Types of angles: what are they and differences (with examples and images)
The types of angles are the different names that the angles receive according to their measure and their relationship with other angles.
An angle is the opening formed by two rays (sides) with the same origin called vertex. For example, within a triangle there are three angles, totaling 180º.
Comparative table of the types of angles
| Angles type | Angle name | Measure (in degrees) |
|---|---|---|
| According to your measure | Acute | Less than 90º |
| Right | 90º | |
| Obtuse | Greater than 90º less than 180º | |
| Flat | 180º | |
| According to the sum of the angles | Complementary | When the sum of the angles is equal to 90º |
| Supplementary | When the sum of the angles is equal to 180º | |
| According to its relationship in space with other angles | Adjacent | The angles together measure 180º |
| Opposed by the vertex | These angles have equal measure | |
| In a row | Variable measures |
Images of the types of angles
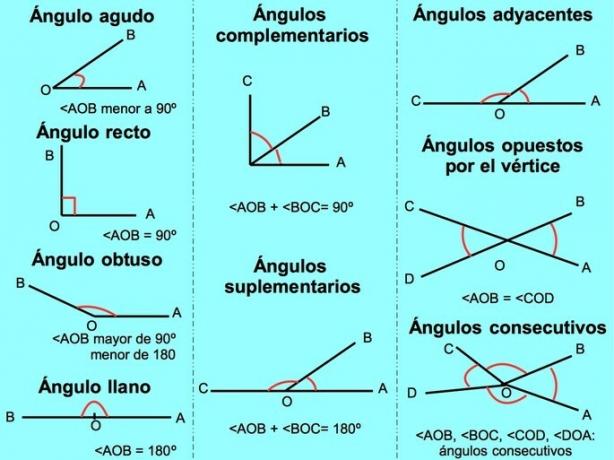
Types of angles according to their measure
This difference between angles refers to simple angles. The angle measure is the opening between the sides of the angle and is expressed in degrees (º).
Acute angle

The acute angle is the angle that measures less than 90º. Examples of acute angles is the angle that is formed when we try to separate the index and middle fingers.
right angle
Is he angle measuring 90º. It is graphed with a square at the vertex of the angle. All the angles of squares and rectangles measure 90º.
Obtuse angle

The angle obtuse is the one who it measures between 90º and 180º. We get examples of obtuse angles in the opening of the wings of some airplanes.
Plain angle
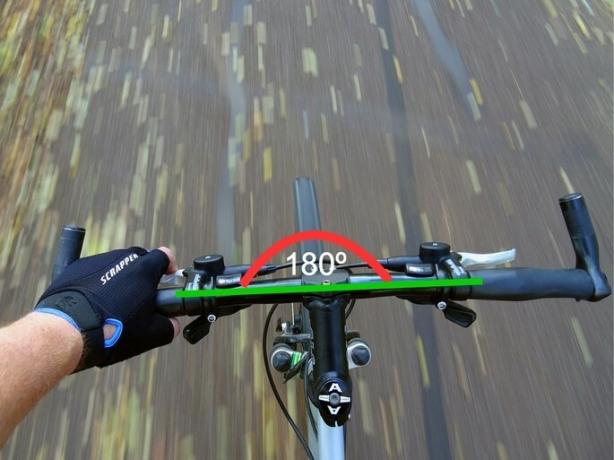

The straight angle is the angle that measures 180º. It looks like a straight line. Two right angles form a straight angle.
Types of angles with respect to their sum
When we have two angles, we can classify them as:
- complementary angles: are those whose sum is equal to 90º. For example, the complementary angle of a 30º angle is another of 60º (30º + 60º = 90º).
- Supplementary angles: are those whose sum is equal to 180º. For example, the supplementary angle of a 30º angle is another 150º (30º + 150º = 180º).
Types of angles according to their position
This difference takes into account the position of one angle with respect to another (s).
Adjacent angles
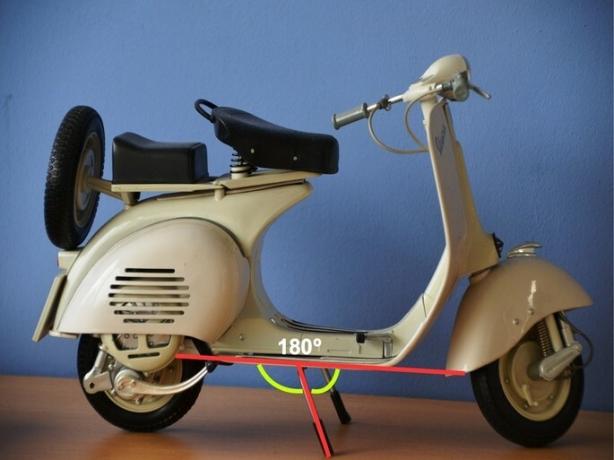

The angles are adjacent when one of the sides is shared and the other sides form a straight line (equal to 180º).
Opposite angles by the vertex

They have the same vertex while the sides are extensions of each other. We can get opposite angles to the vertex when we open a scissors.
Consecutive angles
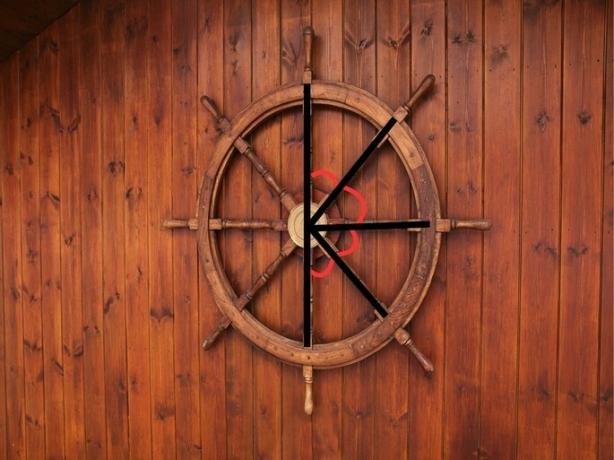

Consecutive angles are those angles that share a side, regardless of its measure or the sum of the two angles. When consecutive angles are formed on one side of a line they add up to 180º. When the angles are consecutive around a point, they add up to 360º. For example, the rudder of a ship has consecutive angles.
See also Circle and circumference.