What are the parts of the Sun and their characteristics
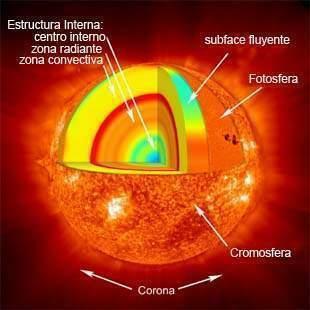
Image: EcuRed
The Sun is the star that illuminates and warms the Earth, located about 30,000 light-years from the center of the Galaxy. It occupies a central place in the Solar System and is composed mainly of the gases helium and hydrogen, with a center that is a large nuclear reactor whose temperature reaches at least 14 million degrees. Next, in this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we are going to carry out a study so that you can discover what are the parts of the sun and their characteristics.
The solar diameter is around 1,392,000 km, with a mass that is 330,000 times that of Earth and 745 times that of all the planets together, and a volume that is 1,300,000 that of our planet. In the Sun, the heat is so high that the material is in a plasma state, separated into ions and electrons. This is known as the fourth state of matter.
The composition of the sun is mainly hydrogen and helium, there are small amounts of heavy metals such as nickel, oxygen, iron, chromium, calcium, carbon, sulfur, neon, silicon and magnesium. It constantly emits a stream of charged particles into space, called
solar wind. Its force is not constant, since it changes depending on the activity of the Sun, and it reacts with the Earth's magnetic field producing what is known as auroras: boreal and austral.When conducting a study of which are the parts of the Sun and their characteristics, we must distinguish between the outermost area, where we find the photosphere,chromosphere Y Crown, and the innermost, with the core,radiative zone Y convective.
In this other lesson we discover you where the sun rises and where it sets.

Image: Slideshare
Within the outer solar zone, several parts must be distinguished:
- Photosphere: It is the shiny surface of the Sun, made up of millions of granules each measuring a few hundred kilometers in diameter. The solar surface persistently changes in appearance as the granules they have an approximate life of about ten minutes. Huge jets of gas are projected from the photosphere called spicules. These can reach a diameter of 15,000 kilometers, although they only remain for a few minutes.
- Chromosphere: It is located above the photosphere and is reddish in color, made up mostly of hydrogen. Masses of fiery hydrogen shoot out of this, which is called bumps, that emanate into the outermost part of the Sun's atmosphere, and have an average length of 100,000 km. Some can stay for weeks.
- Crown: It is the outermost part of the solar atmosphere, composed of hydrogen gas in a tenuous state and at a high temperature. In this solar flares are produced, which are a magnetic phenomenon that emits a large amount of charged particles and radiation.
As a curiosity, in this other lesson you will discover what are the planets closest to the Sun.



