4 phases of the COLD War

One of the central conflicts of the 20th century was the Cold War, being a military, economic, political and ideological confrontation that pitted two large blocks against each other, the capitalist one led by the United States and the communist one led by the USSR. The confrontation between these two blocs was very important for humanity, the result being what was going to mark the world's economic model. To delve into the evolution of this conflict, in this lesson of a Teacher we must talk about the phases of the cold war.
Index
- Origin of the Cold War
- The first of the phases of the Cold War (between 1945 and 1962): from containment to tension
- Second phase of the Cold War (1962 and 1979): détente
- Third phase (1979 to 1985)
- End of the Cold War: 1985 and 1989
Origin of the Cold War.
The Cold War It was a political, social, ideological and economic confrontation that took place between 1945 and 1989. It confronted two blocs of countries, one of them capitalist and led by USA and another from the communist class whose leader was the USSR.
It tends to be considered that the conflict was only between these two giants, but the reality is that many countries participated in this war. This was the case in countries with an important liberal structure such as France or UK, but also from new communist regions such as China or Cuba.
The war ended in 1989 with the the fall of the Berlin Wall. Therefore, it was a very long war, although with many breaks between wars.
The first of the phases of the Cold War (between 1945 and 1962): from containment to tension.
The first phase of the Cold War is one that we can call from containment to tension, since this phase situated between 1945 and 1962, encompasses a start focused on contention.
Both the United States and the USSR understood that in this ideological war they had to take territories to sink the enemy, so a competition was generated between both powers to see who was capable of taking a greater number of regions. A great example was Marshall Plan, according to which the United States gave aid to the regions that had suffered in the Second World War. But these aids had great interests, making the great European nations maintain their capitalist system and, at the same time, owe favors to the Americans.
the USSR, Seeing that the United States gave aid especially to the Germans, he decided start the Berlin Blockade. After the war, Berlin had been divided between the Allies and the USSR he feared that the people in his area would abandon communism and defend the capitalism of the United States and the United Kingdom. The Russians closed the borders, blocking off Berlin. Shortly after, the German Democratic Republic, of a socialist class, and the German Federal Republic of liberal characteristics were created, being separated by the Berlin Wall.
At this point, the tension between capitalists and communists was already enormous, so both they created organizations to focus their allies, these being the Cominform, a union of communist nations, and the NATO, which was a military alliance so that the capitalist nations responded to any communist attack.
While communists and capitalists fought for their influence, several wars broke out throughout the world, and in all of them both blocs intervened to try to increase their influence in them:
- In the Chinese Civil War between 1946 and 1949 the victory went to the communists and it became one of the greatest allies of the USSR.
- In the Korean War, between 1950 and 1953, the nation was split in two, with North Korea being the communist nation and South Korea being the capitalist one.
The final point of this phase of the Cold War we find it in the Cuban missile crisis. The Cuban revolution had made the nation of Cuba ally with the USSR, with a clear communist spirit, being a problem for the United States to have an enemy so close. At a certain moment, the Americans discovered the existence of missiles in Cuba, being close to starting the nuclear war before the dismantling by the Russians of the missiles.
Second phase of the Cold War (1962 and 1979): détente.
The second phase of the Cold War is known as détente, being a period of the conflict between 1962 and 1979, marked by the stress reduction after the conflict progressed.
In this phase, both powers were in a bad moment, due to the serious problems suffered by both during those years:
- The economy in communist bloc was in collapseor, so the USSR had to decrease its military attacks to cut costs.
- Besides, USA I was immersed in watergate scandal that had led to the resignation of President Nixon, in addition that they had suffered the first defeat in their history in Vietnam.
In this situation in which both powers were in such a bad way, there was no other option than to carry out a series of treaties that would bring a decrease in conflicts, calming the environment and bringing relative peace.
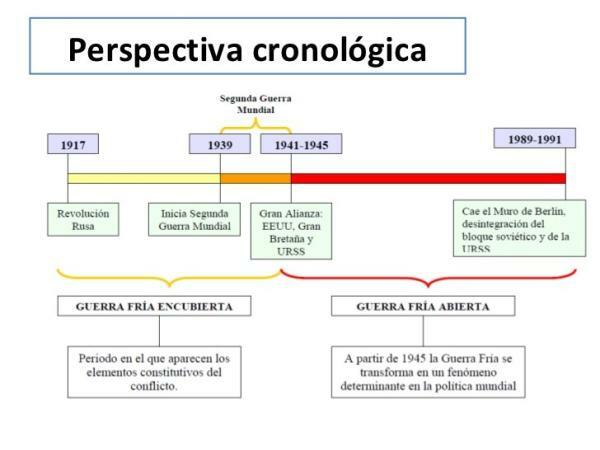
Image: Storytelling
Third phase (1979 to 1985)
The third phase of the Cold War began in 1979 and ended in 1985. It was a period in which both nations They started fighting again having largely overcome its economic and political problems.
In 1979 the USSR invaded Afghanistan and supported the Islamic Revolution and the Sandinista Revolution, which put an end to governments close to the United States in numerous regions such as Iran and Nicaragua. In this situation, President Carter increased military spending to try stop Russian advances on numerous fronts.
After Carter, the new president of the United States was Ronald Regan, who created the call reagan doctrine, according to which the US had the right to overthrow any communist government in the world. After that, the United States began to support any international resistance against a possible communist government, bombing nations like Libya and Grenada, but also supporting guerrillas from nations like Afghanistan and Nicaragua.

End of the Cold War: 1985 and 1989.
To conclude with this lesson on the phases of the Cold War we must talk about the last one, being the last and where the conflict ends, this phase being situated chronologically between 1985 and 1989.
The United States did not stop increasing its troops, focusing a large part of its economy on the war, while the USSR began to be unable to pay so much military spending, even more so after the oil crisis that greatly reduced its wealth. In that situation, the new Russian government, led by Gorbachev, considered that war was not possible, beginning to sign agreements with Reagan to reduce the armament of both.
Slowly, the allies of the USSR were getting closer to the West, disappearing many of the communist states, which were becoming capitalist. This was especially relevant in the Eastern Europe, where the great allies of the USSR were disappearing.
Finally and due to this situation, in 1989 the Maltese Summit, where Gorbachev and George Bush signed the end of the Cold War.
If you want to read more articles similar to Phases of the Cold War, we recommend that you enter our category of History.
Bibliography
- McMAhoN, R. (2009). The Cold War. A brief introduction. Madrid: Alliance.
- Gaddis, J. L. (2008). The Cold War. RBA.
- Lozano, A. (2007). The Cold War. Melusine.