What is the NUCLEOPLASM and its function
Cells are the smallest portion of life that exists, that is why it is said that the "cell" is the unit of life. We can find living beings made up of a single cell (unicellular) and organisms that have many cells with specialized functions (multicellular). There are cells that do not have a nucleus and others with the presence of a nucleus. They are classified as: prokaryotes (without a nucleus) and eukaryotes (with a nucleus).
Within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells we find, among other things, the genetic material or DNA. To talk about nucleoplasm, we must first know what the nucleus is. Join us in this lesson from a Teacher to learn what is the nucleoplasm and its function.
Index
- The cell nucleus and nucleoplasm
- Structures of the cell nucleus
- Nucleoplasm: functions and characteristics
The cell nucleus and nucleoplasm.
All eukaryotic cells they have the peculiarity of having a large body, frequently spherical, which is usually the most important structure in terms of size within eukaryotic cells. This structure is the cell nucleus, it is surrounded by an envelope known as
nuclear Envelope, this envelope separates the internal environment of the nucleus from the cell cytoplasm.It is made up of two membranes, each of which is a lipid bilayer (like the cell membrane, which separates the internal environment from the outside). In the nuclear envelope we find pores, small holess by which certain substances or materials can enter and leave the cell cytoplasm and vice versa, we could say that they constitute a path or passage of substances between the interior of the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
what is nucleoplasm
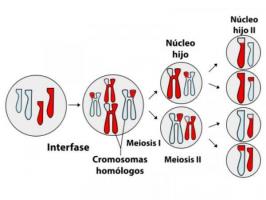
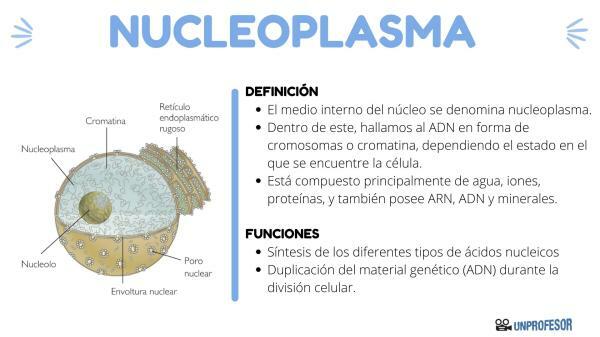
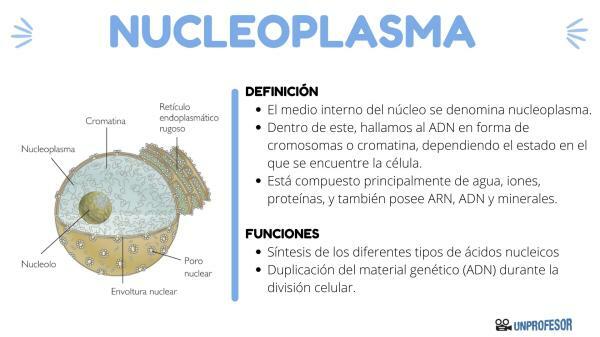
The internal environment of the nucleus is called the nucleoplasm. Within this, we find DNA in the form of chromosomes or chromatin, depending on the state in which the cell is. When the cell is not dividing, the DNA looks like a tangle of thin threads called CHROMATIN. Instead, When the cell enters the stage of cell division, the chromatin condenses and organizes itself into the shape of CHROMOSOMES.
Within the nucleus we can also find corpuscles of remarkable size, called nucleoli.

Structures of the cell nucleus.
Once we know what the nucleoplasm is, we are going to discover what the structure.
- nuclear envelope: The envelope of the nucleus has several functions, the main one is to separate the cytoplasm from the nucleoplasm, that is, it separates the internal environment of the cell from the nucleus that contains the DNA. It has pores that regulate the exchange and passage of substances from the interior of the nucleus to the cell cytoplasm. It protects the genetic material or DNA.
- Nucleoplasm: It is the interior medium of the nucleus, it resembles a gel.
- nucleolus: It can be considered an organelle that is inside the nucleus, it does not have a membrane. Its function is the synthesis and assembly of ribosomal subunits. It is made up of RNA and proteins, forms ribosomal RNA. Each cell has at least one nucleolus, since all cells need ribosomes and they are synthesized here.
- chromatin: It is the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and its associated proteins, which are called histones. They are in the form of filaments forming a ball. Its function is to provide the necessary information so that the cellular organelles can carry out the transcription and synthesis of proteins, they also preserve and duplicate the genetic information contained in the DNA to transmit it in the division cell phone.
- chromosomes: They appear when the chromatin condenses, the DNA acquires rod-shaped structures when the cell begins the stage of reproduction or division of the cell nucleus. Their number or quantity is what determines each species. For example: humans have 46 chromosomes, while cats have a total of 38 chromosomes in their cells.
During the mitosis or cell division, some of these structures are lost: the nuclear envelope disappears, the nucleolus and the chromatin is organized in the form of chromosomes.
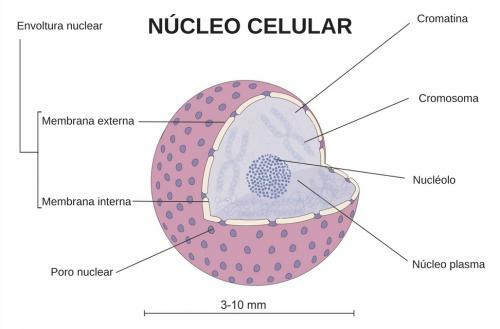
Image: Meanings.com
Nucleoplasm: functions and characteristics.
Let us see what are the functions and characteristics of the nucleoplasm. Nucleoplasm can go by various names, such as nuclear juice or caryoplasma.
What are its characteristics of the nucleoplasm
As mentioned above, the nucleoplasm It is the internal environment of the cell nucleus. it can be considered a colloidal dispersion in the form of a gel. It is composed mainly of water, ions, proteins, and also has RNA, DNA and minerals.
Within the nucleoplasm we find the "nucleoskeleton", It is a matrix of filamentous or fibrillar proteins similar to those found forming the cytoskeleton in the cytoplasm. protein network prevents "knots" from forming in the chromatin and allowing its folding, and regulates the replication and transcription of the DNA.
Within the nucleoplasm we find all the components of the nucleus, mainly genetic material: DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes and the nucleolus.
functions of the nucleoplasm
Since the nucleosome is the internal environment of the nucleus, we can conclude that all the nuclear components are immersed there.
It is the place where genetic information or DNA is found of each organism. The functions of the nucleoplasm are synthesis of the different types of nucleic acids and the duplication of genetic material (DNA) during cell division.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the nucleoplasm and its function, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Jimenez, L. F. and Merchant, H. (2003) "Cellular and molecular biology". Pearson Education, Mexico.
- Rojas Lemus, M., Milán Chávez, R., (2016) "The limits between histology and biochemistry: observing the cell nucleus". Journal of the Faculty of Medicine of the UNAM. Vol. 59, No. 1.