Monopoly: definition and characteristics

Image: Economipedia
The economic markets They are in continuous movement, what today is a product with a large number of economic agents, tomorrow can become a market with a single producer. We live in a world where the economy is a highly discussed topic and where the word “monopoly” is heard more and more every day, so today in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we are going to talk about definition and characteristics of monopoly.
The first thing we need to understand in this lesson is what a monopoly is. Monopoly is a market failure, an imperfect form of market, in which a company is the only provider of a good or service. So people who want to get this good or service can only go to this seller to get it. The word monopoly comes from the Greek, from the terms "mono" (one) and "polein" (to sell), its meaning being that of a market in which only one sells.
The monopoly causes the sole supplier has full control of the product, being able to decide the price without having any type of control, and the quantity of production of the good or service. The type of monopoly can vary depending on different factors, but it is something we will talk about later.

Image: Slideshare
There are several causes that lead to the appearance of a monopoly, both political and economic. Some of the causes that are usually mentioned are the following:
- When the producer exclusively controls a productive value. That is, a company that has all the production capacity of a specific product, making it impossible for other companies to produce it.
- Patent granted to a single producer. What causes the seller to be the only one qualified to sell it, being the only one with the patent.
- The state controls the supply. The country is the only one that can produce the product, or only allows production to a specific company.
- Coexistence of economy of scale.
The characteristics of monopolies are easily traceable. In this lesson on the definition and characteristics of monopoly, we will now talk about what they are the main ones, the ones that most represent the monopolies. The characteristics are as follows:
- A single company that produces and sells a good / service.
- There are no substitute goods or services. That is, no product similar to the main one that can fulfill the same function.
- The number of buyers is large, so there is a high demand that could be used to make several companies profitable by taking care of the product in question.
- Very rigid barriers to market entry. It is difficult to access the market, so the main seller does not usually have competition, resulting in a monopoly. This can happen for various reasons, such as the existence of patents or licenses.
- The seller has the power to set the price, since buyers have no other possibility of where to buy, whatever the price.
- There is no perfect mobility of the factors of production.
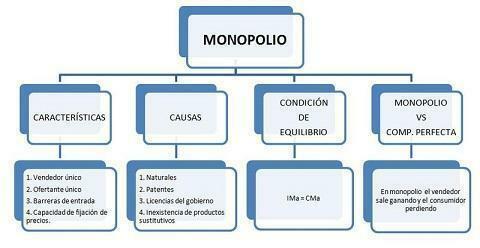
Image: Financial Encyclopedia
To conclude with this lesson on the definition and characteristics of monopoly, we are going to talk about the different types of monopoly What can we find. There are a wide variety of types of monopoly, some being much more common than others. The types of monopoly are as follows:
- Pure monopoly: When there is only one company in an industry. In the real economy it can only be seen when there is an activity carried out through a public concession.
- Artificial monopoly: In this monopoly, the producer uses some means to prevent more products from going to the market than his own.
- Natural monopoly: A company that carries out all the production required by the markets does so at a lower price than if there were more companies competing.
- Watertight: It is the monopoly in the production or sale of a good assumed by a State or granted to individuals in exchange for an income to the treasury.
- Oligopoly: It is a market in which there are a small number of companies that produce a good, which collaborate with each other to exercise power over the market and to increase prices.
- Duopoly:It is a type of oligopoly in which there are two companies that produce the same good.
- Poster: It is an informal agreement between two or more companies whose purpose is to eliminate competition in a certain market.
- Trust: The union of several companies that produce the same product in a single entity. In some countries laws have been created so that they cannot exist.



