What were the COURTS of Cádiz

The Contemporary Age is known for being the period where the great liberal movements appeared and democratic, thus giving rise to the courts, where the people were represented and could have relevance in decision-making. decisions. In the case of Spain, The first opening towards democracy was the Cortes of Cádiz, created when the Spanish territory was under the French yoke during the period known as the Spanish War of Independence. Due to the importance of this event, it is very important to talk about it, and that is why in this lesson from a Teacher we must talk about What were the Cortes of Cádiz.
Index
- The Cortes of Cádiz: short summary
- How did the Court of Cádiz emerge? Historic context
- First decrees of the Cortes of Cádiz
- What was done in the Cortes of Cádiz?
- The Constitution of 1812
- Dissolution and end of the Cortes of Cadiz
The Cortes of Cádiz: short summary.
The Cortes of Cádiz were a constituent and legislative assembly created to fill the Spanish power vacuum caused by
Napoleon's occupation of Spain during 1810. These Cortes met between 1810 and 1814, serving as a display of patriotism and rejection of the French occupation.The Cortes of Cádiz were convened by the Supreme Central Board of Seville, which denied the sovereignty of King Joseph I, imposed by his brother Napoleon. The Central Board of Seville was replaced by the Regency Council of Spain and the Indies as the governing body, being in charge of creating the Cortes.
The Cortes of Cádiz dealt with many reforms, but the main one was the creation of the liberal constitution which created the first rights of this kind for Spanish society. Therefore we can say that the constitution of the Cortes of Cádiz is one of the most important events of our history.
How did the Court of Cádiz emerge? Historic context.
At the beginning of the 19th century, Europe was in a situation of conflict, since the French emperor Napoleon Bonaparte, he sought to conquer all of Europe to bring his liberal ideas to all places. In this situation, Napoleon he sought the support of the Spanish to confront the English, finding it in King Charles IV, who let French troops enter Spain, waiting for them to attack Portugal, this being the great alliance of the United Kingdom. What Carlos did not expect is that these troops would take Spain by force.
In March 1808, the Aranjuez riot, forcing the abdication of King Charles IV, and allowing the accession of Ferdinand VII to the throne. Seeing this, Napoleon thought that the Spanish crown was in serious crisis, and that they were not good allies. Napoleon forced Ferdinand VII to abdicate to his father, and after that Charles IV had to abdicate to Napoleon. These episodes, known as the Bayonne abdications, ended with the coronation as king of Spain of Napoleon's brother, Joseph Bonaparte, also known as Joseph I.
The Spanish decided not to obey Joseph I, since they considered him to be a non-legitimate authority, even giving him a hurtful nickname such as "Pepe Bottle." In this situation the War of Independence, where the Spaniards fought against the French to end the invasion, organizing themselves in the well-known local meetings.
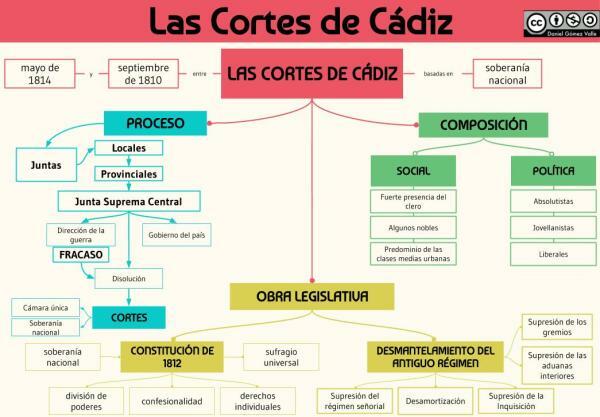
Image: Spanish history blog
First decrees of the Cortes of Cádiz.
In 1810 The first convocation of the Cortes of Cádiz took place, being convened by the Central Board. The Spanish nation had been filled with local and provincial boards that tried to fill the power vacuum, and all of them were centralized in the Central Board. For this reason, when convening the Cortes of Cádiz, each of the boards elected representatives, who would be in charge of representing each province in the convened Cortes.
When the Cortes was convened, most of the elected deputies were bourgeois, since they were the closest to liberal ideas, as they benefited the most from them. The bourgeoisie were educated, knew liberal ideas, and had more time than the rest of the workers, making them ideal to represent the population in the Cortes.
of the Cortes of Cádiz, taking place on the so-called island of León. Even with this, the meetings of the Cortes eventually moved to the city of Cádiz, although it changed depending on the possible attacks that the city suffered from the French.
In the first meetings of the Cortes of Cádiz, several of the main elements that should characterize those meetings were declared. It was considered that the Cortes were the ones that represented and controlled the birth sovereignty, until the return of the King Ferdinand VII, whom they considered a legitimate king. The Cortes recognized the separation of powers, saying that they would be the representatives of the legislative power, while the king would occupy the executive power when he could return.
The first sessions of the Cortes served to lay two important foundations:
- That King Ferdinand VII would continue to be the monarch,
- That the Cortes should have greater power than before the war.
The idea was to go towards a mixed system, or what we currently know as parliamentary monarchy.

