Types of plant reproduction

Image: SlidePlayer
Like all living things, plants are able to reproduce thereby managing to maintain its species and originate new vital plants for the maintenance of life on our planet. The reproduction of plants can vary depending on the species, with both asexual and sexual plants, and there are even different classes within these two large groups. Therefore, in this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to talk about the different types of plant reproduction.
Before beginning this lesson on the different types of plant reproduction that exist, we must discuss to define the plants, knowing the types that exist of them and why some of them are asexualand others are sexual.
Plants are impressive living beings characterized by not having a locomotive capacity that allows to move, by having cell walls composed of cellulose, and by being able to make the call photosynthesis. Of all these characteristics the most important is photosynthesis, being a process that allows plants to nourish themselves, an extremely important function both for plants and for the rest of the living beings that live with them.
Classification of plant reproduction
More than 300,000 species of plants have been discovered, so there is also a huge variety of reproduction types, depending on the kind of plant you want to reproduce. Even with all the plant species that exist, we can speak of two large groups in which we find all species, the following two groups being:
- Plants without flowers: Plants that do not have flowers, dividing into bryophytes Y pteridophytes.
- Plants with flowers: Plants that have flowers, being gymnosperms or angiosperms.

Image: SlidePlayer
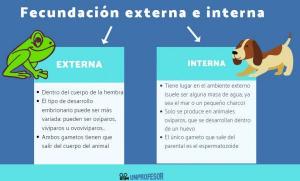
Sexual reproduction is one in which a new being is born due to the union of the genetic material of two parents. In this type of reproduction, the union of two gametes is necessary, one male and one female, either from two different individuals or from just one. Sexual reproduction is the most predominant among plants, and it can be of two types.
Autogamy
Autogamy is that form of sexual reproduction in which the gmale and female methos are produced by only one individual, being a type of reproduction that happens in the same individual. Its greatest advantage over other types of sexual reproduction is that the characteristics are maintained genetics, thereby allowing plants to maintain adaptability to an environment that had their predecessors. Some examples of plants that perform this reproduction are the island species and the undergrowth.
Alogamy
Alogamy is a form of sexual reproduction in which there is a Cross pollination Y fertilization between two different plants. The species that carry out this type of reproduction generate plants with new genetic codes, and therefore plants with greater variability. It is a very predominant type of reproduction in most current flowering plants.
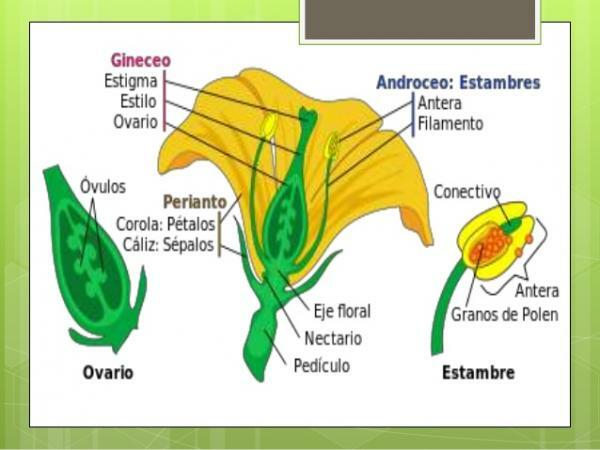
Image: Slideshare
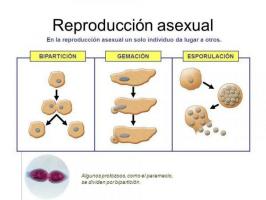
Asexual reproduction is that in which the cell of a being is born a new being identical to the parent, all thanks to the process of mitosis. This type of reproduction usually happens in non-vascular plants, and it is believed that it is done to colonize a new place. There are different kinds of asexual reproduction in plants, which are the following:
- Mitospores: It is reproduction based on spore creation through mitosis, dispersing through the air. Some examples of plants that perform it are fungi and ferns.
- Propagules: Portions of plant tissue that, when separated from them, are capable of creating a being identical to its parent.
- Apomixis: It is an asexual reproduction in which they are used seeds, although without being fertilized. For this reason, the beings that are born from these seeds are identical to the parent.
- Vegetative multiplication: It is the use of a part of a plant to give birth to another of artificial shape, being carried out by man to increase the number of a certain species. There are many types of artificial asexual reproduction performed by man for his own good, some examples being grafts, the stakes and the segments.
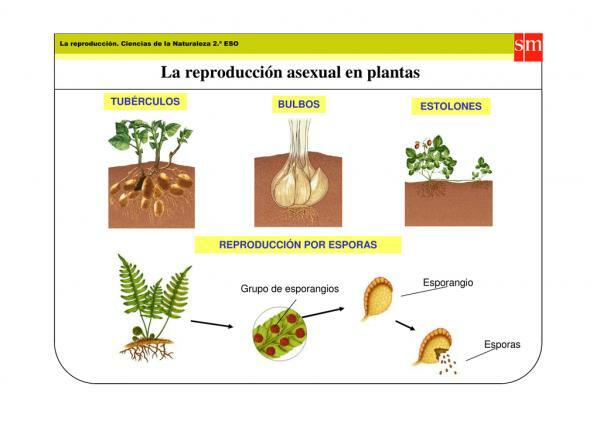
Image: studylib.es