The 13 most important types of plants
Plants are living beings that can use sunlight to produce their own nutrients and on which the rest of the beings that live on Earth depend.
The diversity of plants is immense and covers practically the entire earth's surface. Therefore, botanists have tried to classify them according to common characteristics to facilitate their study and identification. Below, we present the main types of plants and their characteristics.
1. Herbs
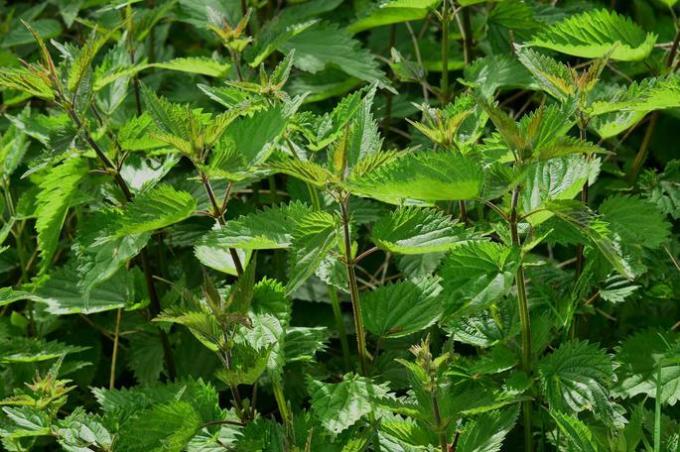

Herbs are upright, non-woody plants, usually small in size. They grow in the soil where they establish their roots, which can be main or adventitious. The stem is flexible and grows in height, but not in diameter, which is why they do not have woody bark.
Herb leaves contain chlorophyll and can be highly variable in shape and size. The photosynthesis process is more efficient in grasses, so their growth is rapid. However, its life cycle is very short, compared to shrubs and trees.
Grasses predominate on the sides of streets and pastures, in clearings and on the edges of the forest.
Examples of herbs are found in the Asteraceae families, such as sunflower and dandelion, and Poaceae or grasses, where wheat, rice and oats are found.
2. Shrubbery
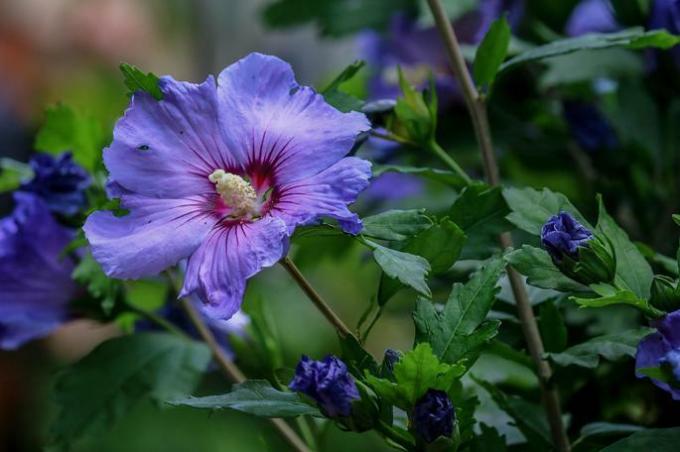

Shrubs are free-growing, upright, woody, vascular plants less than 5 m tall at maturity. Most belong to the angiosperms, although there are some shrubs among the gymnosperms, such as the juniper or juniper.
The stem of the bushes grows in height and thickness, producing a woody bark. They are perennial plants, they can live for several years in optimal conditions.
Examples of bushes are found in rosemary, rose bushes, cayenne peppers and camellia sinensis, the tea tree.
3. Trees
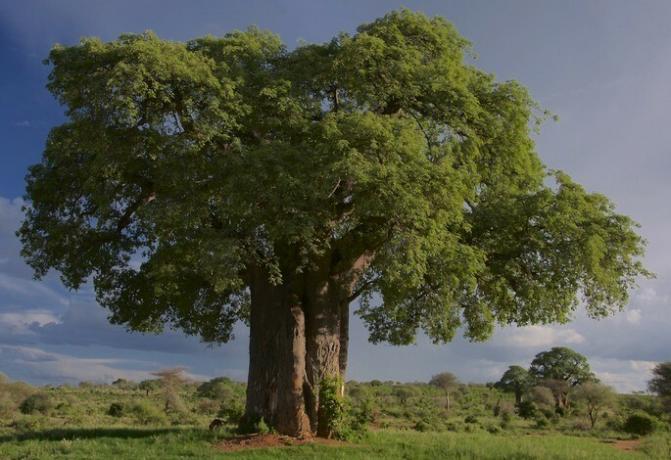

