The NUCLEUS of the neuron

Although it is not the only one, the neuron is one of the main types of cells that make up our brains. The brain, and specifically the neurons, contain some of the behaviors that make humans just that, human.
That is why, throughout history, a large number of researchers and neuroscientists have focused on study the neuron. One of the first things that was discovered about neurons is their particular star shape. Neurons are made up of axons, dendrites, and a nucleus or perikaryon. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will focus on the central part of the neuron: the nucleus. What is the nucleus of the neuron like? What happens inside it? If you want to know more, keep reading!
Index
- What is the neuron and what is it for?
- What is the soma or body of a neuron like?
- What is inside the nucleus of the neuron?
- Function of the nucleus of a neuron
What is the neuron and what is it for?
The neuron is the basic unit of Central Nervous System, since it is the smallest part of it that can generate and transmit a nerve impulse. It is precisely this characteristic that makes it so important: it produces nerve impulses by itself and is capable of transporting them to nearby ones, through the synapse.
This type of cell is very particular, not only because of its morphology but also because of its physiological characteristics: they are highly differentiated, but at the same time have the properties of excitability, conductivity and trophism, typical of little cells differentiated. These properties are what make the production and transport of electrical impulse.
These Electric impulses They are those that allow us to carry out different actions, both voluntarily and involuntarily, physical behaviors, cognitive processes, emotions, etc. If you want more information, here we tell you what the neuron functions most prominent.
What is the soma or body of a neuron like?
It is known as body, soma or perikaryon to the central and most important element of the neuron. Within it is the nucleus of the neuron and from it its processes: dendrites and axon.
The shape and position of the neuronal nucleus it varies according to the type of neuron and its location: it is usually polygonal or multipolar in motor neurons or pyramidal cells; In contrast, the cells of neurons in the posterior root ganglia are generally round and have a single prolongation (they are called unipolar cells).
Within the soma of a neuron we can find: the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Scattered throughout the cytoplasm we find organelles such as mitochondria or lysosomes, common in other cell types, but also bodies more characteristic and proper such as Nissl bodies, which are clusters of rough endoplasmic reticulum responsible for the production of proteins.
In the center of the neuronal soma the nucleus can be found. The nucleus is usually centrally positioned and highly visible, especially in small neurons.

What is inside the nucleus of the neuron?
The core is the central and most important element of the neuronal body. In it, one or two nucleoli and some DNA are normally found, surrounded by a gelatinous liquid called karyoplasma. The entire set of DNA, nucleoli and karyoplasm is delimited by a nuclear membrane.
The karyoplasma and the nuclear membrane of neurons are similar to those of other cells, so they are rarely paid much attention. The only thing that stands out about the nuclear membrane is the large number of nuclear pores that the nuclear envelope has and that its nuclear lamina is quite developed.
The DNA It carries the genetic instructions that govern the formation, growth, function and death of the neuron, so it is not surprising that the nucleus is the most important part of the neuron. The DNA of neurons can be found in two forms: heterochromatin and euchromatin. It is normally found as heterochromatin or dispersed chromatin, since the nucleus of neurons is very active and a large amount of transcription is taking place.
Within the nucleus, in the outermost or polar parts of it, the nucleolus. The nucleolus is in charge of transcribing the DNA from the nucleus to RNA; This RNA will exit through the pores of the nuclear envelope and will finish maturing in the ribosomes present in the cytoplasm of the neuron.
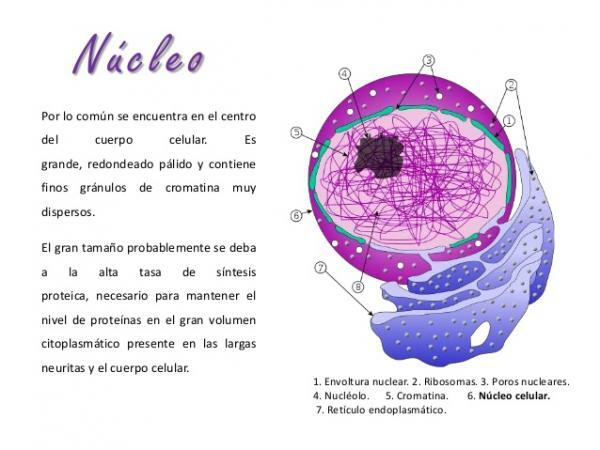
Image: Slideshare
Function of the nucleus of a neuron.
The nucleus is the part of the neuron that orchestra performance of this and keeps it alive since in it is the nucleus of the cell (with the genetic instructions in the DNA inside). The nucleus of neurons is the "brain of the brain."
According to the instructions that come through the dendrites, the nucleus of the neuron is in charge of giving the order to synthesize most of the proteins found in the neuron. The most important of these proteins are those that are going to be part of or cause the initiation of the synthesis of most neurotransmitters.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the nucleus of the neuron like?, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Ambrosiani Fernández, J (2007) Neuroanatomy. The neuron. Sevilla University. Recovered from: https://personal.us.es/ambrosiani/Neuroanatomia_2007/intro5.htm
- Castillero Mimenza, O (s.f) Neuronal soma or pericarion: parts and functions. Psychology and Mind. Recovered from: https://psicologiaymente.com/neurociencias/soma-neuronal