7 characteristics of the MANTLE of the Earth

The surface of planet Earth is made up of several layers with different functions, compositions and characteristics. Between these layers are the Earth's crust, mantle, and core. However, in this lesson from a TEACHER we will focus on the mantle and the characteristics of the earth's mantle. If you are interested in knowing the composition of our planet earth, this article interests you.
Before talking about the characteristics of the Earth's mantle, we are going to discover what is the mantle so that you better understand what we are referring to.
At inside of the earth one is found layer of dense and very hot rock called the earth's mantle. This layer is between the outermost layer of the earth known as the earth's crust and the innermost layer that forms the core.
The Earth's mantle has a thickness of about 3,000 kilometers and is made up mainly of silicates. However, its composition is not uniform throughout its thickness either, the main materials being composed of oxygen, magnesium, aluminum, iron, silica and other metals.
Since the hottest area of the earth is in its core, the temperature of the mantle terrestrial varies depending on its proximity or distance from this nucleus, hovering around a temperature in its most close in around 3,500 ºC and in its most remote areas around 600 ºC.
As we said before, the earth's mantle it is not uniform, but has two well-defined layers:
- A higher viscosity upper mantle, with an interior that moves slowly and is responsible for the tectonic plate movement
- a cloak lower
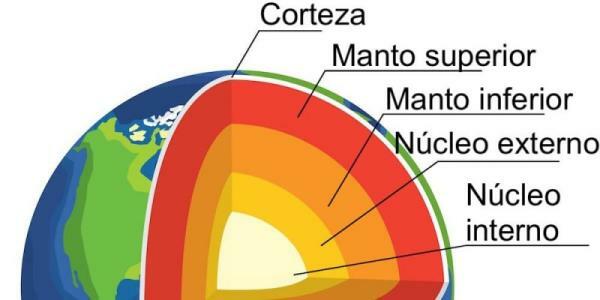
Image: Concept
Now that you know the main characteristics of the Earth's mantle, let's learn more about what this mantle is like and its structure.
The composition of the earth's mantle is its main difference with the core and the earth's crust. Although its composition is not the same throughout its length, its main component is the silicates. These are materials made up of silicon and oxygen and that they may contain small amounts of other elements such as aluminum, calcium or iron.
The Earth's mantle is made up of two well-differentiated layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle. Between the two layers a peculiar acceleration of seismic waves is generated. Its main features They are:
- Upper mantle: the upper part of the mantle begins in a transition zone with the crust, called Mohorovicic discontinuity and is divided into two layers: the asthenosphere and the lithosphere. The upper part of the mantle is mostly solid and is made up of an igneous rock called peridotite and also has compounds of oxygen, silicon, magnesium or iron. In the area of the asthenosphere, the components can flow and allow the movements of the tectonic plates. This structure has a thickness of 600 km and temperatures that range between 200 and 900 ºC.
- Lower mantle: extends from a transition zone that is below the upper mantle and encompasses a zone known as the Gutenberg discontinuity. The lower mantle is a solid layer composed mostly of silicon and magnesium, as is the mineral known as perovskite. This zone has a thickness that goes from 700 km to 2900 km with a higher temperature and pressure than the transition zone and the upper mantle. This layer can be studied thanks to the magmatic material that emerges on certain occasions to the earth's surface.
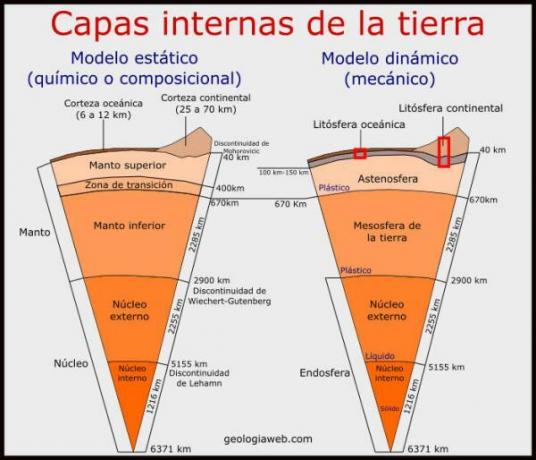
Image: Geology Web
The Earth's mantle makes up most of the Earth's volume and acts as a thermal insulator and refractory Of the surface.
In addition, the movements of the upper mantle and its convection currents allow the tectonic plate movement, which is vital for the dgeological development of the Earth and the survival of the living beings that inhabit it.
Finally, the magma expelled from time to time by volcanism allows create new crust where tectonic plates move apart, and involved in the carbon cycle, which is essential for regulating the Earth's temperature.