Trees are free-growing, woody vascular plants that are at least 5 m tall or 10 cm in diameter at breast height. Trees comprise 25% of all plant species.
Trees have fibrous roots, woody stems, leaves and seeds. Some trees have flowers, they belong to the angiosperms, while the trees of the class of gymnosperms, such as conifers, do not have flowers.
Trees are perennial plants, they can last tens to hundreds of years. The oldest known tree is a pine (Pinus longaeva) which is estimated to be more than 5 thousand years old.
Examples of trees are pines, cedars, firs, redwoods, oaks, and eucalyptus, among others.
You may also be interested in seeing Monocots and Dicots.
4. succulent plants

Succulents are plants that store water in their fleshy tissues. These plants adapted to live in dry and warm regions, transforming their leaves into thorns and their stems into a water reservoir.
Photosynthesis in these plants takes place in the stem and is of the CAM type, that is, they take carbon dioxide at night and carry out the Calvin cycle during the day.
Examples of succulents are cacti, aloes, Kalanchoe and the Crassulaceae.
5. Climbing plants

They are plants that cannot be held upright when they reach maturity. They can be divided into three growth forms:
- herbaceous trunk climbers: they are abundant in humid forests, sometimes they lose their connection with the ground. Examples of climbers are Philodendron, monstera, Syngonium, Asplundia, Evodianthus, Schlegelia.
- vines: Herbaceous or semi-woody climbers that generally do not measure more than 5 m in length.
- vines: climbers with permanent leaves that can measure more than 5 m in length. Examples of lianas are Celastrus, mucuna urens, Chusquea, Hydrangea astrolasia YPassiflora brevifila.
6. epiphytes and hemiepiphytes

Epiphytes are plants that grow on top of other plants without parasitizing their host. In this way they have a physical support, they obtain water and nutrients from materials dissolved in the rain that runs through the stems of the plant that supports them.
Many epiphytic species can be found growing on stones, fallen logs, or layers of moss on the ground. The greatest abundance and diversity of epiphytes is found in the humid forest.
Hemiepiphytes ("half-epiphytes") begin life as epiphytes; as they grow, they send roots into the soil where they gain access to nutrients and water from the soil. Hemiepiphytes can send long aerial roots directly into the ground (Ficus, Clusia) or send them up the trunk of the host tree (Blakea, Markea).
Lianas are different from hemiepiphytes in that they send their stems up from seeds that germinate in the ground.
The families of orchids (Orchidaceae) and bromeliads (Bromeliaceae) are the families with the most epiphytic species, for example Epidendrum, maxillaria Y Pleurothallis.
7. parasites

Parasitic plants insert their adventitious roots into the tissues of other plants to obtain part of their nutrients. They have leaves with chlorophyll, so they are capable of photosynthesis.
There are more than 4 thousand species of parasitic plants. Some are destructive pests of citrus trees and native trees.
Loranthaceae plants, also called matapalos, are common for trees. Other examples are the dodder, antidaphne, Endrophthora Y Phoradendron.
8. saprophytes

Saprophytes are plants that obtain their nutrients from dead organic matter, such as decaying plants. They usually do not have chlorophyll and do not photosynthesize.
Examples of saprophytic plants are found in the Burmanniaceae family, terrestrial saprophytes related to the orchid family.
9. fig trees
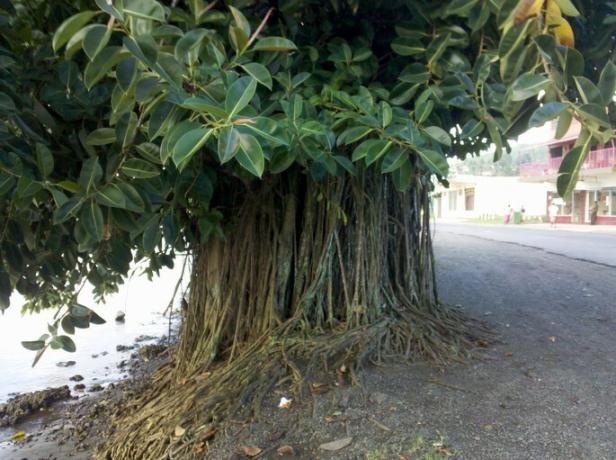

