Differences between republic and monarchy

Image: Sitapati
Throughout history they have developed various forms of government that they have anddifferent political and constitutional structures. Without a doubt, the republic and the monarchy correspond to one of the most opposite political models in the history of politics.
That is why in this section of a teacher we would like to address the main differences between these two forms of government. Find the differences between republic and monarchy They may seem like a very simple task, but all this will depend on the historical period in which we are situated and also on the different types of monarchies to which we refer. As all this could become very complex and the objective of this lesson is to make a comprehensive outline of the main differences between republic and monarchy, we will refer to the differences of the type of monarchy best known historically, the absolute.
As we have discussed in the introduction, there are different types of monarchies: in some, the monarch's power is absolute while, in others, the monarch's participation in government can be defined.
First of all, we are going to define the main types of existing monarchies, absolute monarchy, parliamentary monarchy and constitutional monarchy:
1. Absolute monarchy
The absolute monarchies characterize the Western European political model of century XVIII and that began at the end of the Middle Ages.
Here is a list of the main characteristics of an absolute monarchy:
- The kingdom of is of hereditary and lifetime character.
- The power of the monarch emanates from God and therefore his will is above the law.
- Concentration of power of the monarch in terms of competition judicial, executive and legislative.
- Wide bureaucracy and diplomacy who worked at court for the service of the king and the kingdom.
- Support for the monarch of the privileged groups, among them the most prominent nobility and the clergy.
- Centralized administration that would allow the collection of heavy taxes.
While it is true that absolute monarchies had their peak in the Western Europe of the Modern age. Even so, there are currently countries where this type of organization exists where the monarch has absolute power, such as Saudi Arabia Y Taste, among other.
2. Parliamentary monarchy
The parliamentary monarchiesare typical of current democratic countries, where the king as a figure of Head of state, exercises the power regulated by the parliament and the executive. To define in an informal way the form of government of a parliamentary monarchy, the phrase of '' the king reigns but he does not rule ''. An example of a parliamentary monarchy is the one we currently have in Spain.
Here is a list of the main ones characteristics of a parliamentary monarchy:
- It is considered the origin of the parliamentary monarchies with England of the Modern Age, where it was tried to limit the absolute power of the monarch.
- The Chambers and the government are the ones who exercise power while the king must stay out of political changes.
- The role of the king is represent the unity of the state.
- The king contains legal immunity and is financially supported by the people, him and the entire royal family.
- The king must obey the laws of the constitution.
3. Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchies emerge in countries with a long monarchy tradition as a mechanism of adaptation to changes in the forms of government. Specifically, this type of monarchies arose from the principles of the thinkers XVII and XVIII who defended the division of powers and political reform in European countries. An example of a constitutional monarchy in existence today is that of the Netherlands.
Here is a list of the main ones features of a constitutional monarchy:
- The monarch is the head of state in which his powers lie limited by a constitution.
- The reign of the monarchy is hereditary and lifetime.
- Depending on the country, the king may have more or less executive power depending on whether it is considered a '' strong '' or '' weak '' constitutional monarchy, or simply the monarch has symbolic attributions.
- Among the main functions of the king we can find the appointment of the prime minister, command of foreign relations, granting honors.
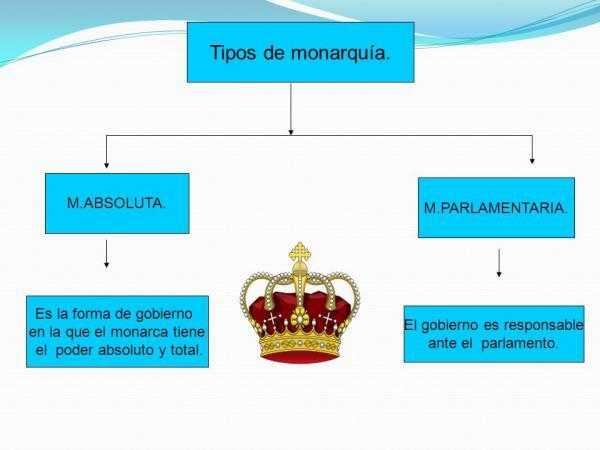
Image: Slideplayer
If we analyze the word ''republic'', we will find out that it derives from Latin '' res publica '', that is, the public thing or thing of the town. The Republic is a form of state where the exercise of government falls on one or more people chosen by means of a elected system of popular or parliamentary voting. Therefore, a republic can be presidential or parliamentary.
East voting system must be free and secret so that the participation of the citizen without conditions is ensured. The person who holds the office of President of the Republic will be for a specified time.
As with the monarchy, the case of the republic can also find several types, such as the Federal Republic (USA), wave Centralist republic(France). In general, the types of republics share the same system of separation of powers between the executive, legislative and judicial to ensure a balance of state between freedom, justice and equality.
Next, we summarize the main characteristics of a republic:
- Popular sovereignty: as we have said, sovereignty is chosen by the people through the Universal suffrage.
- Periodicity in the exercise of power: the person or persons who exercise power will do so for a specified period of time.
- Separation of powers in executive, legislative and judicial.

Image: Slideshare
At this point in the lesson, we can certainly conclude that monarchy and republic are two totally opposite forms of government. As we have been reading, we have already been able to observe the differences between one political organization and another. Still, let's gather the main differences between monarchy and republic:
- SOVEREIGNTY: while in a republic sovereignty is popular, in an absolute monarchy it is the idea of a legitimate divine dynasty. Therefore, in a republic it is the people who elect the ruler while in an absolute monarchy it is the succession within a divine dynasty.
- DURATION OF GOVERNMENT / REIGN: While in a republic the ruler is elected for a specified period (usually 4 years), in a monarchy the king holds a lifetime office until he decides to succeed the crown.
- SEPARATION OF POWERS: While in a republic there is a separation of powers (executive, judicial and legislative), in the absolute monarchy, these three main powers fall on the figure of the king.
- ACCEPTANCE OF A CONSTITUTION: while in a republic the constitution includes the rights and duties of citizens, in an absolute monarchy there is no such regulation.
- THE PARLAMENT: in a republic the core of state politics takes place in a parliament elected by suffrage universal (since this type of suffrage exists) while in an absolute monarchy this governing body does not exist.

Image: Sitapati
To finish the topic of differences between the monarchy and the republic, it is important that we take into account the different types that exist within each of these forms of government to be able to make a correct definition and, therefore, to be able to make a difference.
Remember: it is not the same to talk about a absolute monarchy what of a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy.