All ORGANS of the URINARY system
The urinary system It is one of the most important systems in the excretion mechanism of higher animals, its function is to eliminate substances and waste products that, if accumulated, are toxic to the body. Through this system, in addition to water, nitrogenous waste is eliminated.
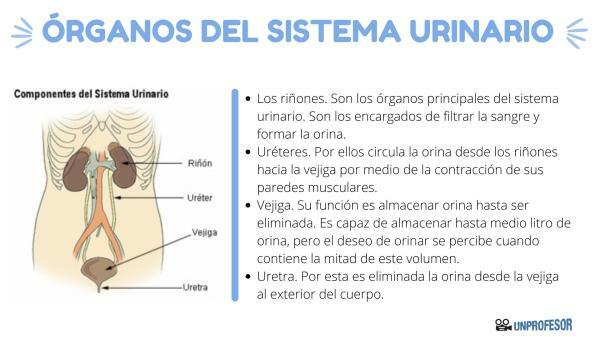
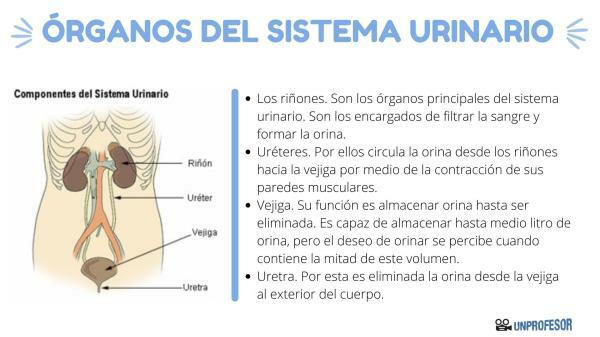
The urinary system is made up of the following organs: the kidneys and the urinary tract, where we find the ureters, the bladder and the urethra. In this lesson of a PROFESSOR we will dedicate ourselves to knowing the urinary system organs. Join us to discover them!
Index
- Urinary system
- Description and function of the organs of the urinary system
- What is thirst?
Urinary system.
Before starting to describe the organs of the urinary system, we want to share with you some of the functions of the urinary system.
The urinary system is part of the excretion function of the body. The excretory organs fulfill the function of keeping the amount of water in the body constant, eliminating metabolic waste and other substances into the environment.
What are the excretory products of the body?
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Nitrogenous wastes such as urea and uric acid
- mineral salts in excess
- Other substances such as medicines, food additives (preservatives, dyes), etc.
The circulatory system he is in charge of pick up all this debris metabolism in the blood and carry them to each excretory organ for elimination.
The urinary system is responsible for filtering the blood, remove waste and eliminate it through urine. The blood reaches the kidneys through the renal artery, once inside the organs, it branches into multiple blood vessels, each time thinner.
Each kidney has a million tubules inside. coiled that make up units called nephrons, each nephron is in contact with these blood capillaries through which the exchange of waste substances occurs.
Next we tell you what are the organs of the urinary system...
Description and function of the organs of the urinary system.
We are going to know which are the organs of the urinary system individually.
The kidneys
- Description: They are the main organs of the urinary system. They are two dark red organs, their shape is similar to that of a bean, they are located on both sides of the spine, in the back of the abdomen, below the waist. Each kidney weighs about 140 grams. In a longitudinal section of the organ, two regions can be differentiated: the external one, which is named as kidney cortex, and the internal one, which is the kidney medulla. The renal pelvis It is the area where all the urine collecting ducts converge.
- Functions: As mentioned above, they are the most important organs of the urinary system, since they are responsible for filtering the blood and forming the urine. They also maintain the balance of salts and water. They also participate in an endocrine function by producing hormones such as erythropoietin, which intervenes in the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, and renin, which causes increased pressure arterial.
ureters
These organs of the urinary system resemble two muscular tubes around 25 cm long, each coming from each kidney, more specifically the renal pelvis of the kidneys. Through them, urine circulates from the kidneys to the bladder by means of the contraction of its muscular walls.
Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ with elastic walls.located in the lower abdomen. Its function is to store urine until it is eliminated. This happens thanks to the fact that its muscular and elastic walls are able to relax when it is full and contract when it is empty. It is capable of storing up to half a liter of urine, but the desire to urinate is perceived when it contains half this volume.
The liquid contained in the bladder presses on its walls, stimulating certain nerve receptors, whose signals are translated into the sensation of the need to evacuate. We call this phenomenon micturition reflex, controlled by the nervous system, in urination a series of muscles intervene whose coordinated action allows the emptying of the bladder.
Urethra
The urethraIt is a tube that comes from the bladder. By this urine is eliminated from the bladder to the outside of the body. At the beginning of the urethra is the internal urethral sphincter of involuntary action, which prevents the passage of urine from the bladder until a certain pressure is reached.
At the other extreme we find the external urethral sphincter of voluntary action, is what allows us to control the output of urine. When we relax this sphincter, we allow urine to flow out, even though the bladder is not completely full. This muscle can be voluntarily controlled by people from the age of 2 years.
Curiosity: The male urethra is longer than the female one and functions as a urinary and genital tract at the same time.
What is thirst?
Thirst is an indicator that a large amount of water has been eliminated from the body through urine or perspiration, indicating that lost water must be replaced.
Dehydration in humans occurs when more water is lost than is taken in. One of the causes can be vomiting and diarrhea during a gastrointestinal illness. The problem with dehydration is that in addition to losing water, we lose sodium and potassium ions that are essential for other processes in the body. Symptoms of dehydration can be dizziness and a dry mouth.
How can the effects be reversed?
It is essential to rehydrate, little by little, with drinks that contain sodium and potassium mineral salts in order to restore the lost water balance.
If you want to read more articles similar to Organs of the urinary system, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Adúriz-Bravo, A.; Bardi, M. G.; Busts, d. EITHER.; Fried, D. J.; Hardmeier, P. m. and Suares H. g. (2006). Biology. Human anatomy and physiology. Genetics. Evolution- Perspectives Series-. Editorial Santillana. Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- Bocalandro, N.; Frid, D.; Socolovsky, L. (2010). Biology 4 IS. Exchanges of matter and energy, from the cell to the ecosystem. Editorial Estrada. San Isidro, province of Buenos Aires, Argentina.