Figs begin their life as epiphytes, that is, they live on a plant. As they grow, they send adventitious roots downward, which become a web that encloses the trunk of the host tree.
Growing on top of the plant, they can tower over it, competing with it for light and nutrients. This can cause the death of the host tree, so the fig tree can persist for several decades as an independently growing tree.
The species of the genus ficus They are the best known fig trees.
You may also be interested in seeing angiosperm and gymnosperm.
10. ferns

Ferns are vascular plants with roots, stems and leaves, without flowers, belonging to the Polypodiophyta division. They are the first vascular plants in the evolutionary tree of plants. These appeared more than 350 million years ago, in the Devonian period of the Paleozoic era.
The stem of the fern is underground, which is known as a rhizome. From it depart the adventitious roots that are shaped like small threads.
Fern leaves are known as fronds or fronds. They can be as small as 2 cm and as large as 22 meters. On the underside of the leaves are the spores.
Ferns are differentiated by their life cycle divided into two generations (sexual and asexual) and by the fact that they reproduce by means of spores.
Ferns are found in almost all environments, wet and dry, although they are more abundant in the cloud forest. They are perennial, that is, they can live for many years.
Examples of ferns are Cheilanthes, Woodsia, Polypodium, Asplenium, Thelypteris and small trees like angiopteris, cyathea Y Cnemidarian.
11. mosses
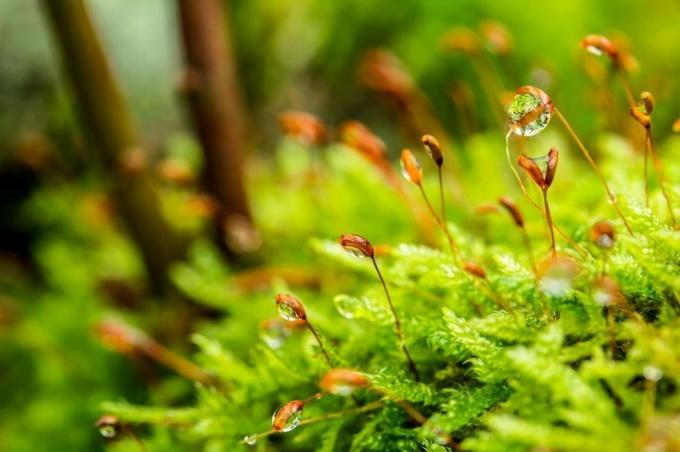

Mosses are small, non-vascular plants, that is, they do not have internal vessels (xylem and phloem) for water transport. They belong to the bryophyte division and are found in most environments around the world.
These plants are perennial: when the environment dries out, the mosses dry out but do not die. When the water returns, they begin to grow again. They also tend to grow close together forming dense mounds.
Examples of mosses are grimmy, Pohlia Y sphagnum.
Mosses are important in the establishment of other species. They colonize bare surfaces and dissolve rock with acids that seep from their cells. The leaves and stems trap and hold dust particles, creating small soil pockets where spores and seeds of vascular plants can germinate.
12. liverworts

Liverworts can be flat, lobed plants or resemble mosses. It was given this name because of its resemblance to the human liver.
Like mosses, liverworts are small non-vascular plants. The leaves usually have two rounded lobes, without a midrib or conductive tissue. The cells are rich in chlorophyll, so they are green and carry out photosynthesis.
Examples of liverworts are Monoclea, Cephaloziella, marchantia, Lophocolea, Riccia Y Ricciocarpus.
13. insectivorous plants

Insectivorous plants, or also called carnivorous plants, grow in environments with a very low availability of nutrients. They have specialized leaves to catch and digest insects, from which they obtain minerals and nitrogen.
Insectivorous plants carry out photosynthesis, so they can capture carbon dioxide and transform it into carbohydrates.
Examples of insectivorous plants are flytraps (Dionaea muscipula) and the cobra lily (Darlingtonia californica).
References
Fester, K., R. (2011). Botany for Dummies. Wiley Publishing. USA USA
Haber, W. (2014). Plants and vegetation. Monteverde: ecology and conservation of a tropical cloud forest. Oxford University Press. Available in: http://digitalcommons. bowdoin. edu/scholarsbookshelf/3/.(Revised April 2022), 56-138
Open Stax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. Oct 21, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]