Brief SUMMARY of the THOUGHT of EPICURUS of Samos

Image: Filosofia & Co
In this lesson from a TEACHER, we will do a brief summary of the thought of Epicurus of Samos (341 a. C. - Athens, 270 BC C.), a Greek philosopher who founded the school known as "The garden", in Athens, a place where everyone, women, prostitutes and slaves, was allowed to enter school, something very unusual in its time. Epicurus will defend a philosophy based on the search for pleasure, warning, that this search must be moderate and directed by reason. Happiness consists, then, in the prudent administration of pleasures and pains, ataraxia or imperturbability of mind and friendship. If you want to know more about Epicureanism, continue reading this article.
Yes OK Epicurus of Samos defends a philosophy based on the pursuit of pleasure, he will emphasize the need to control pleasure, to know how to administer it, in the same way as pain. The philosopher would affirm that fatality, destiny, does not govern the nature and life of human beings, but chance. Otherwise, there would be no room for freedom, and therefore no room for hedonism, the name given to philosophical doctrine based on
pursuit of pleasure. But unlike other hedonistic thinkers, like Aristippus, who defended the pursuit of all pleasures, especially physical and immediate pleasure, Epicurus, bet on a rational pleasure, more moderate. It is a pleasure, therefore, intelligent.All living beings, affirms the philosopher, seek pleasure and turn away from pain. But it warns of the need to avoid excesses in order to avoid future evils. Furthermore, it places the pleasures of the spirit above the bodily ones. The supreme pleasure is intellectual. The ideal state is the ataraxia, in greek ἀταραξία.
Pleasure is the good first. It is the beginning of all likes and dislikes. It is the absence of pain in the body and restlessness in the soul.
Epicurus denounces excesses, but also abstinence, defending the middle ground, moderation, both in physical pleasures, as in the spiritual ones, making use of philosophy, which is understood by the thinker, as a means to help find the happiness.
Philosophy is an activity that with speeches and reasoning seeks a happy life.
The teachings of Epicurus have reached our days through texts such as By rerum natura, from Lucretius, is an exposition of the teachings of Epicurus. We also find the trace of his thought in fragments of Diogenes Laertius, among others.
The philosophy of Epicurus is totally opposite to Plato's by denying the existence of a supersensible reality and affirming that there is no other reality than the sensible world, which is made up of atoms, and by showing a deep rejection of political activities. Happiness is not in the polis, but in self-sufficiency, ataraxia, simplicity, moderation and friendly relationships.

Image: Slideshare
We continue this summary of the thought of Epicurus to speak of the canonical philosophy of this thinker. We said that the canonical is the part of philosophy that examines the way we know and the way to distinguish what is true from what is false. As well, Epicurus affirms that the basis of all knowledge is sensation. This is produced from the images of things, which are perceived by the senses. The human being reacts to sensation, either with pleasure, or with pain, which generates some feelings. These feelings constitute the foundation of morality, according to the philosopher.
There are no innate ideas, but "general ideas", which are produced by the repetition of different sensations that are recorded in the memory. But only if these sensations are clear enough can they serve as a foundation for morality, otherwise, the human being would inevitably fall into error.
Get used to thinking that death for us is nothing, because all good and all evil reside in sensations, and precisely death consists in being deprived of sensation. Therefore, the right conviction that death is nothing to us makes the mortality of life pleasant to us; not because it adds an indefinite time, but because it deprives us of an inordinate desire for immortality.
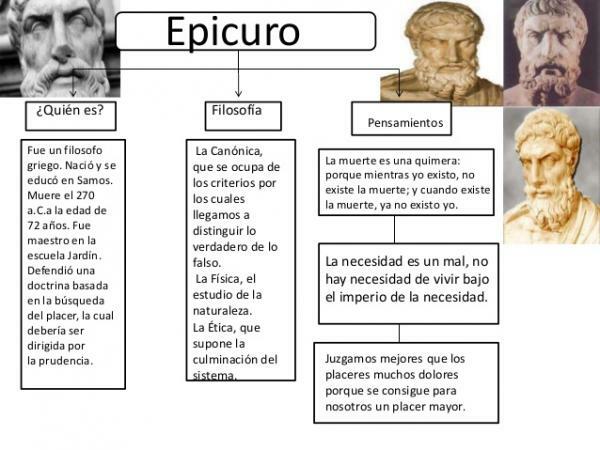
Image: Slideshare
Epicurus opposes Platonic dualism, by affirming that only the sensible world exists and denying the reality of the world of ideas. Reality, says the thinker, is constituted by atoms or extensive elements, with a weight and a shape, and by the vacuum, which would be the space through which these atoms fluctuate. Combined with each other, these atoms give rise to all the things that exist in the world.
The human being himself is made up of atoms, just like his soul, which, like the body, is material, therefore, it also dies with the body. Atoms are eternal, and therefore reality is also. There is neither a beginning nor an end.
"Of course everything was always as it is now, and will always be the same."
The difference between the atomimo of Epicurus and that ofDemocritus, is that the first introduces the random in the movement of atoms, thus leaving room for Liberty, without which the hedonism.
And we end this summary of Epicurus's thought to talk about the ethics of his thought. Every purpose in the thought of Epicurus is ethics and philosophy, constitutes a tool to achieve happiness, understood as autonomy or autarkeia and imperturbability of mind or ataraxia.
That no one, while young, be reluctant to philosophize, nor, when they grow old, tire of philosophizing. Because, to achieve soul health, he is never too old or too young.
To be happy, the human being must avoid fear and the accumulation of material goods. There is no need to fear the gods, nor failure, nor pain, nor death. It is totally absurd and irrational and has no foundation.
Thus, death is not real neither for the living nor for the dead, since it is far from the former and, when it approaches the latter, they have already disappeared..

Image: Slideshare