Main CHARACTERISTICS of ISOTOPES

Image: Planets
All the matter that makes up our planet is made up of atoms. But all atoms are not the same, atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons. Sometimes the number of these subatomic particles are not the same, are not balanced, and species such as the isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (for example, hydrogen) but that do not have the same number of neutrons. This "imbalance" causes the characteristics of isotopes of the same element are not equal. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will look at all these characteristics in detail. We started!
Index
- What is an isotope?
- Atomic characteristics of isotopes
- A curious application of isotopes: isotopic marking
- Characteristics of isotopes of the same element
What is an isotope?
Before talking about the characteristics of isotopes, it is important to know better what this consists of. subatomic particle. We could say what the isotopes are "subgroups" of atoms: They are atoms of the same element but that differ in certain things.
Isotopes are two atoms with the same number of protons (the same atomic number), but different number of neutrons (different atomic mass). The isotopes of the same element are usually named with the name of the element followed by its atomic mass. It is well known andl carbon fourteen (C14), which is used to determine the age of fossils but carbon has other isotopes such as carbon 12 and carbon 13, which are more stable than other isotopes of carbon such as carbon 8 or carbon carbon 22.
In our case, all these atoms are carbon atoms so they have an atomic number of 6 (Z = 6) but carbon 12 (“normal” carbon) has an atomic weight of 12 versus the atomic weight of 14 of carbon 14 or the atomic weight of 8 of carbon C8.
These differences between the different isotopes can cause the atoms to have different characteristics, behaviors with atoms of other elements, half-lives, etc.
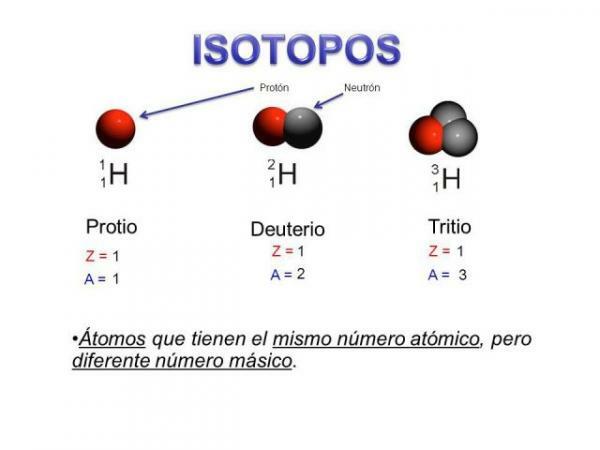
Image: Your Tasks
Atomic characteristics of isotopes.
- The first characteristic of isotopes at the atomic level is that all isotopes are atoms of the same element.
- This main characteristic leads us to a second characteristic: all isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number, that is, the same number of protons.
- All isotopes of an element have the same number of protons.
- The isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons, that is, different mass number or atomic mass.

Image: EHU
A curious application of isotopes: isotopic marking.
Isotopic labeling is a technique that uses two very important characteristics of isotopes: that all isotopes react in the same way in chemical reactions and that some of them have radioactivity.
During a chemical reaction, two or more substances, called reagents, they combine their atoms to form other different substances resulting from different combinations, the so-called products. The isotopic marking is a technique by which we can introduce the radioactive isotope of a reagent into the reaction, so that This will react in a normal way and we can locate it at any time thanks to the radioactivity that emit.
Other variants of this technique allow us to identify different isotopes of a reagent by mass spectrometry or infrared spectroscopy.

Image: Slideplayer
Characteristics of the isotopes of the same element.
As a consequence of the atomic characteristics seen in the previous section, the isotopes of the same element may have other types of characteristics, which we will describe below.
- Isotopes of the same element have different mass. Physical properties such as density, which will be different for the different isotopes of the same element.
- Certain chemical properties they depend on the type of element that is, and therefore they will not be different for the different isotopes of an element. An example is the solubility, what's it gonna be constant for all isotopes of an element.
- Closely related to their equality in chemical properties is the following characteristic of isotopes: isotopes of the same element react in the same way in chemical reactions. This means that if the carbon 12 atom (the most common or "normal" atom) reacts with two oxygen atoms To form the carbon dioxide molecule, we know that those of the other isotopes of carbon are also they will. This is a very important property for many practical applications of isotopes and radioisotopes.
- The isotopes of an element can be of natural or artificial origin. If the isotope in question can be found in nature, without the hand of man having intervened in its creation, we are facing an isotope natural whereas if it has been created in nuclear reactors, particle accelerators or radioisotope generators we say that it is artificial. the same element can have natural and artificial isotopes.
- Isotopes can be radioactive or non-radioactive. Radioactive isotopes are those in which there is an excess of energy, which the atom tends to eliminate to go from an unstable state to one of more stability.
- Related to the previous characteristics we can say that the isotopes radioactive they have a variable life time. The lifetime is the time it takes for the isotope to disintegrate, that is, to stop having that excess energy that makes it unstable. There are radioactive isotopes that are very unstable and have a life time of seconds while others take hours or even years to disintegrate and become more stable isotopes. Artificially created atoms normally have a much shorter life or decay time than natural ones.
If you want to read more articles similar to Characteristics of isotopes, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.
Bibliography
- Briceño V, G. (s.f) Isotopes.
- Belmonte, A. (May 15, 2019). Properties of the atom.
- Wikipedia (October 22, 2019). Isotope.