Philip II of Spain: summary biography

Philip II of Spain, also know as "the prudent"It was characterized because during his reign the Spanish monarchy was the first European power in reach the largest territorial extension until then since it incorporated territories of all the continents. He was King of Spain, Portugal, Sicily, Naples, Sardinia, sovereign of the Netherlands, Duke of Milan and Burgundy, and King of England and Ireland. Next, in this lesson from a TEACHER we offer you a brief biography of Philip II of Spain commenting on those most outstanding aspects of his life.
Index
- Philip II (1527-1598)
- The reign of Philip II (1556 - 1598)
- The foreign policy of Philip II
- Spanish presence in the Atlantic
Philip II (1527-1598)
We started this brief biography of Philip II of Spain speaking of the early years of this Spanish monarch. Felipe was the son of Carlos I of Spain and Isabel of Portugal, both made sure that he received the best education because in the future he would end up being King of Spain.
His teachers instilled in him a passion for letters and art, Juan Martínez Silíceo made sure that he learned Latin, Italian and French and Juan de Zúñiga taught him the trade of arms, with only fifteen years he participated in the defense of Perpignan.
At age 18, he had his first child, Carlos, and was widowed by his first wife, María Manuela de Portugal. Before he was king already during his father's reign he took over the government on several occasions due to the absence of this, due to the conflicts in the Netherlands (1539) and Germany (1543, yes, under the guidance of the Regency Council, even so, this allowed him to gain experience.
Already in 1554 his father Carlos I of Spain and V of the Holy Roman Empire he gave her the crown of Naples and the Duchy of Milan. This same year he ended up marrying María Tudor, daughter of King Henry VIII of England, for which Philip II was crowned as king consort of England.
Between 1555 and 1556 his father decided to abdicate, converting his son, Felipe II in the new king of SpainFor this reason, he received the crowns of Castile and Aragon, Sicily and the Netherlands, leaving Austria and the German Empire to Fernando I of Habsburg, the younger brother of Carlos V.
The reign of Philip II (1556 - 1598)
We continue with this brief biography of Felipe II of Spain speaking, now, of the reign. The first thing the monarch did after ascending to power was reinforce and modernize the administration of the Hispanic monarchy, distancing them from those medieval traditions and the ambition for world domination very often during the reign of his father.
There were major reforms especially in the government and justice system, carried out a centralized bureaucracy and carried out a personal and direct supervision of the affairs of the State. Also another of the great changes is that he moved the court to Madrid, making it the capital of the Spanish monarchy.
In the financial field it had more problems since the great military expenses made that on three occasions (1560, 1575, 1596) the Spanish monarchy found itself bankrupt.
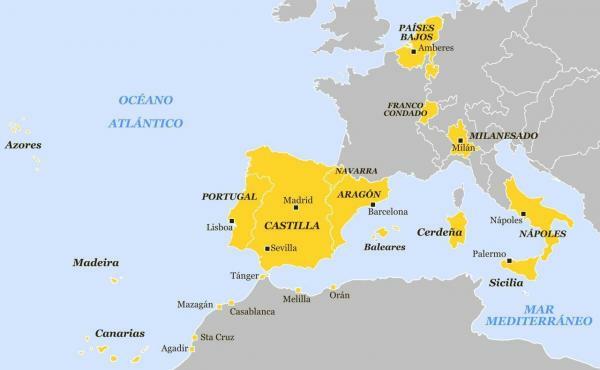
The foreign policy of Felipe II.
We continue with the summary of the biography of Felipe II speaking of one of the main strategies of his reign: foreign policy. As we said before, the Holy Roman German Empire It passed into the hands of Fernando I of Habsburg which favored the international policy of Felipe II because Spain was free from imperial obligations.
One of the first projects that he had to abandon on the basis of foreign policy was the purpose of alliance with England when he again became the widower of Mary Tudor in 1558. The military triumphs of the Battles of San Quentin Y Gravelins pacified the periodic conflict that he had with France for this the peace of Cateâu Cambrésis In 1559, this pact was also reinforced thanks to the marriage of Felipe II with Elizabeth of Valois, daughter of Enrique II of France; this was really a prevailing fact since France had been the rival power during the reign of his father Charles V and now it was no longer a problem for Spain.
In this way, Felipe II was able to direct his foreign policy towards the Mediterranean and thus curb the Islamic power led by the Ottoman Empire, for this he had to suppress an internal rebellion of the Moors in Granada in which plotting the coming danger he formed the Holy league in which Venice, Genoa and the Papacy joined Spain, in this way another of the great battles of the Spanish empire was obtained, the Battle of Lepanto (1571), which meant a decrease in tension for the control of the Mediterranean.
Later he reoriented his foreign policy towards the Netherlands to address the serious situation of uprisings against Spanish rule carried out by Protestantism, however and despite the enormous military effort led by Generals Luis de Requeséns, Don Juan de Austria and Alejandro Farnesio, many of the northern provinces declared themselves independent and were never recovered by Spain.

Spanish presence in the Atlantic.
The Atlantic orientation meant the annexation of Portugal to Spain in 1580, and not only Portugal but all the possessions that it had in Africa and Asia, in this way Philip II reigned as Philip I of Portugal. It was here after this invasion of the Lusitanian country when the Spanish empire reached its greatest territorial extension.
Between 1584 and 1590 it was also allowed to intervene in the succession dispute of France, taking advantage of the wars of religion, for this support to the Catholic side and he tried to get his daughter Isabel Clara Eugenia to seize power against the Protestant side of Enrique de Navarra, future Henry IV of France, however, got Henry IV to renounce Protestantism so France finally stayed in orbit catholic.
The Spanish presence in the Atlantic increased the tension with England, which in addition to offering their aid to the Protestant rebels in the Netherlands, English corsairs often stole many of the merchandise that were in the Spanish galleons of the Caribbean area, all this led to Philip II planning a punitive expedition against England the “ Great and Happily Armada"Composed of 130 ships, 2000 rowers and 20,000 soldiers who set sail from Lisbon in 1588 to Flanders so that the troops would increase in numbers of soldiers.
In their first encounter the technical superiority of the English proved to be greater than the Spanish and after some disastrous battles carried out in the North Sea, the Spanish Armada decided to return, on the return a strong storm ended with the defeat of the expedition, and as a result of this failure it was sarcastically renamed by the British as the "Armada Invincible". From this moment on you could say that begins the decline of the Spanish Empire in Europe.
The decline already coincided with the old age of Felipe II who died on September 13, 1598 at the age of 71 in the Escorial Monastery, built under his command.
If you want to read more articles similar to Philip II of Spain: summary biography, we recommend that you enter our category of Story.



