10 most important CONTRIBUTIONS of EPICURO de Samos

Today we are going to delve into one of the most important figures in Hellenistic philosophy, Epicurus of Samos (341-270 BC. C.). Founder of the philosophical current known as Epicureanism, based on the pursuit of happiness through the management of pleasures and the suppression of pain.
His teachings soon spread from Athens to the entire Mediterranean and lasted six centuries after the death of its founder. However, during the Middle Ages Epicureanism began to be rejected and to decline. It will not be until the Renaissance when the philosophy of Epicurus is recovered and spread to this day with authors such as John Locke, Baruch Spinoza, John Stuart Mill, Auguste Comte, Karl Marx or Nietzsche.
If you want to know more about most important contributions of Epicurus He keeps reading because in a PROFESSOR we explain them to you.
Epicurus He was born in 341 BC C. within a humble family from the island of Samos (Athenian colony). His father, who was a teacher, was responsible for his education of him until at the age of fourteen he became a student of the philosopher
Gullible (Disciple of Plato and whose he afterwards he will radically reject).Years later, after completing his military service and completing his formative years, Epicurus began to teach philosophy in Mytilene (Lesbos), in Lámpsaco and, finally, in Athens. Place where he founded his school "The garden"Where he consolidated his doctrine and where he was imparting his teachings until his death in 270 BC. C.
After his death, the Epicureanismexpanded not only as a philosophical current but as a Lifestyle based on freedom, solidarity, friendship and the pursuit of happiness through the management of pleasures and the suppression of fear / pain.
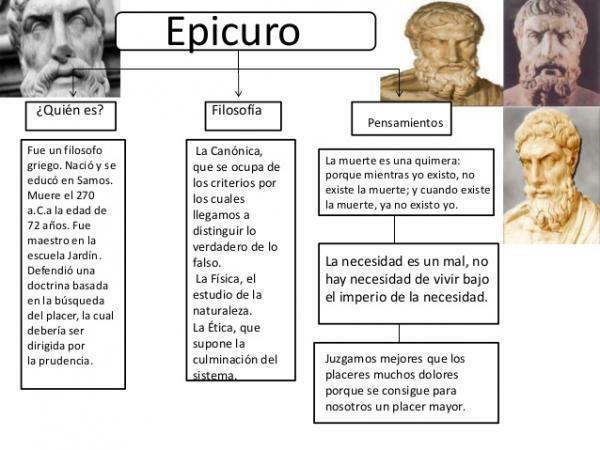
Parts of Epicurus thought
Likewise, his philosophy is divided into three different parts:
- The Canonical: Based on the criteria that an individual has to distinguish what is true from what is false. The theory of knowledge.
- Physics: Based on the study of nature and, according to which, all reality is formed by atoms (with extension, weight and shape) and the infinite void (where atoms move).
- Ethics: It is the most important part (the Canonical and Physics are subordinate to it) and it is the culmination of its philosophical system. Its objective is to help and guide the individual towards happiness through the study of philosophy.
Finally, it should be noted that Epicurus wrote endless manuscripts, approximately 340, of which only three have reached us thanks to Diogenes Laercio:
- Letter to Herodotus, about physics.
- Letter to Pitocles, on astronomy, cosmology and meteorology.
- Letter to Meneceo, on ethics.
Although Epicureanism enjoyed great importance in Greece, Rome and EgyptFrom the arrival of Christianity and the Middle Ages, this doctrine began to be lost and distorted, since it directly clashed with the precepts of the prevailing religion in the West. However, during Humanismand by the hand of Pierre Gassemdi (1592-1655) Epicurus' legacy was recovered and his figure began to be rediscovered throughout Europe.
Thanks to this rediscovery, today we know Epicureanism and its most important contributions, of which many are still very relevant. Let's study the most important ones:
Atomic physics
Following the thesis of Leucippus and Democritus, he establishes that all things are composed of random combinations of atoms and an infinite void (where the atoms move). These have always existed and are the ones that create and destroy everything, therefore, natural phenomena are the work of atomic physics / the laws of atoms and not of the gods.
His concept of religion
If gods exist, they are on a much higher plane than human beings, so much so that they do not care about their affairs and ignore them. Therefore, we do not have to fear them, because they are not going to interfere in our lives or in our destiny. Thus, Epicurus does not believe in divine Providence and affirms that destiny is the work of the individual himself, who is free.
"Gods? Maybe there are. I neither affirm nor deny it, because I neither know nor have the means to know it. But I know, because life teaches me this every day, that if they exist they don't care about us "
The tetrapharmaceutical
although this "four-part cure" is devised by Philodemus of Gadara (110 BC. C.-40 d. C.), is totally based on the doctrine of Epicurus: 1) We must free ourselves from the gods and we must not fear them. 2) We should not be afraid of death. 3) Pleasure in its proper measure is good. 4) We must avoid pain.
Your concept of pleasure
For Epicurus there are necessary pleasures (eating, drinking ...) and unnecessary pleasures (fame, power and excesses). Of these two pleasures, the unnecessary ones must be avoided and the necessary ones must be covered, since they are the ones that lead us to happiness. In this way, what we must do is manage and control those negative pleasures / passions through prudence. It is what Epicurus defines as ataraxia.
"Pleasure is the good first. It is the beginning of all likes and dislikes. It is the absence of pain in the body”
His concept of life
The individual must live in serenity, with tranquility, in coexistence, rejecting material goods, in solidarity, away from the big cities (in self-sufficient communes like "El Jardín") and avoiding everything that destabilize. As for the example excess of pleasure or politics, for this reason, it is established that it is better for the citizen not to participate in politics.
His concept of philosophy
Philosophy is the necessary tool that guides us and helps us find happiness, distancing ourselves from the passions that unbalance us. Therefore, everyone must have access to it.
"Philosophy is an activity that with speeches and reasoning seeks a happy life"
Rejection of fear
The human being moves between pleasure and fear. The latter must be avoided because it is negative for our life. Like the fear of death, which is an absurd fear because when we live it does not exist and when we die it no longer exists.
“Death is a chimera: because while I exist, death does not exist; and when death exists, I no longer exist "
Egalitarianism
Epicurus' concept of egalitarianism is introduced through his concept of access to knowledge. For him, everyone (women and men of different social classes) has the right to knowledge, since we are all equal.
Your concept of language
Language is the product of the individual's own development and serves to express emotions. In addition, it is changing and evolutionary, therefore, if we find its origin (the essence of the first language) we will get closer to its true meaning.
The ethics of reciprocity or the Golden Rule
In our life we must act thinking how we would like to be treated ourselves, to treat others with respect.



