3 most important ROMAN philosophers

Lucretius, Seneca, Epictetus, Marcus Aurelius or Cicero They are some of the most important Roman philosophers. At unPROFESOR.com we delve into the Roman philosophy and its main representatives.
Roman philosophy always tends to be approached as if it were an appendix to Greek philosophy, specifically Hellenistic philosophy. However, if we stop to think about philosophy as the self-awareness that a civilization or an era has about itself, then Roman philosophy has its own entity since the Roman philosophers did reflect on the historical moment in which they lived and what their role was in the world.
In this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we present to you the most important roman philosophers and what was his contribution to Roman thought and Western philosophy.
Index
- Contributions of Roman philosophers to the history of philosophy
- Lucretius, one of the most important Roman philosophers
- Lucius Anneeus Seneca
- Marcus Tullius Cicero
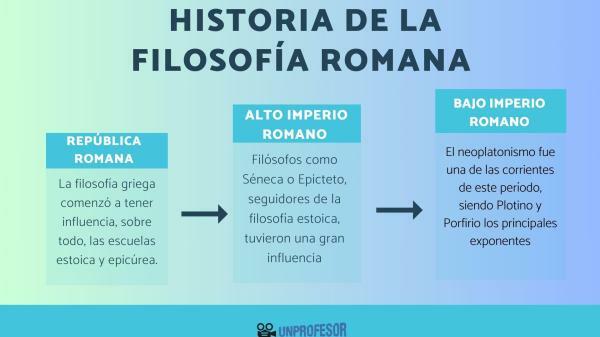
Contributions of Roman philosophers to the history of philosophy.
Before starting to list the most important Roman philosophers, it is essential to know why these thinkers are so relevant in the history of our thought. The Romans were not alien to the search for wisdom desired by all civilizations. And, although few theoretical texts have been preserved from before the 1st century BC, we do know that philosophy was also a matter in which the intellectuals of Roman times devoted themselves.
Thus, although they were not overly concerned with theories about the origin and constitution of the universe, Roman thinkers did make a important contribution in terms of morality, ethics and the philosophy of behavior. For them, philosophy was useful as it constituted a practical guide for life. A thought that philosophers such as Cicero, Seneca and Lucretius delved into, considering the moral reflections of Cato the Censor as one of the first contributions to philosophy.
Be that as it may, it is undeniable that the academic schools that the Greek philosophers brought to Rome, such as the school of Stoicism or the Peripatetic of Athens, had a great influence and led the Roman world to fully delve into Greek philosophy and disseminate it. by being the main translators of Greek philosophical texts into Latin.
Here we leave you a summary of the history of Roman philosophy.
Lucretius, one of the most important Roman philosophers.
The most important roman philosophers They fall within a series of philosophical schools, some with Hellenizing roots. Among the most prominent figures of Roman philosophy we can highlight Lucretius.
Titus Lucretius Caro (c. 99 a. DC. 55 a. C.) was a Roman poet and philosopher belonging to the school of epicureans. This school sought happiness, considering that the supreme good for human beings was pleasure, that is, absence of pain and detachment from matters concerning the State, in addition to a critical attitude towards traditions.
The apolitical character, so far removed from the idiosyncrasy of the Roman world, was one of the factors that prevented Epicureanism from taking root in Rome beyond the figure of Lucretius.
Here we discover what were the main contributions of Lucretius.

Lucius Anneus Seneca.
Seneca (Córdoba 4, Rome 65 AD. C.) constitutes one of the great figures of the Roman Stoic school, a school that arrived in Rome from Greece and whose first followers were Roman philosophers such as Panecio of Rhodes (184-110 BC) C.) and Poseidonium of Apamea (135-51 BC) C.), Cicero's teacher.
He stoicism was a philosophical doctrine that indicated that the Universe is animated by a divine flame called “Logos”, the ultimate purpose of life being Virtue understood as living in accordance with the laws of nature. Seneca is the most prominent figure of the second era of Stoicism.
In addition to being a philosopher, Seneca was a great writer and he cultivated genres such as tragedy and satire. His philosophical ideas claimed the stoic side of life and firmness of spirit: joy, prudence and will, despising wealth and encouraging its use in a beneficial way. He also postulated the dominion of the spirit over the reverses of fortune, praising virtue as the highest good of the human being and rejecting anguish, anger and boredom.
For Seneca the soul was superior to the body and God was a kind of divine spirit or mind that revived in man. These ideas led to Seneca being admired by ancient Christianity and medieval philosophers. by touching on moral issues regarding the dignity of man and advocating a way of life of high morality.
Epictetus (50-130 d. C.), Flavius Arrian or Marcus Aurelius (161-218 AD. C.) are other Roman philosophers who followed the doctrines of stoic school.

Marcus Tullius Cicero.
Marcus Tullius Cicero (106-43 BC) C.) is another of the most important Roman philosophers. He was the introducer of Greek philosophical doctrines in Rome by synthesizing the original works and making them more accessible to the translate them from Greek to Latin. It must be taken into account that only an educated elite knew Greek and it was necessary to create a Latin philosophical terminology.
Cicero had a predilection for Plato's philosophy, presenting two stages in his philosophical production. A first stage in which, after his exile, Cicero writes with the hope that the old republican regime will be recovered (“De re publica”, “De Legibus”) and a second phase in which the ethical, moral or religious treaties (“Paradoxa Stoicorum”, “Academica” or “De finibus bonorum et malorum”, among others).
As far as his ideology is concerned, Cicero is considered the first philosopher to propose a philosophy of progress and hope. Thus, Cicero estimates that thought advances towards infinite progress towards the Truth. Happiness would be the search for that truth and not its possession, something totally impossible.
Virtue lies in achieving happiness by reconciling respect for the body and everything that belongs to it. Cicero is a humanist and reworks concepts such as culture, love, friendship, virtue or education from the perspective of Greek philanthropy and paideia. Cicero advocated mutual respect among human beings, considering that we all possess a divine spark. That humanism of Cicero continues to be one of the ideals of Western civilization.

If you want to read more articles similar to Most important Roman philosophers, we recommend that you enter our category of Philosophy.
Bibliography
- LISI, Francisco L.; OF MADRID, Carlos III University. Roman philosophical literature. Notebooks of Greek and Latin Literature, 2005, vol. 5 p. 134-155.
- PINA POLO, Francisco, Marco Tulio Cicero. Ariel, 2005.
- UTCHENKO, Lvovich. Cicero and his time. AKAL Editions, 1987.
- WILSON, Emily. Seneca. Rialp Editions, 2016.
- ZAMBRANO, María; SENECA, Lucius Annaeus. The living thought of Seneca. Madrid: Cátedra, 1987.



