Function of the PLACENTA

To talk about the placenta, we must first mention that not all animals have it. Placental mammals are the class of animals that present this temporary organ, it is typical of females, since that is where the embryo will develop. The placenta is formed in the uterus and is essential to ensure the growth and survival of the fetus during pregnancy. pregnancy. After childbirth occurs, the placenta is discarded, which is why it is said to be an ephemeral organ.
In this lesson from a Teacher we will tell you what is the function of the placentaJoin us in this discovery.
Before discovering what the function of the placenta is, we are going to discover what the placenta is. It's a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy and performs essential functions in the gestation of the fetus. It begins to form at the same time that the implantation of the embryo occurs in the wall of the female uterus.
the placenta separates the fetus from the mother's uterine lining. The blood vessels of the umbilical cord are the ones that connect the placental circulation to the fetal one. The placenta, along with its membranes, are expelled after delivery, in a process called delivery.
parts of the placenta
The placenta is made up of two parts:
- Maternal portion: The uterine epithelium develops from the wall of the uterus at embryo implantation.
- fetal portion: Called chorion, it is provided with villi and covered by a membrane called Amnion. We also find the yolk sac and the allantois.
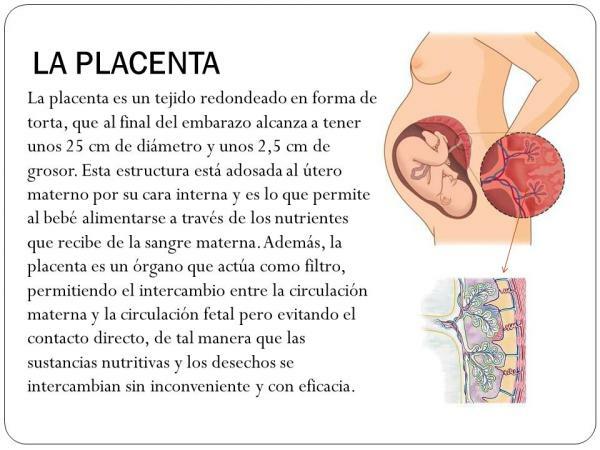
Image: Slideplayer
In general, the functions performed by the placenta have to do with the exchanges that occur between mother and fetus. The placenta allows the exchange of nutrients and oxygen between them, secretes hormones and protects the fetus from the mother's immune response, preventing it from being rejected as a foreign body.
exchange function
One of the most important functions is exchange of substances that occurs between the mother and the fetus. Gas exchange is the primary function of this organ, followed by the exchange of nutrients and the excretion of waste substances.
Through the mother pass the oxygen, water, glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, hormones, antibodies, some drugs and some pathogenic microorganisms. That is why it is essential that the mother take better care of herself at the time of pregnancy, since everything that enters her body will pass to the developing fetus. Instead, from the fetus to the mother pass only metabolic waste such as urea, and carbon dioxide.
hormone function
The placenta is not an organ that has a nervous connection, That is why the communication pathway is chemical, and is carried out through hormones that travel through the blood. There are various hormones that the placenta will produce from its development and that trigger processes related to maintaining the structures that will carry out the pregnancy, one of them is the well-known progesterone, most of this hormone passes into the mother's blood circulation and part is captured by the fetus for the development of corticosteroids fetal.
Another hormone is estrogen, it makes the uterus, breasts and external genitalia increase in size. Placental lactogen stimulates the secretion of the mammary glands and growth of the fetal organs. Lastly, chorionic gonadotropin keeps the corpus luteum in the ovaries functional, which will help continue the production of progesterone, androgens, and estrogens.
immune function
The fetus has a large amount of foreign proteins for the mother's body, which come genetically from the father. That is why there is a mechanism that makes the fetus compatible with the mother's body and prevents the mother from rejecting it as if it were a foreign body. This occurs thanks to the fact that the placenta produces immunosuppressive factors.

There are different types of placentas based on the number of cell layers between the mother's blood and the embryo. In the case of human beings, the chorion of the embryo sac and the epithelium of the uterine mucosa of the mother grow fused, this implies that if they are separated, hemorrhage occurs. This type of placenta is called deciduous.
The placenta and umbilical cord form a transport system. so that substances can reach the fetus. Inside the amnion, we find the amniotic fluid, we can say that the embryo floats in this fluid held by the umbilical cord. This liquid serves to cushion shocks and jolts, allows the fetus to move, has antibacterial properties that provide some protection, and serves as a nutrient reservoir.
Image: Assisted Reproduction
- Flores Perez, F. A. Human embryology. Reading material no. 06. Los Angeles University of Chimbote. Faculty of Health Sciences. Professional school of obstetrics.
- Morgan Ortiz, F. (2015). "Anatomy and physiology of the placenta and amniotic fluid". Center for Research and Teaching in Health Sciences (CIDOCS) of the Autonomous University of Sinaloa. Hospital Angeles Culiacan.
Roa, I., Smok, C. S., Prieto, R. g. (2012). "Placenta, comparative anatomy and histology". Int. J. Morphol., 30(4):1490-1496.



