How is rain formed
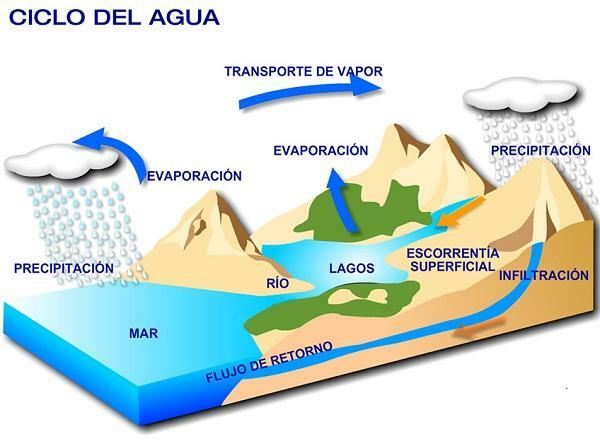
Image: Arkiplus
Within the climatological aspects, rain is one of the most interesting that there can be. Have you ever wondered how and why does it rain? Do you know the different types of rain that exist? Join us in this lesson from a TEACHER and discover in this summary for children on how rain is formed. In this way we will bring you closer to a very complex phenomenon that is of vital importance for life on our planet, as it helps in the fields of crops, in addition to cleaning our atmosphere. In addition, you will know the different types of rain that exist and the stages through which the water cycle passes.
Index
- The water cycle
- The formation of the rain
- The different types of rain
- The need for rain
The water cycle.
Before starting to talk about how rain is formed in this summary for children we must talk about the water cycle, since it is the essential element to understand later the subject that we are going to deal with in our lesson.
As we know, water on our planet runs through rivers, which end up flowing into the oceans. But not all the water that comes from the rivers ends up being expelled into the oceans in that way, because a large part is evaporated in the process, thus beginning the true water cycle.
The evaporation It can occur anywhere on the globe, that is, in oceans, lakes, rivers, land... and is produced by rising temperatures. Because of this, the water particles rise to the atmosphere where they are trapped in pockets of air, which form clouds.
An example of this can be seen when we get up early in the morning to go, for example, to school and we go through the fog, on many occasions the car then gets wet, that's because the fog is made up of particles of water.
In this other lesson from a TEACHER we will discover the different parts of a river and their characteristics.
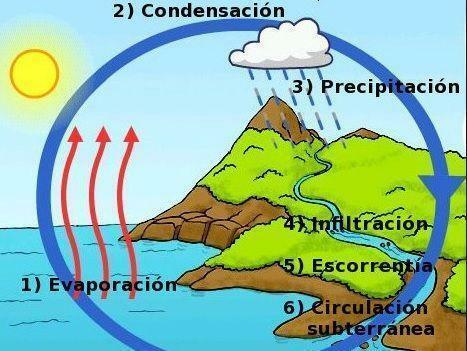
Image: Slideshare
The formation of the rain.
Continuing with our summary on how rain is formed, we started talking from the moment when the water particles have reached the atmosphere. More than one 10% of the Earth's total water, normally the particles are usually dispersed and will only precipitate to the ground if they are concentrated.
They tend to concentrate when a cold front hits the atmosphere which makes it have less retention of water particles and, therefore, it must expel a certain amount. This usually happens, for example, when a certain amount of clouds loaded with water particles arrives in the Andes and they come into relationship With the low temperatures on the tops, this causes the particles to condense and fall back to the ground in the form of rain. If, for example, the temperatures are minus zero degrees, the precipitation will be in the form of hail or snow.
Another way in which it can rain is when there is a large amount of dust particles, as for example happens many times in Spain. Have you ever wondered why it rains mud? This usually happens when there is a large amount of particles from the Sahara locked up in the atmosphere. This, when in contact with the water particles, causes them to condense, unite and go down to the earth brown drops of water, due to the large amount of dust belonging to the Sahara desert that was in her.
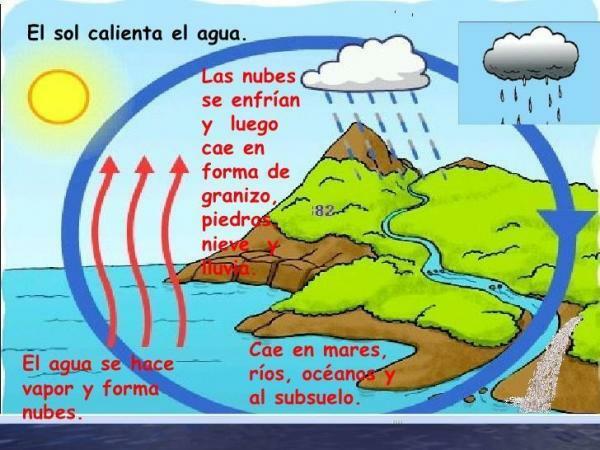
Image: Slideshare
The different types of rain.
As we have been talking throughout our summary of the formation of the rain, we know that a change in temperature in the atmosphere is sufficient To make large amounts of water precipitate back to the land or to the oceans, we will now mention three fundamental types of rains:
- Convection rain: it occurs when the lower layer of the atmosphere heats up when it comes into contact with the earth's surface, as the air begins to become lighter and causes the water particles that were inside to begin to precipitate. This is typical of warm areas, or we can also relate them to the typical summer storms such as those that exist in Spain, they are usually short in time, although sometimes a large amount of water falls, producing some damage.
- Orographic rain: it is the one mentioned in the previous point, when a mass of humid air collides with a mountain range, rises towards the top, if it runs into a body of water, it condenses it and produces rain.
- Cyclonal or frontal rain: It is typical of temperate latitudes and normally occurs when two air masses of different temperatures come into contact. These are the ones mentioned in many cases by the news when they talk about storms, as they are usually preceded by quite unstable weather.
The need for rain.
To conclude with our summary we must talk about the need of rain for human life, since water is essential for life on our planet, many of the chemical reactions that occur (if not all) occur in an aqueous medium.
In this way it is essential for the fields, as it is a natural way of watering the plants since supplies large amounts of water regularly. For this reason, the problem of greenhouse effect, as it has been shown that both the level of rainfall and the intervals are changing, causing our planet to be making it drier, that is why we must take care not to overload it, because rain is the only form of regeneration that our planet.
In addition to clean the atmosphere causing the dust particles in the air to go down and with it the level of allergies also goes down (because the Allergy-causing particles move through the air, if it rains from time to time the atmosphere is cleaned from these particles).
If you want to read more articles similar to How Rain Is Made - Summary for Children, we recommend that you enter our category of geology.



