Amphibians: definition, characteristics and examples

The group of vertebrates It is made up of 5 different kinds of animals, all of them unique and with wonderful and very curious characteristics. Among them we can find migrating animals, viviparous animals, and even animals that are capable of metamorphosis, just like insects. The latter are amphibians, a group of extraordinary animals, and therefore in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we are going to offer you the definition, characteristics and examples of amphibians.
Amphibians are a group of Vertebrate animals, anamniotes, tetrapods and cold-blooded. They are vertebrates because they have backbones, anamniotes because they do not have amnion, tetrapods because They have 4 manipulative legs, and cold blooded because they regulate their temperature from the environment.
Amphibians are recognized as the oldest terrestrial vertebrates, existing a huge amount of amphibian species that have been extinct over the centuries. For this reason, at present they are only divided into a few groups, having disappeared a large number of groups of amphibians.
Amphibian characteristics
Being a small group, there are a series of common characteristics in all amphibians, which are shared by the vast majority of species. Some of these characteristics are the following:
- They are oviparous, that is, they reproduce from the laying of eggs.
- They are able to perform a metamorphosis, similar to that carried out by many invertebrates.
- Their way of feeding can vary between species and depending on their age, and they can be both herbivores and carnivores.
- Its skin is unique, being permeable and having neither skin nor scales. Some species may have toxic skin.
- They are vertebrates, so they have backbones.
- Your breath is gill in its tadpole phase, passing to pulmonary in its adult stage.
- Your heart has three cameras.
- In their young phase they live in water, while in the adult stage they become semi-terrestrial.
- They are animals of cold blood, being unable to control their body heat.
- They are tetrapods, possessing 4 manipulative legs.

Image: Slideshare
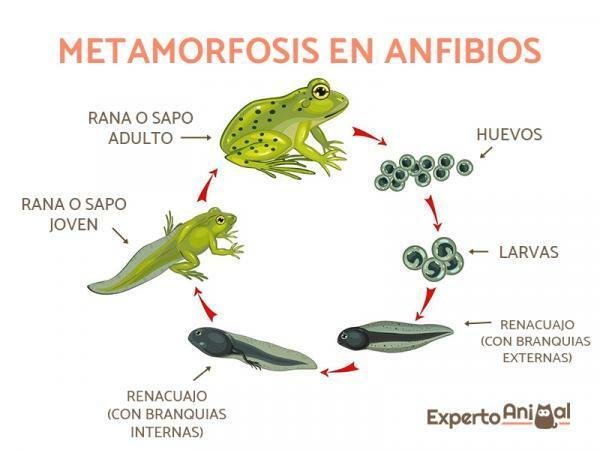
One of the most surprising elements of amphibians is their metamorphosis, and they can go through very different phases throughout their growth. Therefore in this lesson we must briefly summarize how this metamorphosis happens, and its phases.
Egg
The first phase of amphibians is that of the egg, being the way in which they come out of the parent. The eggs are placed by the mother in the water, she being helped in this process by the male. These eggs are called soft, that is, those that are fertilized by the male once they have gone abroad, being a external fertilization.
The eggs are very small, gelatinous in shape, and very close together. They are protected by a large number of membranes, trying not to break from blows or not be eaten by predators.
Larvae and tadpoles
Larvae hatch from the eggs, a kind of head that does not even have a tail yet. At this time the animal already has gills, so it quickly adapts to the aquatic environment. A few days later the animal undergoes its first metamorphosis, becoming a tadpole.
Tadpoles are made up of a head and a tail, with a shape similar to that of fish. They live in fresh water, possessing gills to breathe, and being herbivorous in most cases. The life of the tadpole is usually three months, at which time the metamorphosis happens again, and the animal evolves to its adult phase
Adult phase
The tadpole is changing little by little, appearing four paws with which it can be adapted to the terrestrial environment, and finally losing its tail characteristic. Its respiration becomes pulmonary, and its diet changes to a carnivorous one. This is the final phase of amphibians, no more transformations happening in the animal.
To continue with this lesson on definition, characteristics and examples of amphibians, we must talk about the different groups that amphibians are made of. The three groups of amphibians are as follows:
- Anurans: Are the largest group of amphibians, existing more than 6000 different species. They are animals characterized by spending a large part of their life in or near water. In their adult stage they do not have a tail, having a wide and short body, which ends in a leg whose main use is jumping. Some examples of anurans are frogs and toads.
- Gymnastics: They are the most unknown group of amphibians, since in popular culture they have not been shown as much as the other two groups. They are amphibians without legs, which live underground in humid areas. An example of this group are the cecilias.
- Caudates: They are a group of amphibians made up of just under 700 species. They are characterized by having a long tail and not having any type of middle ear. The salamanders they are the greatest example of caudates.
If you want to read more articles similar to Amphibians: definition, characteristics and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.

