12 stages of Ancient EGYPT

Ancient Egypt is one of the most important cultures of the Ancient Age, being one of the civilizations that was active for the longest years, and forming an important part of the evolution of classical populations. The history of Egypt is long and complex, and to understand its evolution in this lesson from a Teacher we must talk about the stages of Ancient Egypt.
Index
- What are the stages of Ancient Egypt: chronologically
- Predynastic period, the first of the stages of Ancient Egypt
- early dynastic period
- Archaic Period, another of the stages of Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Egypt Period
- first intermediate period
- middle kingdom
- Second Intermediate Period
- new kingdom
- Third Intermediate Period
- late period
- Hellenistic or Ptolemaic Period
- Roman Period of Ancient Egypt: the last of the stages
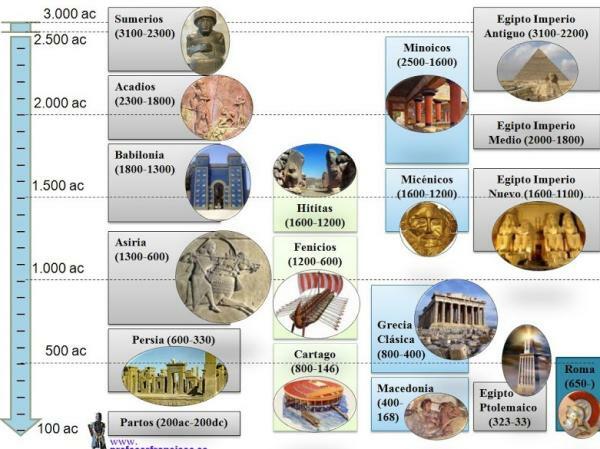
What are the stages of Ancient Egypt: chronologically.
Here is a review of the stages of ancient egypt divided chronologically:
- Predynastic period: between 5500 a. c. and 3300 B.C. C.
- Early dynastic period: between 3300 a. c. and 3050 B.C. C.
- Archaic Period: between the years 3050 a. c. and 2890 B.C. c.
- Period of Ancient Egypt: years 2686 a. c. and 2181 B.C. c.
- First intermediate period: between 2160 a. c. and 2,055 a. c.
- Middle Kingdom: years 2050 a. c. and 1740 B.C. c.
- Second Intermediate Period: years 1650 a. c. and 1550 B.C. c.
- New Kingdom: years 1550 a. c. and 1070 B.C. c.
- Third Intermediate Period: between 1070 a. c. and 664 B.C. C.
- Late Period: between 664 a. c. and 332 B.C. c.
- Hellenistic or Ptolemaic Period: years 332 a. c. and 30 a.m. c.
- Roman period: between 30 a. c. and 640 AD c.
Predynastic period, the first of the stages of Ancient Egypt.
The first of the stages of Ancient Egypt is known as predynastic Period, being called that way because it happened before the first dynasties arising from the unification of Egypt. Regarding its chronology, we can place it between 5500 B.C. c. and 3300 B.C. C.., beginning with the arrival of the first settlers to the Nile, since they were looking for a source of water to be able to form a town.
This period is framed within the Chalcolithic or Copper Age, being, therefore, a time in which writing was not yet available, and as a result the sources are archaeological and more complicated to obtain.
The population of this period were the first sedentary, achieving this through the discovery of the agriculture and livestock. There were many cultures that formed this land, grouping together in the so-called nomos, and forming two great kingdoms that would be Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt.

