Parts of the human cell
All living things are made up of cells.. We find them forming part of unicellular and multicellular living beings, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Our tissues and organs are made up of at least two hundred different cells. There is a main classification of cells: the most primitive and simple are known as prokaryotic cells, they are found Forming part of microscopic single-celled organisms known as bacteria, these cells do not possess membranous organelles or core.
On the other hand, we find eukaryotic cells, more evolved, have DNA within a nucleus and membranous organelles specialized in various functions. Plants are made up of plant cells, which vary greatly from cells found in animals. In this lesson from a Teacher we will tell you what are the parts of the human cell.
When speaking of the cells of the human body, reference is made specifically to the animal eukaryotic cells. Let's see what are the parts of the human cell and their functions.
The cells belonging to the human body have a size that can range from 10 to 30 micrometers in diameter. diameter, have various shapes and structures, the shape is associated with the function that the cell.
Let's start with the structures common to all cells such as the cell membrane, the cytoplasm and the genetic material, which, with the exception of the prokaryotic cells, in eukaryotes it is found within a nucleus, separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear envelope or membrane.
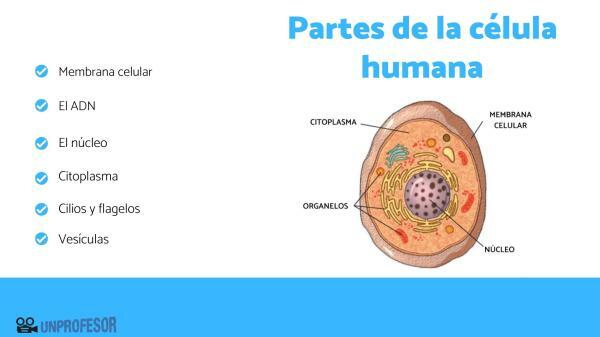
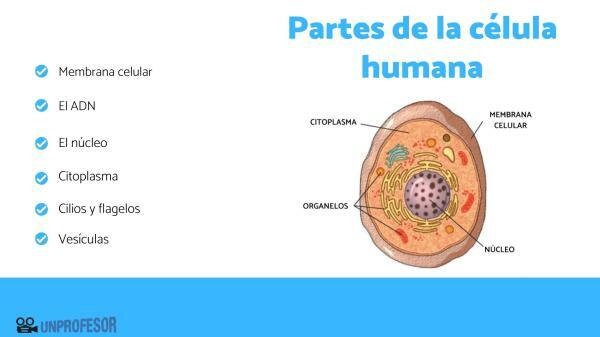
The cell parts human are as follows:
- Cellular membrane: It is essential to constrain the interior from the exterior of the cell and defines it as a separate entity from its surroundings. The membrane regulates the entry and exit of various substances into and out of the cell. In eukaryotic cells the membrane also defines compartments and organelles. Its structure is formed by a double layer of phospholipids and proteins, cholesterol and some glycolipids. The membrane is a fluid and dynamic structure, it has the ability to mobilize its structures such as lipids and proteins, which is why it is known as a "fluid mosaic" model.
- The DNA: It is the hereditary material that contains the information to direct the life of the cell. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid,
- The nucleus: Found only in eukaryotic cells, it is a large body, often spherical in shape. It is surrounded by a membrane, which separates it from the cell interior, but in turn, it has pores to allow the passage of substances from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and vice versa. Inside the nucleus we find the genetic material or DNA in the form of chromosomes or chromatin. There are cells in the human body that do not have a nucleus, an example of which are red blood cells, and there are human cells that have two nuclei, examples of which are cells of liver tissue or cartilaginous.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, in addition to containing the cytosol, which is a mixture of substances dissolved in an aqueous medium, has the organelles and the cytoskeleton. We can imagine the cytoskeleton as a web of proteins that resembles a spider's web, giving the cell its shape and directing the movements that occur within it.
- Cilia and flagella: Most cells in the human body have cilia or microvilli that fulfill various functions: they allow movement of gametes in the reproductive system, clean the respiratory tract, allow absorption of substances in the digestive system, etc The flagellum is a structure similar to a whip-shaped tail that allows the movement of cells in aqueous media. In the case of human cells we can mention the sperm.
- Vesicles: They fulfill various functions, participate in the incorporation of various substances into the interior of the cell by invagination of the plasma membrane, store or digest products of disposal. Some form from cell membranes, others in organelles such as the Golgi apparatus and the rough endoplasmic reticulum.