The 6 stages of pregnancy (and their characteristics)
Pregnancy is the period of development of the fetus in the uterus, which goes from conception to delivery. A baby develops during approximately 40 weeks of gestation (280 days), these weeks are divided into three trimesters and each one has its growth milestones. Before conception, a series of physiological mechanisms are necessary that allow the implantation of the fertilized ovum.
Within 24 hours of the sperm and egg uniting, the zygote (fertilized egg) begins to divide into many cells, which will go on to form all of the baby's organs and tissues. The baby goes through various stages of development: first as a blastocyst, then as an embryo, and finally as a fetus at 8 weeks gestation.
In this article we will detail the aspects of the gestation period, from conception to birth, including the most common developmental milestones that occur in the different stages of pregnancy.
- Related article: "Perinatal psychology: what is it and what functions does it perform?"
The main stages of pregnancy
Here you will find a summary of the stages of pregnancy, classified by blocks according to the qualitative changes that occur in the mother and in the embryo or fetus.
1. First stage: Conception
From adolescence to about fifty years of age, the body goes through a monthly reproductive cycle, which can end in pregnancy (if fertilization occurs) or menstruation. The menstrual cycle continues without interruption throughout the reproductive years.
There are multiple stages in a cycle that ends in pregnancy, this process begins with ovulation. A group of eggs called oocytes prepare to leave the ovary together, each of these immature eggs develops inside a fluid-filled cyst called a follicle. One of the eggs in the follicle will continue to develop throughout the cycle, while the rest of the follicles will disappear by the action of the mature follicle. The mature follicle then breaks open and releases the egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube.
Ovulation occurs about two weeks before the start of the next menstrual cycle, usually coinciding with the middle of the period.
After ovulation, the open follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum, which releases the so-called female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone.
Progesterone prepares the lining of the uterus (endometrium) to receive the possible fertilized egg; The endometrium is the place where the ovum nests and develops once fertilized. If fertilization does not occur during a cycle, this lining is shed and is the origin of menstruation.
Fertilization normally occurs two weeks after the last menstrual period. At the time of conception, the egg is fertilized by a particular sperm, and the proteins on the egg's coat change to prevent other sperm from entering. It is really the egg that chooses the sperm, and not the other way around, as when talking about the fastest sperm.
The genetic makeup, like the genetic sex of the baby, are already determined at the time of fertilization, each parent contributes half of her genetic heritage.
- You may be interested: "How to overcome a couple crisis due to fertility problems"
2. Second stage: 24 hours after conception
The egg begins to divide rapidly within 24 hours of fertilization and it remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Once in the uterus, the fertilized egg, now called a blastocyst, has to adhere to the endometrium, in the phase known as implantation.
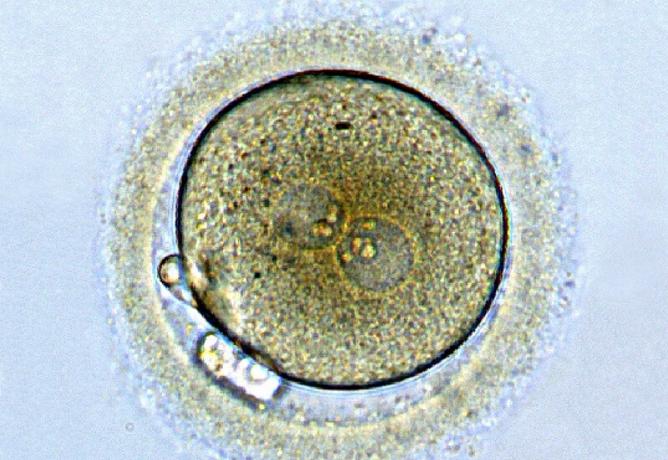
Before implantation, the blastocyst sheds its protective membrane. After the blastocyst successfully attaches to the endometrium, the two exchange hormones. Some people notice light bleeding for a day or two after implantation, it is natural and frequent bleeding. At this time, the endometrium thickens and the cervix (which opens into the birth canal) becomes clogged with mucus.
Three weeks after conception, the cells of the blastocyst already form a small mass or embryo.. At this time, the first nerve cells have also developed.
- Related article: "The 10 hormones of pregnancy (and their functions)"
3. First trimester
The first three months of pregnancy make up the first trimester, which covers the period of time from when the egg is fertilized until the fetus is around 12 weeks old. During this trimester, the fertilized egg develops into a fetus with more defined features such as hands, nose, and feet.
3.1. first month of pregnancy
The embryo grows inside a fluid-filled sac that forms around the fertilized egg. This sac is called the amniotic sac and helps protect the growing baby.
During this time, the placenta also develops.. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers waste from the growing fetus to the person. pregnant woman to be eliminated and in the opposite way the baby receives the nutrients through the placenta. The placenta is interconnected with the embryo through the umbilical cord.
In the first few weeks, a kind of primitive face forms with large dark circles where the eyes will go, and the mouth, lower jaw and throat begin to form. The formation of the first blood cells gives rise to circulation. By the end of the fourth week, the tiny heart tube beats 65 times a minute..
At the end of the first month, the fetus is a little smaller than a grain of rice, the embryo measures between 0.4 and 1 mm.
- You may be interested: "The development of the nervous system during gestation"
3.2. second month of pregnancy
The face is still developing. Ear folds are forming on the side of the head. Vestiges appear that will eventually become arms and legs. Eyes and fingers and toes are also beginning to form.
The neural tube (brain, spinal cord, and all other neural tissues) is defined and the digestive system begins to develop. Bones begin to replace cartilage, and the head is larger than the rest of the body at this time.