early dynastic period.
We continue to know the stages of Ancient Egypt to talk about the protodynastic period, a period little documented, and even in many sources it tends not to be used because of how similar it is to predynastic. Located between the 3300 B.C. c. and 3050 B.C. C.., is also called as Dynasty 0, Late Predynastic or Naqada III Period, being basically the final moment of the period before the dynasties.
In this period is when the first big cities are born of Egypt, some of which would remain for centuries, such as Nubet or Nejeb. Being the majority of these cities in Upper Egypt, where the first pharaohs founded huge cities to show their power, and how evolved they were compared to other territories.
The first pharaohs appear at this time and, therefore, this period is considered as dynasty 0, being linked to the god Horus, one of the Egyptian gods more important. They were rulers of great chiefdoms, and they commanded the first great armies of the time.
Archaic Period, another of the stages of Ancient Egypt.
The Archaic Period of Ancient Egypt took place between the years 3050 a. c. and 2890 B.C. c., being the moment in which many of the elements that define Egypt are forged and for which many historians mark the emergence of the true Ancient Egypt.
At the time this stage begins, Egypt was divided in two, being Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. We are not sure of the events that brought about the union of both regions, but we do know that the first pharaohs were in charge of unifying the two areas so that Egypt emerged as a great state territorial.
During this stage Egypt was comprised between the first cataract of the Nile and up to the Mediterranean Sea, being a huge expanse of land ruled by the pharaohs and whose capital was placed in Tinis, being the reason why this period is also known as Tinita Period.
During this period there was the rule of the 1st and 2nd dynasty, being considered as the founders of Egypt as such. These rulers were in charge of forming many of the bases of the Egyptian state, such as the hieroglyphics or relations with the states of the environment.

Period of Ancient Egypt.
The Ancient Period of Ancient Egypt is framed between the years 2686 BC c. and 2181 B.C. c., being considered as one of the periods of greater prosperity economy and stability of all Egyptian history. This period was marked by the change of capital to memphis, being where the first pyramids began to be created by order of the pharaohs of the time.
The pharaohs of the Ancient Period were part of the 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th dynasties all of them being dynasties with a strong centralization, in which the pharaoh as god in the world was able to make all the decisions.
At the end of the period, the high clergy begins to have greater power due to the increasing relevance of religion, achieving important positions and having a lot of political relevance. At this time the nomarchs also arose, being local governors who in later periods would have a lot of power.

Image: YouTube
First intermediate period.
The first intermediate period is another of the stages of Ancient Egypt. Between 2160 B.C. c. and 2,055 a. c. the so-called first intermediate period of Egyptian history took place, being so called for being a period marked by great changes, and which, therefore, does not correspond to the characteristics of any other stage. The dynasties of this period were from the VII to the IX, being weaker than that of the previous period.
The growing power of the rulers made Egypt was decentralizing, Pharaoh having less and less power, and causing numerous conflicts and confrontations between those who wanted to centralize power again against those regions that wanted to have more autonomy.
Others big changes of this period were:
- The rise of Osiris as the main god
- The rise of the middle classes
- The growth of literary texts
- The birth of some of the greatest cities

Middle Empire.
The Middle Kingdom took place between the years 2050 a. c. and 1740 B.C. c., being marked by the return to centralization, and the return of power to the pharaoh, which he had lost during the previous stage.
The pharaohs of the period, belonging to the 11th and 12th dynasties They are considered to be some of the most important and powerful in Egyptian history. For the first time in centuries, the Egyptians began to look beyond their borders, attacking nearby regions to expand Egypt's power and extent.
In the last years of the Middle Kingdom the hyksos attacked the egyptian regions from the Near East, taking almost all of Egypt in a few years and thereby bringing down the Middle Kingdom.

