Macroeconomics: definition and examples

Economics is a very complex science, since it tries to analyze changing values that can be modified by many different elements. Its scope of study is so broad that it is usually divided into different economic branches, one of the most important being the so-called macroeconomics. For all this, today in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we are going to talk about the definition and examples of macroeconomics.
Macroeconomics is one of the many branches that make up the study of economics. It is the one in charge of studying the operation of the economy in a country as a whole. To do this, it uses a series of aggregate variables, including employment and the consumption of goods and services.
Therefore we can say that macroeconomics studies economic phenomena that happen within a state. But these phenomena must always be related to the consumer, since without their data we cannot get to have correct figures.
Its usefulness is based on the fact that by studying economic units, macroeconomics shows the evolution and economic growth that happens in a territory over a period of time.
Characteristics of macroeconomics
Macroeconomics has many more characteristics than those we have discussed, since it is one of the largest branches of the entire study of economics. Some of its characteristics are the following:
- Study the evolution of employment and unemployment rates.
- Study economic growth and inflation.
- Try to prevent economic crises.
- Create models of possible economic variants.
- Study the relationship between consumer and business.
- Find the total quantities of goods and services.

Image: Slideshare
The main objective of macroeconomics is the analysis of the economy of a country to seek economic growth through capital accumulation, trying prevent and avoid the various problems that arise in the economy of a state.
For the study of all this macroeconomics use three different variables that allow you to see the economic evolution, although with some caveats. These three variables are the following:
- Gross domestic product: Also called GDP, calculates the goods and services of a given country during a given period of time.
- Gross national product: Also called GNP, goods and services produced in the country during a period of time.
- Net national product: Also called PNN, it is the sum of all the investments of a country.

Image: Slideshare
Macroeconomics is a very broad branch, and therefore there are many issues that it deals with to achieve its objectives. For this reason, it is important to identify what these issues are and to know a small definition about them.
Economic growth
One of the main long-term objectives of macroeconomics, studies the rhythm of the production of goods and services. Through its study it is possible to understand why some countries grow faster than others.
Productivity
A factor that marks the economy, since high productivity increases wealth. Some of the factors that modify it are unemployment and technical improvement.
Business cycles
Analyze the reason for economic cycles, that is, the phases that a country's economy goes through. Existing more positive cycles and more negative cycles.
Unemployment
One of the main themes of macroeconomics. Study the evolution of unemployment, why it can increase or decrease over a period of time and the measures that can be taken to reduce it.
Inflation
The increase in the price of goods and services in a country is analyzed and how this affects well-being. For this reason, it is also in charge of studying deflation, which is the decrease in the price of goods and services.
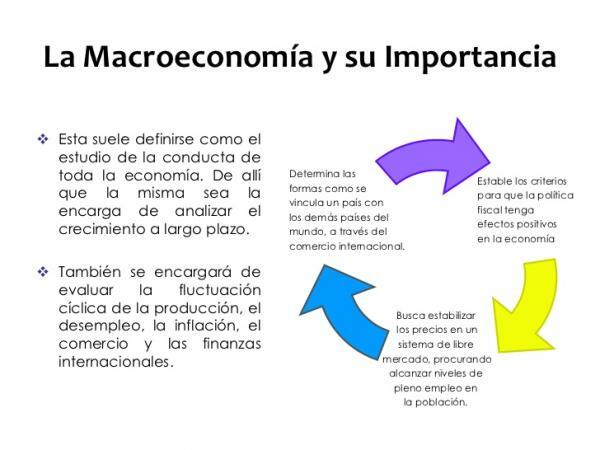
Image: Google Sites
To conclude this lesson on the definition and examples of macroeconomics, we must talk about some macroeconomics examples in order to fully understand what this branch of economics refers to.
It should be taken into account that due to the large number of topics that the examples are plotting are very numerous, being practically all the economic aspects that happen within a country and that affect to a great scale. Some examples are the following:
- Exports and imports of goods between countries.
- The creation of infrastructures.
- Work of companies and families.
- Evolution of a good during a certain time.
- Increase in the production of a good.
- The inflation of a product.
- The salaries of a company.