PARASITE animals: classification + EXAMPLES!! [with photos]

It is usually called parasite to an organism that It feeds on the substances that another living being makes of different species, living inside or on its surface, which usually causes some damage or disease. Normally, it is defined as a very close symbiotic relationship.
Although in practice they are only called parasites protozoa, helminths and arthropods, in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will see what are parasitic animals, with examples according to the dependency relationship between the two organisms and the place in the body that the parasite occupies. The vast majority are from these groups, but other organisms, such as fungi, can also be large parasites.
Before talking about parasitic animals it is important that we understand the definition of parasite. Parasites are organisms that use others, the hosts or guest, to obtain some benefit. In this way, a species expands its ability to survive easily, using other species to meet some of its basic and vital needs.
We normally think of nutritional needs, but hosts can cover functions such as
propagule dispersion (which improves the ability of parasites to spread or spread), serve as shelter, etc. As we will see below, the parasite-host relationships can be varied.The parasitism relationship provides the parasite of a very great advantage for its survival, reason why it tends to evolve seeking more and more to improve its relation with the host. In fact, parasites are generally very selective with respect to their hosts, reaching a high percentage of cases to be exclusive of a species or, in bacteria, of a bacterial strain.
In turn, the host usually is harmed somehow: loss of blood, discomfort on its surface, worsens your immune response, etc. For this reason, it is very common that the hosts have also adapted to the presence of the parasite and have developed defense mechanisms.
Plants often produce toxins, for example, that discourage parasitic fungi, to bacteria, as well as herbivores; Humans produce antibodies to fight bacteria and viruses that try to parasitize us. This relationship of continual change and adaptation supports red queen hypothesis.
Examples of parasites in nature
In nature we can find numerous examples of parasites at all scales: the viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, protistsand many animals. To study them, they can be classified according to several characteristics: the size of the parasite, the relationship between the size of the host and that of the parasite, depending on the specificity of the host, etc. In this lesson from a teacher we will see the two most common: according to the part of the host's body that is parasitized and according to the dependence of the parasite.

Image: Docsity
We are going to know which are the parasitic animals. To do this, we classify them saccording to the part of the host's body they occupy. We have the following:
- Ectoparasites. The parasite lives on the surface of the host: skin, mucous membranes, open cavities, etc. In this type of parasitization, the host is usually classified as infected or infested.
- Endoparasites. The parasite lives inside the host, that is, it has had to enter the interior of the organism itself.
- Hyperparasites. Parasites that parasitize a parasite are called hyperparasites.
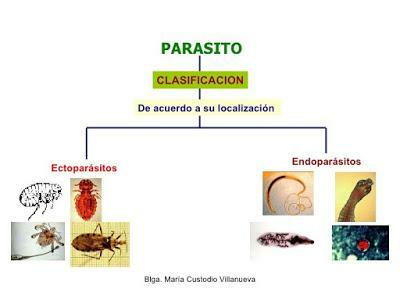
Image: Livestock world
Finally, let's move on to see examples of parasitic animals of each of the categories seen above:
- What examples of ectoparasites we can find the bacteria that inhabit our mouths. In a healthy tooth can be found, among others: Haemophilus parainfluenza, Gemella haemolysans, Slackia exigua, and the species Rothia. Another example is Malassezia pachydermatis, a yeast that can infect the mouth, ears, genitals and feet of healthy dogs and that prevents our pets from being infected by pathogenic fungi.
- The most common example of endoparasites are human intestinal parasites, such as you had or protozoa, but protozoa of the genus Leishmaniathat cause leishmaniasis in dogs and humans.
- Within the category of hyperparasites we can find a few examples, such as the genre Plasmodium, a protozoa that parasitize mosquitoes of the genus Anophelesto use them as a means of dispersal and infection of humans, causing malaria or malaria. Another example is Cordyceps militaris, a fungus that parasitizes the pine processionary (Thaumetopoea pytiocampa), a parasite of the Scots pine (Pinus pinea).
- There are many examples of obligatory parasites permanent, but the most widespread is that of viruses that parasitize bacteria (bacteriophages).
- As examples of facultative parasites we have Botrytis cinerea Y Strongyloides stercoralis. Botrytis cinerea is a fungus that can live on dead plant tissues or as a parasite on the leaves, stems and fruits of different species of living plants while Strongyloides stercoralis it is able to live freely, but only the female parasitizes the human intestinal mucosa.
- Finally we have an example of intestinal parasites: the larvae of flies or insects that feed on flour such as the mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). In hot countries like India, these animals feed on flour, which can be ingested by man, and the larvae or eggs can resist gastric juices long enough to develop, causing damage to the host.
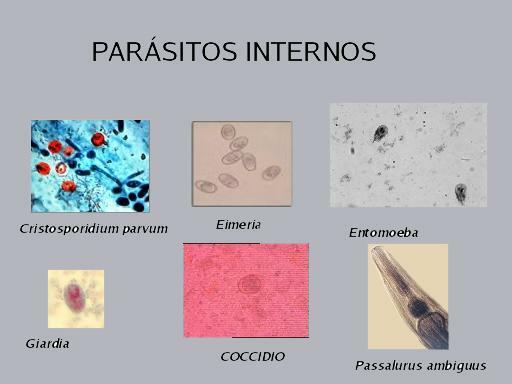
Image: Chinchillas