10 characteristics of classical PHILOSOPHY

In a teacher's lesson we traveled to the Classic Greece (S. VII a. C.- V d. C.) and we delve into the origin of philosophy, specifically we are going to study the characteristics of classical philosophy. A science that was born under the auspices of the Greek critical spirit, highly influenced by its good geographical situation, and of great philosophers such as Socrates (470-399 BC. C.), Plato (427-347 a. C.) or Aristotle (384-322 a. C.), among others. Sages who for the first time began to search for a rational explanation of the world around them.
If you want to know more about the origin and characteristics of classical philosophy, keep reading because in a PROFESSOR we explain it to you. Begin the journey to Ancient Greece!
Before explaining the characteristics of classical philosophy, it is necessary to briefly study the framework in which it develops and its main representatives. In this way, the first thing we must do is analyze its etymology, and we have to, the word Philosophy is the union of two Greek terms:
sharp edges= attraction and shopia= wisdom, that is, taste or attraction to philosophy. Likewise, we know that it could be minted around 530 BC. C. and that is attributed to the Greek mathematician and philosopher Pythagoras(569-479 a. C.).Likewise, a philosopher in Greece would be that person who has the desire to learn and of acquire knowledge, one who feels attraction towards wisdom. And, according to Pythagoras, the philosopher would be an individual different from the rest, a third kind of person characterized by questioning, observing, studying and learning without profit.
Thus, Western philosophy and philosophers arose in Classical Greece, in a context and a medium geographic area in which commercial and cultural contacts led to the birth of a spirit critical. Also, for the first time myth and mythology are questioned as a tool to expose the world through the intervention of the gods (Homer and the Iliad / Odyssey or Hesiod and Theogony) and the logos, through which it is sought to explain what is inexplicable through reason. It goes beyond mere divine intervention.
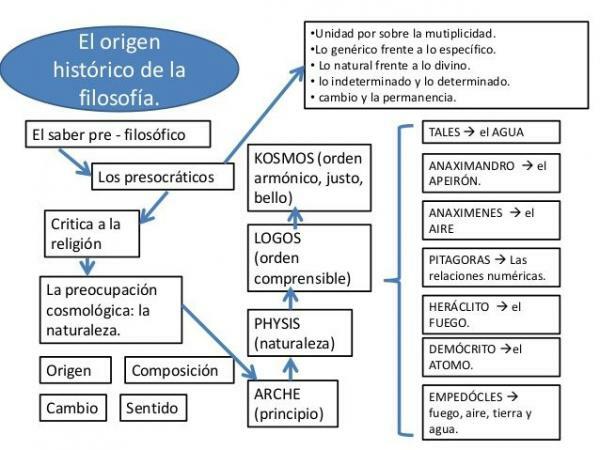
Image: Pinterest
So that you better understand what this current consisted of, here we leave you a list with the main characteristics of classical philosophy. They are as follows:
- Classical philosophy is the basis and the cradle of western philosophy: It was born in the Greek context, continues in Rome, directly influences medieval patristic philosophy, takes on a leading role in the Renaissance and continues to this day.
- For the first time in the West the world around the individual is questioned, leaving aside the religious explanation. From classical philosophy it is sought to know and understand things, reality and the world from a rational method and not only from experience.
- The logos overlaps the mythos: it begins to establish reasoning from reason and away from religion. Even philosophers like Epicurus consider the existence of gods.
- The philosopher is an individual who does not take things for granted, which questions, criticizes and rethinks things from a solid argument. They are the first humanists in history.
- Philosophy stands as a science that seeks wisdom and enrich the knowledge of the individual and, therefore, for the first time, interest will be shown in various topics and disciplines: the nature of the man, knowledge, history, religion, morality, existence, law, beauty, language or politics.
- With classical philosophy are born the first philosophical currents and schools that have been influencing throughout the history of philosophy: Platonism, Sophism, Aristotelianism, Stoicism, Hedonism, Skepticism or Epicureanism.
- From the hand of great philosophers the study and analysis of ethics (analyzes morality, virtue, happiness and human behaviors), logic (rational procedures), physics / metaphysics (study of nature and its structure), aesthetics (study of beauty and its norms) political philosophy (analyzes the models of power, their structure and their relationships) or the rhetoric / philosophy of language (studies language as part of our nature and its use for a purpose).
- Classical philosophy results in a vast and great philosophical work of great sages who marked a milestone in the history of philosophy: Socrates (Socratic maieutics and the dialectical debate to achieve knowledge), Plato (the theory of ideas, according to which, the world is divided into two: the sensible and the intelligible = the true / the world of ideas) and Aristotle (theory of the four causes - matter, form, agent and purpose - to understand the movement).
- The human being begins to gain prominence in front of the divinity and, in this sense, the idea begins to develop that the individual is the one who traces his own destiny.
- It is established that the individual is the holder of a innate knowledge and its function is to develop it by acquiring wisdom to put aside the worst of vices, ignorance.