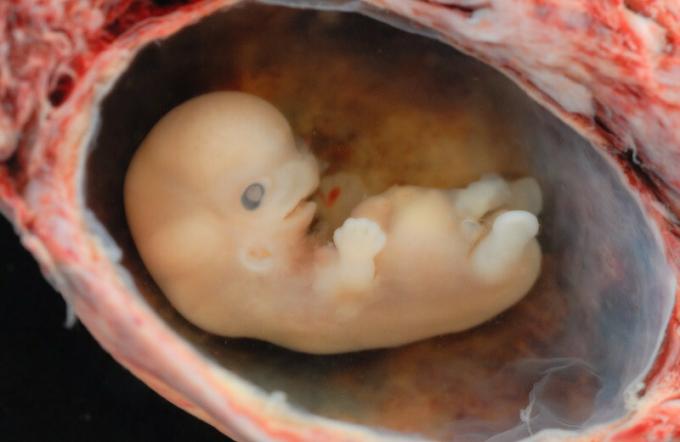
Health professionals call a developing baby after the eighth week a fetus, rather than an embryo. Usually around 6 weeks the heartbeat can be detected.
The fetus measures about 13-18 millimeters and can weigh about 3 grams.
3.3. third month of pregnancy
The fetus is now about 9 weeks old and many things have started to form. The arms, feet, hands and fingers are fully developed. The fetus is also beginning to explore by moving its mouth and fists. Fingernails, toenails, and external ears continue to form. Teeth begin to form under the gums.
By the end of the third month, the structure of the fetus is fully formed and all the limbs and organs have begun to develop, and will continue to do so until they are 100% functional. The urinary and circulatory systems are already working, also the liver that produces bile
Although gender is still difficult to detect with ultrasound, the reproductive organs have also developed. The fetus undergoes the most important development in the first three months of pregnancy, so the chance of losing the baby decreases after that point.
At the end of the third month, the fetus measures about 6 cm and about 14 g.
- Related article: "What happens psychologically after the abortion, and what to do?"
4. Second quarter
By the middle of pregnancy, most people feel fine. Morning sickness is usually gone and so are early pregnancy aches.
The fetus begins to develop facial features in this month and you can begin to feel the baby move within the womb. About At 20 weeks pregnant, parents find out the sex their baby will be assigned during an ultrasound called an anatomical examination, where the physical development of the baby is also checked.
4.1. fourth month of pregnancy
The doppler instrument is capable of detecting the heartbeat of the fetus. Fingers and toes are defined. Eyelashes, eyebrows, nails, and hair begin to form. Bones and teeth are forming, becoming denser.
At four months, the baby has a functional nervous system and can suck his thumb, yawn, stretch and even grimace. The genitals and reproductive organs are fully formed, and doctors can determine the sex to be assigned on ultrasound.
4.2. fifth month of pregnancy
The fetus begins to grow hair on its head and begins to develop muscles in the fifth month. At this stage of pregnancy, the fetus can begin to move its limbs and its movements can be felt. This first movement is called acceleration and feels like a fluttering sensation.
In the first week of life, the fetus's hair called lanugo covers the shoulders, back, and temples. This fine hair protects the fetus and falls out early in the baby's life.
The skin is covered by a thick white substance called vernix caseosa. It is believed to be covered with skin, it prevents the fetus's skin from being exposed to too much amniotic fluid for too long. Just before birth, the vernix caseosa layer is shed.
By five months, the baby weighs about a pound and is about 10 inches long.
- You may be interested: "Parturiphobia (childbirth phobia): symptoms, causes and treatment"
4.3. Sixth month of pregnancy
The skin of the fetus is reddish, wrinkled, and veins can be seen through the skin, which is translucent. At this stage, the eyes open and the eyelids begin to separate. Hand and foot prints can be seen. The fetus can hear sounds and move in response, or even by increasing the heart rate. Sometimes the fetus makes jerky movements if it hiccups.
The fetus weighs about 750 g and measures about 30 centimeters at the end of the sixth month. With intensive care, a premature baby could live past 23 weeks.
5. Transition: seventh month of pregnancy
The fetus continues to mature and develop more and more fat deposits throughout its body. The position of the fetus often changes and may even move in response to certain sounds, lights, or pain. Hearing is fully developed and amniotic fluid also begins to decrease in the seventh month. The chances of survival of the baby from the seventh month are almost 100%.
At the end of the seventh month, the baby is approximately more than 40 centimeters long and already weighs about 1 kg.
6. Third trimester
The third trimester helps the fetus prepare for birth. Towards the end of pregnancy, the fetus gains weight at a very rapid rate. This body fat will help the baby to survive, also after birth.
Although popular culture only indicates nine months of pregnancy, it can be one month more; a healthy pregnancy lasts up to ten months. The typical pregnancy has a period of 40 weeks.
The doctor will watch more closely as the due date approaches. If you are more than two weeks past your due date and labor is not starting naturally, induction may be started; the doctor may recommend medications to induce labor and deliver the baby.
6.1. eighth month of pregnancy
The fetus continues to grow and develop and more kicks can be felt. The brain is developing rapidly and the fetus can see and hear. The fetus is also accumulating more body fat. Most of the internal systems are well formed, but the lungs may not be fully mature yet.
The fetus measures between 45 and 50 cm and gains approximately an average of 225 g per week
6.2. 9th month of pregnancy
The lungs are almost or fully mature. The fetus can move its head, close its eyes, react to sound, light and touch. Their muscles have developed, they can even blink and grasp.
When the baby is 37 weeks, it is considered full term. His brain and her body are ready to live outside the womb. The baby can weigh around 3.2 kg and be between 45 and 53 cm long.
6.3. tenth month of pregnancy
From this moment the delivery is imminent. As the fetus moves into the birthing position, less movement may be felt in the uterus. The space is narrower and the uterus may be retracting to prepare for delivery. The person may also feel very uncomfortable as the baby moves down the pelvis.