Image: Slideshare
What was done in the Cortes of Cádiz?
The Cortes of Cádiz took advantage of the time, and in a short period they were able to extract a lot of renovations. The idea was to achieve important advances, and achieve rights that were not yet available.
We must keep in mind that not all members of the Cortes had the same thoughts, and we may find various types of deputies:
- On the one hand there were those called liberals, who defended the ideas of the French Revolution and sought revolutionary reforms.
- Then there were the moderate, who sought reforms that would create a division of powers between the king and the Cortes.
- Lastly, there were the absolutists, who sought to maintain the absolute monarchy and estate society, not wanting changes of any kind.
Over time, The liberals were the great winners, in what is usually considered the first liberal revolution in Spain. Liberals sought to end all kinds of absolutism, and approve a Constitution that would allow us not to go backwards. Even with this, the deputies from other sides had to negotiate, so the results had elements of the 3 groups of people.
Between the first reforms of the Cortes of Cádiz we can find:
- Abolition of the manor regime
- Elimination of the Spanish Inquisition
- The end of the awards
- The confiscation of a large part of religious property.
Many of these elements occurred for the first time in Spanish territory, although they had already been present in other European regions with liberal processes.

The Constitution of 1812.
Without a doubt, the most important element of the Cortes of Cádiz was the creation of the Spanish Constitution of 1812, being known as the Pepa for having been approved in San José, and which is considered the first Constitution in the history of Spain.
The Constitution of 1812 was promulgated on March 19, 1812, at a time when Spain was still under the rule of the French. It was approved by representatives of all the provinces, although the American states had less participation due to the complexity of the distance from the peninsula.
Characteristics of the Constitution of 1812
The Constitution of 1812 is the first norm of this kind in the history of Spain, and therefore has a series of characteristics very important to understand the relevance it had. Therefore, some of the main characteristics of the Constitution of 1812 are the following:
- He speaks for the first time about sovereignty of the nation by the Spanish people. For many historians, this is when the concept of Spain as a nation was born.
- Recognizes the nationality of all Spaniards, both to those who lived in the Iberian Peninsula, and to all those who lived in the Spanish colonies in American territory. The loss of these elements shortly after is in part what is considered to have started the independence processes of Latin American nations.
- For the first time there is talk of a series of individual, political and civil liberties that all Spaniards should have. As the months passed, important rights such as freedom of the press were consolidated, which today we see as something basic, but which until that moment was not considered a right.
- It was announced for the first time separation of powers, so the king stopped being absolute and centralized the entire state in his figure. The idea was to move to a kind of parliamentary monarchy, in which the king would have executive power, while the Cortes would retain legislative power.
- It was recognized the figure of the king by the grace of God, but he no longer had all the power, being just another figure in Spanish politics. This is considered to have been a request from the absolutists, who, even with changes, wanted the idea of the king's divine origin to be maintained.
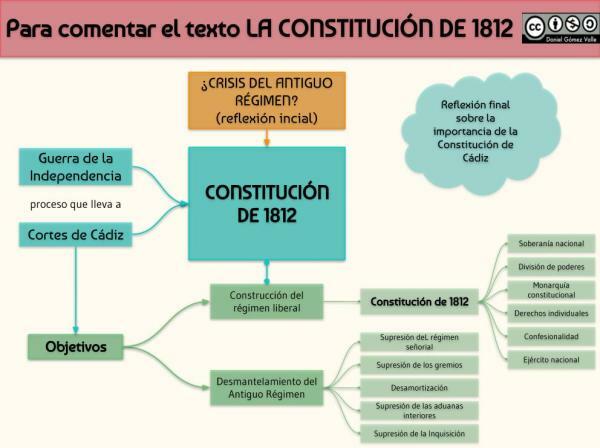
Image: Daniel and the fifteen
Dissolution and end of the Cortes of Cadiz.
To continue this lesson about the Cortes of Cádiz, we must talk about their dissolution, in order to understand what the end of one of the most important organizations in history was like Spanish.
In 1813, Napoleon's troops began to retreat due to pressure from the Spanish, who had been using guerrilla strategies for some time to stop French superiority. At the end of the year, and after numerous defeats on various fronts, Napoleon proposed the return of Ferdinand VII to the Spanish throne in exchange for peace.
In March 1814, King Ferdinand was liberated by the French and returned to Spain, being received with joy by the liberal Spaniards. At first, the monarch promised to maintain what was said in the Constitution, but two months after his arrival (and partly due to the manifesto of 70 absolutist deputies) annulled the Constitution of 1812. Along with this annulment, the dissolution of the Cortes, the imprisonment of the revolutionary liberals and the return to absolutism also took place. Being for this the end of the Cortes of Cádiz.
This entire act of Fernando VII to regain power took place in May 1814 with the publication of the Valencia Decree. In this decree the king proclaimed his divine origin, and renounced all actions of the Cortes of Cádiz as a Coup attempt to take power. It was with this decree that the Constitution of 1812, and a large part of the laws of the Cortes of Cádiz, were annulled.
Even so, the influence of the Cortes of Cádiz remained long after its dissolution, and therefore many of its reforms returned over time, marking the path for the following revolutionaries.
It could be said that with the Cortes of Cádiz Both national sovereignty and Spanish democracy were born.
If you want to read more articles similar to What were the Cortes of Cádiz, we recommend that you enter our category of History.
Bibliography
- Suarez, F. (1982). The Cortes of Cádiz (Vol. 10). Madrid: Rialp.
- Ledesma, M. Q. (1991). The Cortes of Cádiz and Spanish society. Yesterday, (1), 167-206.
- Enciso, I., & Alonso-Muñumer, I. AND. (1999). The Cortes of Cádiz (Vol. 72). Akal Editions.



