Hippocampus: functions and structure of the memory organ
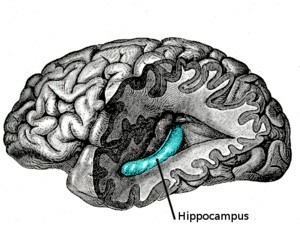
The hippocampus is one of the parts of the brain more important.
It is situated in what is known as limbic system, and is closely related to both the mental processes related to the memory as with those that have to do with the production and regulation of emotional states, in addition to intervening in space navigation, that is, the way in which we imagine movement through space concrete.
The anatomy of the hippocampus
The etymology of the term "hippocampus", a word coined by the anatomist Giulio Cesare Aranzio, refers to the similarity between this brain structure with a seahorse. Is about a small organ with a curved, elongated shape, located on the inside of the temporal lobe and goes from the hypothalamus to the amygdala. Therefore, each brain has two hippocampi: one in each hemisphere of the brain.
In addition, the hippocampus is associated with a part of the cerebral cortex known as the archicortex, which is one of the most ancient regions of the human brain; that is, it appeared many millions of years ago in our evolutionary line. That is why the hippocampus is so well connected to other parts of the limbic system, that it appeared to provide answers to some of the most basic needs of our most ancient mammalian ancestors. remote. In turn, this fact already allows us to intuit that the mental processes related to emotions are linked to the functions of the hippocampus. Let's see what they are.
The functions of the hippocampus
The main function of the hippocampus is to mediate the generation and retrieval of memories in conjunction with many areas scattered throughout the cortex and with other areas of the limbic system.
Therefore, it has a very important role in the consolidation of the learning carried out, since on the one hand it allows certain information to pass into long-term memory and on the other links this type of content with certain positive or negative values, depending on whether these memories have been associated with pleasant or painful experiences (physiological or psychologically).
They are mental processes linked to emotion those that determine whether the value of an experience stored as a memory is positive or negative. What we experience as emotions has a functional part that has to do with the way we learn to behave following learned rules that work in our favor: avoid repeating mistakes and re-experience sensations nice.
The hippocampus and memory
It could be thought that the hippocampus is the part of the brain where long-term memories are stored. However, the reality is more complex than this idea.
The relationship between the hippocampus and long-term memories is not so direct: this body acts as a mediator, or directory, of memories, whose appearance and disappearance is associated, from what is known about the operation of the memory, to the activation and deactivation of networks of neurons distributed over many areas of the brain. In other words, the hippocampus does not "contain" memories, but acts as an activation node that allows different memories distributed in different parts of the brain to be activated.
In addition, the hippocampus is more related to some types of memory than to others. Specifically, plays a role in declarative memory management, that is, one whose contents can be expressed verbally; However, non-declarative memory, which intervenes in the memorization of movement patterns and motor skills (such as dancing or cycling), is rather regulated by structures such as ganglia basal and cerebellum.
It is known that an injury in this area of the brain usually causes anterograde and retrograde amnesia in the production and evocation of memories related to declarative memory, but non-declarative memory is usually preserved. A person with a severely damaged hippocampus can continue to learn, for example, manual skills (although he would not remember learning this process).

The hippocampus in space navigation
From what is known about the hippocampus, this brain structure also seems to intervene in the way we perceive space, that is, the way in which we keep in mind a three-dimensional space through which we move, taking into account its volumes and references.
In fact, inside the hippocampus a type of neurons called place cells have been discovered, about which you can read more in this article.
The hippocampus under the disease
The region of the hippocampal formation is one of the first areas in which diseases such as dementia or the Alzheimer's. That is why people who begin to experience this disease see their abilities to forming new memories or recalling more or less recent autobiographical information are diminished.
However, even if the hippocampus is badly damaged, usually the oldest and most relevant memories about the person's life take a long time to disappear, which could mean that with the passage of time the oldest and most relevant memories are "becoming more and more independent" of the hippocampus.
Bibliographic references:
- López-Pousa S., Vilalta Franch J., Llinàs Reglà J. (2002). Dementia Manual, 2nd Edition. Prous Science, Barcelona.
- Martínez Lage J.M., Láinez Andrés J.M. (2000). Alzheimer's: theory and practice. Ediciones medical classroom, Madrid.


