Difference between monocots and dicots
The monocots are the flowering plants whose seeds have a cotyledon and the dicotyledonous are those flowering plants whose seeds have two cotyledons. A cotyledon is a leaf-like structure found in the seed, it is an embryonic leaf.
Within the plant kingdom, those seed plants are divided into gymnosperms and angiosperms. Angiosperms are the group of plants that have flowers, within which we get the monocots and dicots or eudicots.
| Monocotyledonous | Dicotyledonous | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Class of plants whose seeds have a cotyledon | Class of plant whose seeds have two cotyledons |
| Phylogenetic class | Liliopsida | Magnoliopsida |
| Type of plants | Herbaceous | Annuals and trees |
| Seed germination | Hypogeal | Epigea or hypogea |
| Sheets | Simple, isobilateral symmetry, parallel veins | Simple or complex, dorsiventral symmetry, reticulated veins |
| Stems | Solid or hollow | Solid |
| Cambium | Absent | Present |
| Vascular bundles | Scattered | Concentric |
| Root system | Adventitia, diameter does not vary | Derivative, diameter increases in size |
| flowers | Number of petals equal to 3 or their multiples | Number of petals equal to 4 or 5 or their multiples |
| Examples | Rice (Oryza sativa), corn (Zea corn), banana or plantain (Muse sp) | Grape (Vitis vinifera), Beans (Phaseolus sp.), mango (Mangifera sp.) |
What is a monocot?
A monocot is a class of flower-producing plant (class Liliopsida) whose seeds have a cotyledon. They are predominantly herbaceous.
Seeds
Monocot seeds have a well-developed endosperm. Starch and proteins necessary for the initial growth of the plant are stored in the seed. Germination is hypogeal, that is, the cotyledon remains underground.
Monocotyledonous leaves
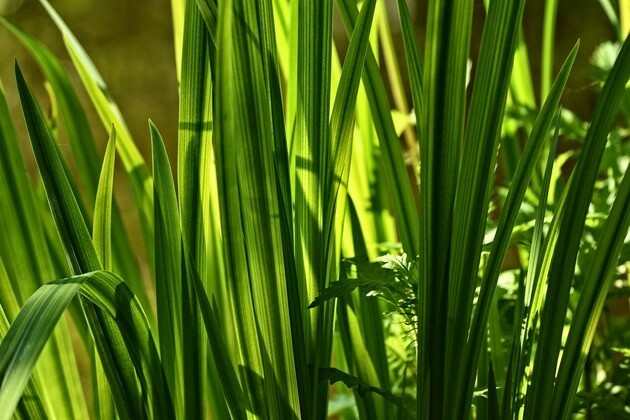

Monocot leaves are simple with isobilateral symmetry. They have parallel veins, smooth edges, and a long sheath, which covers the stem. The stomata are equally distributed on the surfaces of the leaves.
Root and stem
The main root is not developed and the root system is adventitious.
The stem can be hollow or full. Vascular bundles are scattered throughout the stem. The stems and roots do not have cambium and their diameter does not vary.
flowers
The flowers have a simple calyx with a multiple number of petals of three.
Examples of monocots
This class contains 25% of the flowering plants and is divided into the following subclasses:
- Alismatidae,
- Liliidae
- Arecidae
- Commelinidae
The most important families are Poaceae (oats, rice, wheat), Liliaceae (onion, garlic, tulips), Bromeliaceae (bromeliads and pineapples), Orchidaceae (orchids), Iridaceae (crocuses, gladioli and iris).
What is dicotyledonous?
The dicotyledon (class Magnoliopsida) is a class of flowering plants whose seeds have two lateral cotyledons.
Seeds
In the seed starch, proteins and fats are stored, which are used for the initial growth of the plant. The germination of dicots is hypogeal or epigeal, that is, the cotyledons can be below or above the ground, respectively.
Dicotyledonous leaves
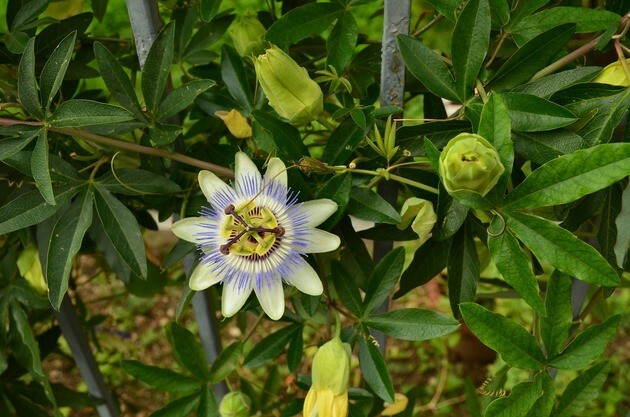

The leaves are simple or complex, with dorsoventral symmetry. They have reticulated veins, often with uneven, serrated, or sectioned edges. The stomata are on the lower surface of the leaves.
Roots and stem
Dicots have a secondary root system derived from a primary root.
The stems are solid. The vascular bundles in the stems are concentric. The stems and roots have cambium and their diameter can grow.
flowers
The number of flower petals is equal to or a multiple of four and five.
Examples of dicots
The Magnoliopsida class has six subclasses:
- Magnoliidae,
- Hamamelidae,
- Caryophyllidae,
- Rosidae,
- Dilleniidae,
- Asteridae,
Some also include the subclasses Ranunculidae Y Lamiidae.
The most important families are the Fabaceae (legumes), Lamiaceae (mint, lavender, oregano, rosemary), Rosaceae (rose, blackberry), Cucurbitaceae (pumpkin or squash, melon, cucumber) and Cactaceae (Cactus).
It may also interest you Angiosperm and gymnosperm.


She has a PhD in Biochemistry from the Venezuelan Institute of Scientific Research (IVIC), with a degree in Bioanalysis from the Central University of Venezuela.