Second Intermediate Period.
The Second Intermediate Period took place between the years 1650 B.C. c. and 1550 B.C. C.., Being a period in which the nation fragmented due to the attack of the Hyksos, causing Egypt to enter a hard crisis political, territorial and economic.
Over the years, the Egyptian rulers of Thebes begin a independence process against the hicsos, declaring the 17th dynasty, and uniting the Egyptian people against foreign peoples. At the end of the period, Emperor Ahmose manages to defeat the Hyksos and regain control of Egypt.
New Kingdom.
The New Kingdom is another of the stages of Ancient Egypt. It took place between years 1550 a. c. and 1070 B.C. c., being marked by a process of extension never seen before in Egypt and, therefore, being one of the most important periods in Egyptian history. The dynasties that ruled this period were from the XVIII to the XX, belonging to these some of the most important pharaohs in history.
After defeating the Hicsas, pharaoh Ahmose began campaigns to expand the territory of Egypt, beginning these attacks on Asia and Nubia. Subsequent pharaohs continued Ahmose's actions, as they realized that expansion helped improve trade, opening up new routes with Asia and the Mediterranean nations.
For centuries, the Egyptians They faced numerous Asian peoples, such as the Hittites, but also other European tribes such as the Sea Peoples, who would later take territories in Greece. Thanks to these battles, the Egyptians reached their maximum extension with territories in Syria, Canaan, all Nubia and an extension that reached as far as the Euphrates.
At the end of this period, Egypt was in serious trouble, caused by continuous attacks by the Sea Peoples and Libyans, but also by the corruption of Egypt itself. All these events led to a new division of the Egyptians.

Third Intermediate Period.
The last of the intermediate periods took place between 1070 B.C. c. and 664 B.C. c., being a stage marked by a great division of Egypt, causing that the entire region was divided in two: Upper Egypt with its capital in Thebes and Lower Egypt with its capital in Tanis.
Throughout this stage, the two regions had numerous confrontations with each other, but they also had to face other nations, such as when they were conquered by the Assyrians.
This stage was marked by a huge weakness of the region, being one of the lowest moments in Egyptian history, completely changing society and the economy and ceasing to be the great world power.
Late Period.
Located between the 664 B.C. c. and 332 B.C. c., is considered by many as the last stage of total independence by the Egyptians. The arrival of Pharaoh Psamético I brought an attempt to reunify the entire region, with changes in trade and a great centralization in Memphis.
The attempts to strengthen Egypt do not work because of the great power of the nearby empires, which are too powerful for the Egyptians, and are very interested in taking their land. Finally, the Persians they took all Egypt, transforming it into a satrapy, that is, into a province of the Persians.
Egypt remained in this position until the Macedonian general Alexander the Great attacked the region, conquering it and carrying the Greek ideals, transforming Egypt into a Hellenistic state.
Hellenistic or Ptolemaic period.
The Hellenistic or Ptolemaic period is one of the most outstanding stages of Ancient Egypt. It took place between years 332 a. c. and 30 a.m. c., being the time in which the power of Egypt was in the hands of Greek descendants.
At first, Egypt passed to the Macedonian Empire of Alexander the Great, but after his death his conquests were divided among his trusted men, Egypt passing into the hands of Ptolemy. For years, his successors kept the name of Ptolemy, which is why this period is called Ptolemaic.
Over the years, the region has less and less power, becoming one less region at the international level, and having more and more greater relevance the influence of the Romans.
Finally, after the death of Cleopatra VII, the dynasty of the pharaohs disappears and Egypt becomes a Roman province.

Roman Period of Ancient Egypt: the last of the stages.
To conclude this lesson on the stages of ancient Egypt, we must talk about the last of these stages being one in which little of the influence of Egypt remained.
The last period is located between 30 a. c. and 640 AD c., being the period in which Egypt was a Roman province. The loss of independence took place after Octavio entered Alexandria, from where he took control of the region, which became a Roman province.
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Egypt remained a province of the Byzantine Empire, who were the successors of the Romans. Finally in 640 AD. C., Egypt was conquered by Arab peoples, thus ending the last vestiges of Ancient Egypt.

If you want to read more articles similar to Stages of Ancient Egypt, we recommend that you enter our category of History.
Bibliography
- Grimal, N. (2004). history of ancient egypt (Vol. 184). AKAL Editions.
- Shaw, I. (2010). History of ancient Egypt. language, 2, 70.
- Alcaine, M. R. L. (2010). The Ancient Egyptian Kingdom: Tinite Stage, Predynastic and III-IV Dynasties. History Class Magazine, (3), 31.


