public spaces and later, in a domestic way.
Computers, internet, space travel (20th century)
In the middle of the 20th century, the first computers were unveiled. Although they were large machines with little data processing capacity, the technology used in their design evolved to become what they are today: small, portable devices with data processing capacity multimedia. This evolution was driven, in turn, by the development of the internet, which changed the way we communicate and receive and send information.
On the other hand, in 1969 the human being reached the Moon for the first time, opening the doors to new technological developments that would allow space exploration and that would even have applications practices. An example is memory foam that is used in many mattresses today, as it was a material developed by NASA to make airplane seats more comfortable.
Quantum computing, artificial intelligence, space tourism (21st century)
Today, the evolution of digital technology is driven by quantum computing, which enables the processing of large amounts of data that are impossible to process with the computers of use common. In addition, solutions based on artificial intelligence are developed with the aim of replacing some activities carried out by humans in the long term.
For its part, space technology has already evolved in such a way that they are already investigating ways to turn other planets into habitable places for humans. It is also possible to make tourist trips 100 kilometers above the Earth, which is what is considered the beginning of outer space.
See also:
- Advantages and disadvantages of the Internet
- Advantages and disadvantages of technology
- Computer types