Temperature scales: Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin and Rankine
Temperature is a property of matter that represents the internal movement of the particles that constitute it. The instrument used to measure it is the thermometer.
The most commonly used temperature scales today are:
- Celsius or centigrade scale (ºC)
- Fahrenheit scale (ºF)
- Kelvin Scale (K)
There is a fourth scale, the Rankine scale, which is in disuse. Each scale is based on certain phenomena or fixed points, which served to define the range and degrees of measurement. For example, the Celsius scale was defined from the melting point and boiling point of water.
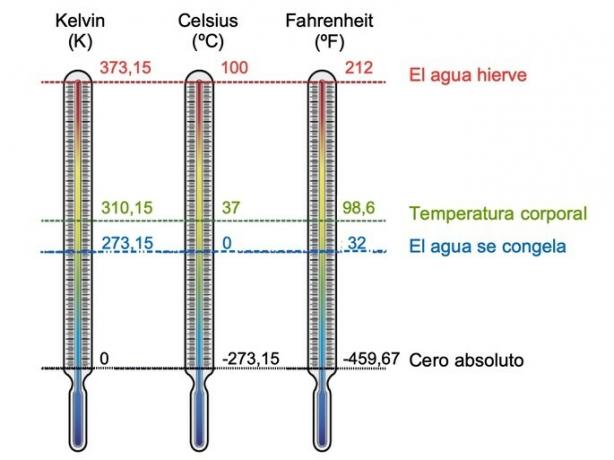
Absolute zero is the coldest temperature that can be recorded. This happens because the speed of the particles or their kinetic energy becomes zero, that is, the particles stop.
The equivalences of absolute zero in the different scales are:
- Celsius: -273ºC
- Fahrenheit: -459.7ºF
- Kelvin: 0K
Fahrenheit scale
The Fahrenheit scale is the temperature scale used in the United States, Liberia, and the Bahamas, among others. Its symbol is °F and it is read in degrees Fahrenheit.
Physicist Daniel Fahrenheit (1686-1736) described the scale named after him in 1724. It is based on two fixed points: the temperature at which water freezes (32ºF) and the temperature at which water boils (212ºF). The difference between these two points is 180 degrees, so each degree represents 1/180.
Originally, Fahrenheit formulated the scale using three fixed points: the highest point was the temperature of the human body (96ºF), the The middle point was the temperature of a mixture of ice and water (32ºF), and the lowest point was the temperature of a mixture of equal parts ice, salt, and water (0ºF).
To convert degrees Fahrenheit from degrees Celsius the following formula is used:
Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit = (9/5 temperature in degrees Celsius) + 32
That is: the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit is equal to nine-fifths of the temperature in degrees Celsius plus 32. For example, if we want to convert the room temperature from 23 ºC to ºF we do the following:
TºF=9/5 x (23 ºC) + 32= 41.4 +32= 73.4 ºF.
So, 23ºC is equal to 73.4ºF. The Fahrenheit scale and the Celsius scale intersect at -40º, that is, -40ºC is equal to -40ºF.
Celsius or centigrade scale
The Celsius scale is the most widely used temperature scale worldwide. Its symbol is ºC and it is read degrees Celsius or centigrade.
In 1742, the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701-1744) proposed two fixed points to make his scale of temperature: the melting point of ice would represent 0 ºC and the boiling point of water would be 100 °C
The Celsius scale and the Kelvin scale are related by the formula:
Temperature in degrees Celsius (ºC) = Temperature in Kelvin (K)- 273.15
For example, we want to convert 300 K to Centigrade. To do this we subtract 273.15 from 300 K:
TºC=300K-273.15= 26.85ºC
That is, 300K is 26.85 ºC.
Kelvin scale
The kelvin is the unit for temperature in the International System and the most used in the scientific context. Its symbol is K and it is read kelvin. For example, the solar corona has a temperature of 1 million kelvins, while the interior of the Sun measures 10 million kelvins.
To define the kelvin, we need to know that the triple point of water is the point where we can find water in its three states: liquid, solid and gas.
This temperature was established as 273.16 K by international agreement in 1954. Hence a kelvin is defined as the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
The Kelvin scale is the only one based on thermodynamic principles and not on how a certain material behaves.
William Thomson (1824-1907), known as Lord Kelvin, pioneered the concept of absolute temperature in thermodynamic terms. He insisted that the concept of absolute temperature should not be tied to any property of any particular material substance, and that temperature should be a physical quantity measurable.
Rankine scale
The Rankine scale is a thermodynamic temperature that has the symbol ºR and is read degrees rankin. It is named after the engineer and physicist William Rankine who proposed it in 1859.
The Rankine scale uses the degree like the Fahrenheit degree, but is measured from absolute zero like the Kelvin scale. This scale is currently deprecated.
Conversion formulas between temperature scales
Knowing the relationships between each temperature scale, we can make the corresponding conversions following the following formulas:
| starting ºC | Starting from K | Starting in °F | From ºR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| at ºC | - | TC=TK-273.15 | TC=5/9(TF-32) | TC=5/9TR-273.15 |
| A K | T\K=Tc +273 | - | TK=5/9(TF+459.67) | TK=5/9TR |
| at °F | TF=9/5TC +32 | TF=9/5TK-459.67 | - | TF=TR-459.67 |
| A ºR | TR=9/5TC+491.67 | TR=9/5TK | TR=TF+459.67 | - |
You may also be interested in seeing:
- Difference Between Heat and Temperature
- Conduction, convection and radiation
- States of matter and properties of matter
References
Machin, G. (2017) Chapter 4 Temperature scales: past, present and future: 1700-2050. In: Cooper M, Grozler J. Precise Dimensions A history of units from 1791-2018. IOP Publishing
Temperature and thermometric scales. In: Slavat, J (director) (1988) Salvat Encyclopedia of Science and Technology- volume 13. Salvat editors. Barcelona, Spain.
Zayn, S. (2021) Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics. IOP Publishing.

