Brainstem: functions and structures
The brain is almost always associated with a kind of oval with a rough surface full of folds, but below this cerebral cortex there are a multitude of very important structures.
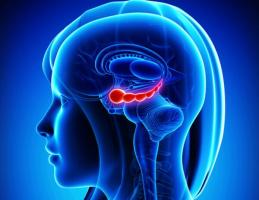
In fact, if we were to consider the importance of each of the parts of the brain judging them according to how relevant they are to our survival, we would conclude that the most fundamental structure is one that neither has the folded shape of the cortex nor is it shaped like an oval. Se deals with the brainstem, or brainstem, located in the lowest part of the brain and in direct contact with the spinal cord.
What is the brain stem?
The brainstem, sometimes called brain stem, is a part of the brain shaped like a cylinder or elongated cone and that is located between the rest of the brain and the spinal cord. That means that the brainstem is aligned with the neural fibers that run through the spinal cord under the spinal cord; specifically, it passes in front of the cerebellum.
Therefore, it is the part of the brain that is anatomically lower and closer to the neck. Furthermore, most of the
cranial nerves (or cranial nerves) come out of the brain stem.The brain stem is made up of both parts of white matter as in some areas where the Gray matter, which means that It runs through both connection areas and areas in which the bodies of neurons are concentrated forming nuclei of control.

Brain stem functions
Although the brain stem is attached to the spinal cord and its shape can be confused with a prolongation of the spinal cord, its main function it is not to act as a simple bridge between the brain and the nerves that run through the human body.
The brain stem is the part of the human brain It houses the most primitive and ancestral functions, and it appeared in our evolutionary line in species that did not resemble human beings at all. It is part of what, according to Paul MacLean's 3 Brain Theory, it has been called "reptilian brain", precisely because it has been associated with ancient physiological processes (although MacLean's ideas are not considered valid, among other things, because they are based on a very simplified view of the evolution of the brain human.
Thus, the brain stem is responsible for performing the most basic tasks of the nervous system for our survival, those which we can hardly influence voluntarily and which have been automated from millions of years of evolution precisely so that our wrong decisions or our distractions do not cost us our lives.
Maintaining vital signs
Among the functions in which the brainstem plays a fundamental role are: regulation and maintenance of heart rate and automatic control of respiration. That is why the brain stem is made up of vital centers that, when damaged, can cause immediate death.
Other somewhat less important but nearly as primitive functions of the brainstem are control of hiccups, sneezing and coughing, sucking, swallowing, vomiting and sensitivity to pain. It also has a very important role in regulating arousal levels.. Specifically, a network of neurons distributed in part by the brainstem called the reticular formation intervenes both in the regulation of the circadian cycle (sleep-wake) and in the maintenance of consciousness.
A communication bridge with the spinal cord
In addition to all these functions, of course, the brainstem serves to communicate the cranial nerves and the spinal cord with the brain, thus being the communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body both in the afferences and in the efferences. This is a more passive role than the previous ones, but it is equally essential for the survival of the brain and the whole organism in general.
Parts of the brainstem
The brain stem is made up of three main structures: the midbrain, the brainstem bridge and the medulla oblongata.
1. Midbrain
The midbrain is the structure of the brainstem located in a higher position and, therefore, closer to structures located in the upper part, such as the thalamus. Like other parts of the brain stem, it is involved in such primitive functions as the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and body temperature, but it also plays a role in reacting quickly to visual and auditory stimuli in a reflexive way, as well as in controlling certain movements.
The two basic components of the midbrain are structures called tectum Y tegmentum.
2. Brainstem bridge
The brainstem bridge, or pons, is located just below the midbrain and above the medulla oblongata. On its back side (closest to the nape) is the cerebellum. This structure is the largest part of the brain stem, and its anterior surface sags outward as if it were half an egg.
This part of the brain stem intervenes in the control of breathing, in the transition between sleep phases and in the regulation of the level of consciousness, among other basic survival processes.
3. Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata (or brainstem) is located in the lowest part of the brain stem. It controls all kinds of automatic processes totally necessary for survival, such as cardiac control or secretion of gastric substances. In addition, it is the part that communicates with the spinal cord directly.
Also, it is in this part of the brainstem where is the decussation of the pyramids, that is, the point at which the nerve fibers change from half body to go from right to left and vice versa (which explains that one half of the body is controlled by the opposite half of the brain).
- If you want to know more about the medulla oblongata and its parts, this article may interest you: "Medulla oblongata: anatomical structure and functions".